Chapter 08: Principles of Basic Techniques and Laboratory Safety
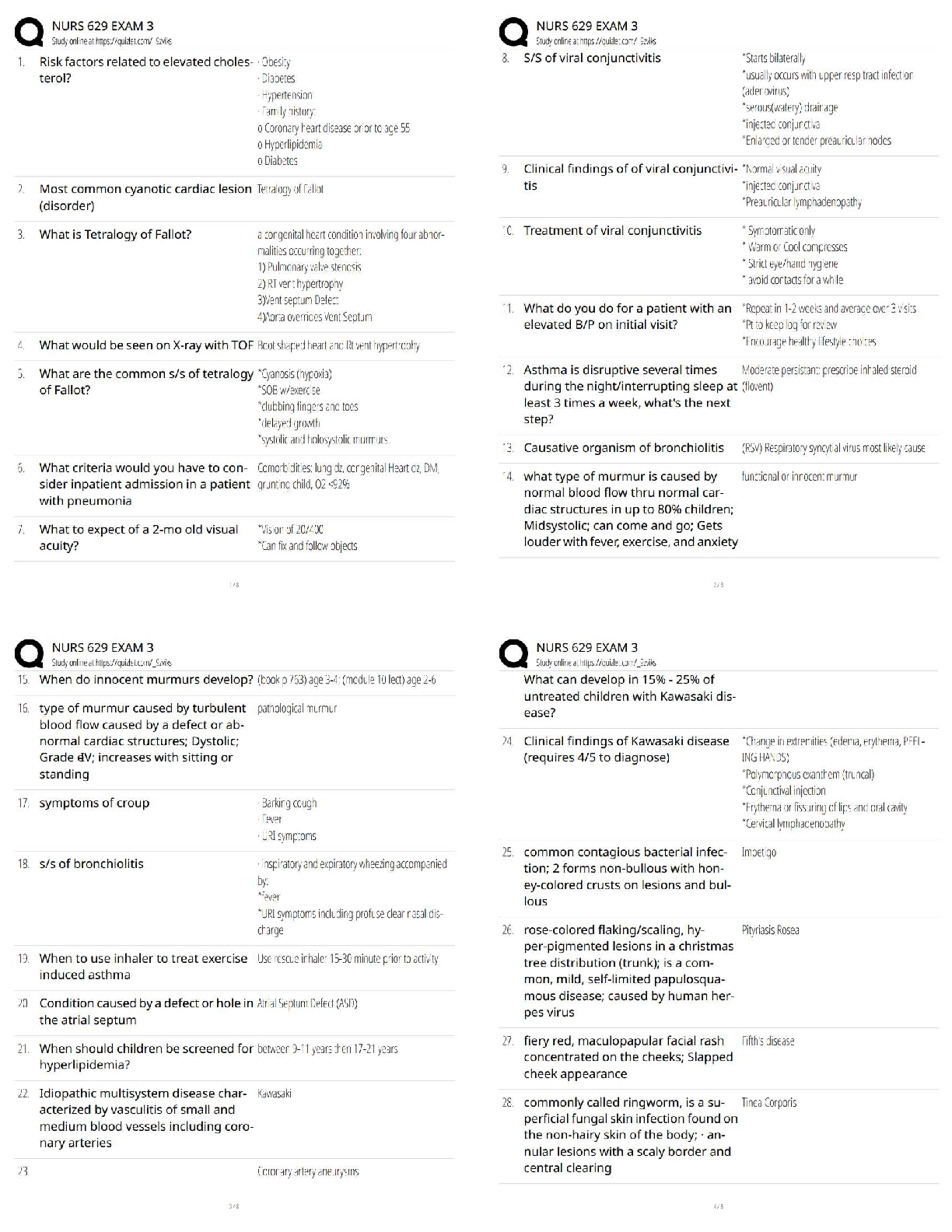
MULTIPLE CHOICE
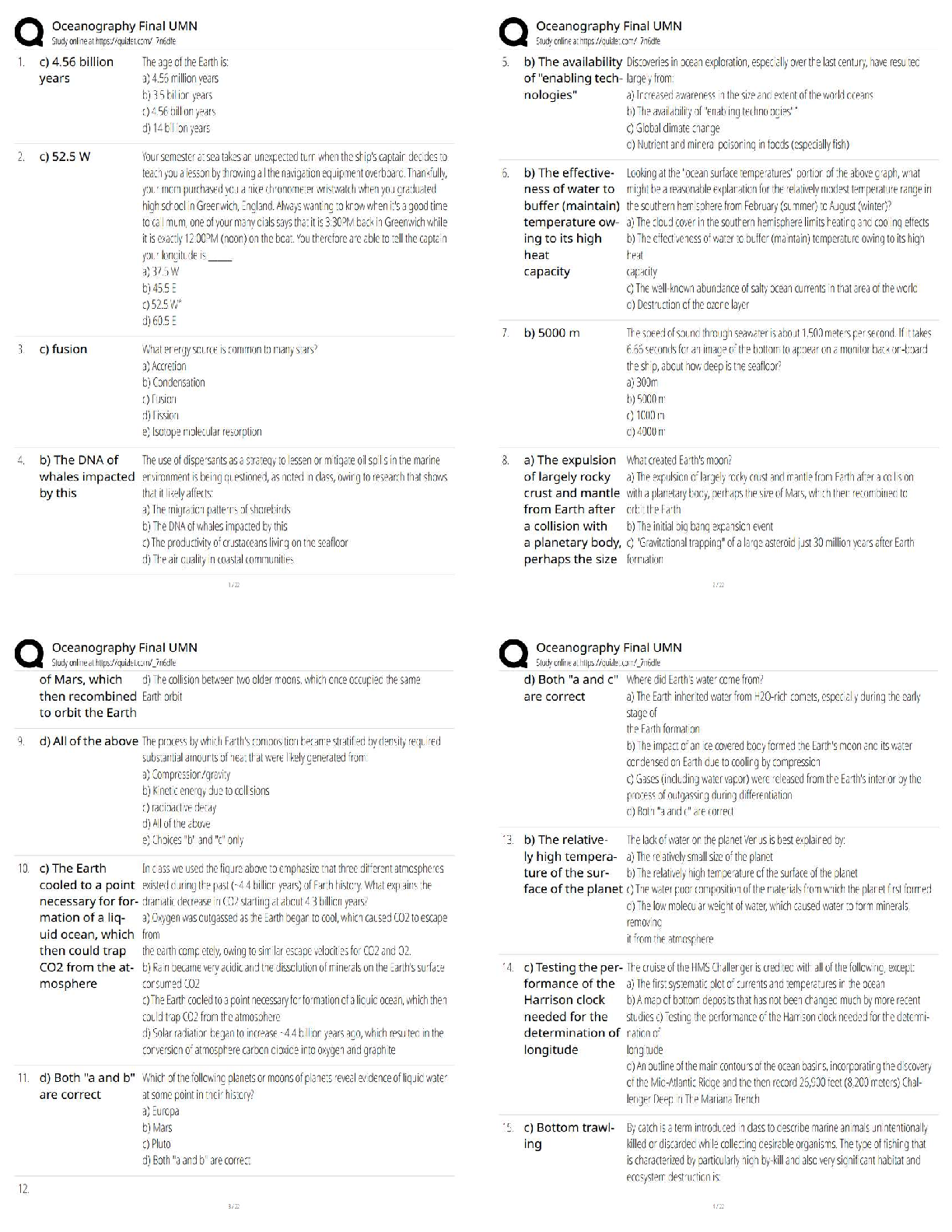
1. To make 20 mL of a 0.1 g/L solution from a 10 mg/mL stock solution, you should add _____ mL of the stock solution to _____ mL of
...
Chapter 08: Principles of Basic Techniques and Laboratory Safety
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. To make 20 mL of a 0.1 g/L solution from a 10 mg/mL stock solution, you should add _____ mL of the stock solution to _____ mL of solvent.
a. 2; 18
b. 10; 10
c. 1; 19
d. 0.2; 19.8
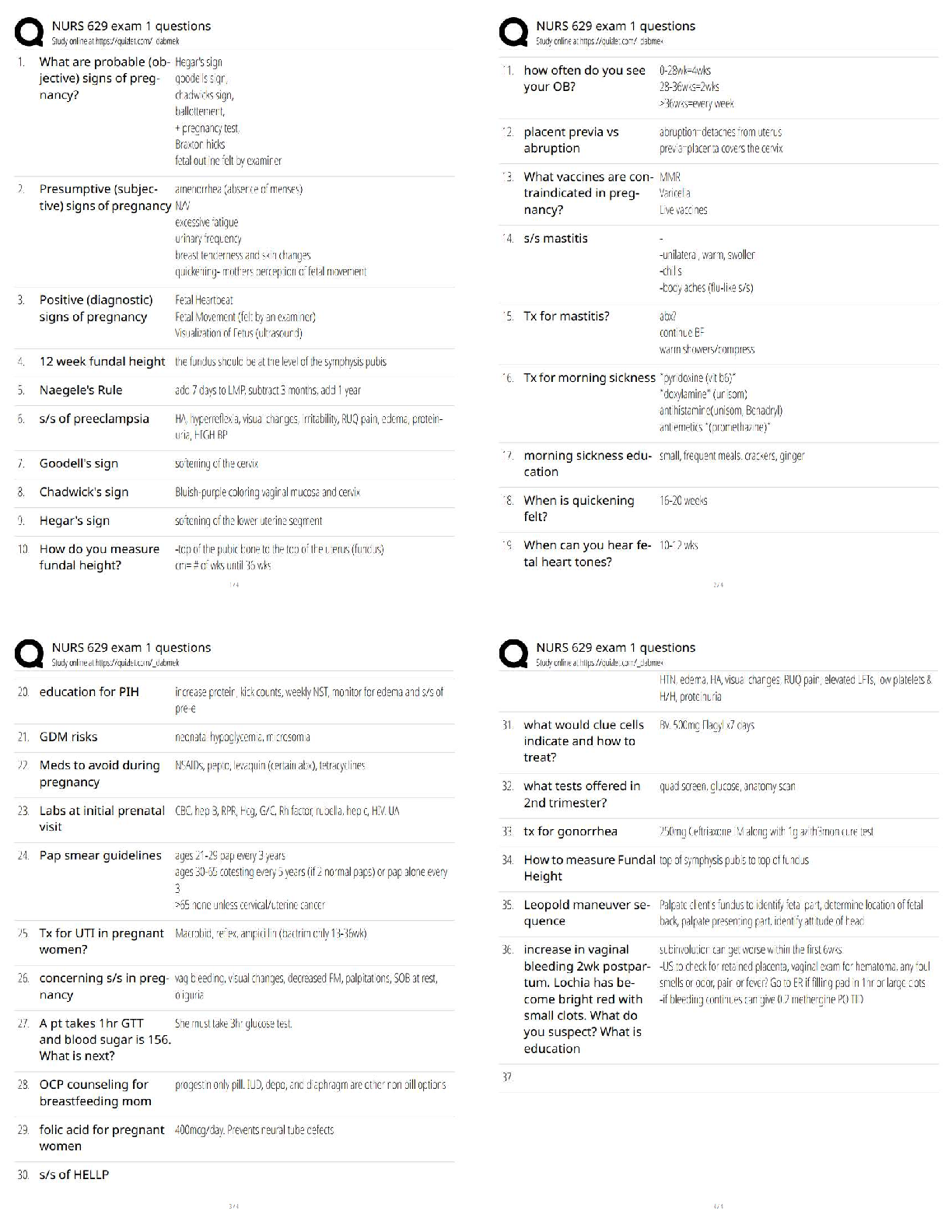
2. Which one of the following statements concerning type I water is not correct?
a. Type I water is acceptable for analytical purposes.
b. Testing that requires minimal interferences (such as iron or enzyme analysis) requires the use of type I water.
c. Type I water is obtained from distillation only and contains a few impurities.
d. Type I water results in part from ion exchange purification and reverse osmosis.
3. What is the relative centrifugal force (RCF) for a centrifuge spinning at 1200 rpm with a rotor head radius of 8 inches?
a. 32.7 g
b. 3200 g
c. 130 g
d. 1300 g
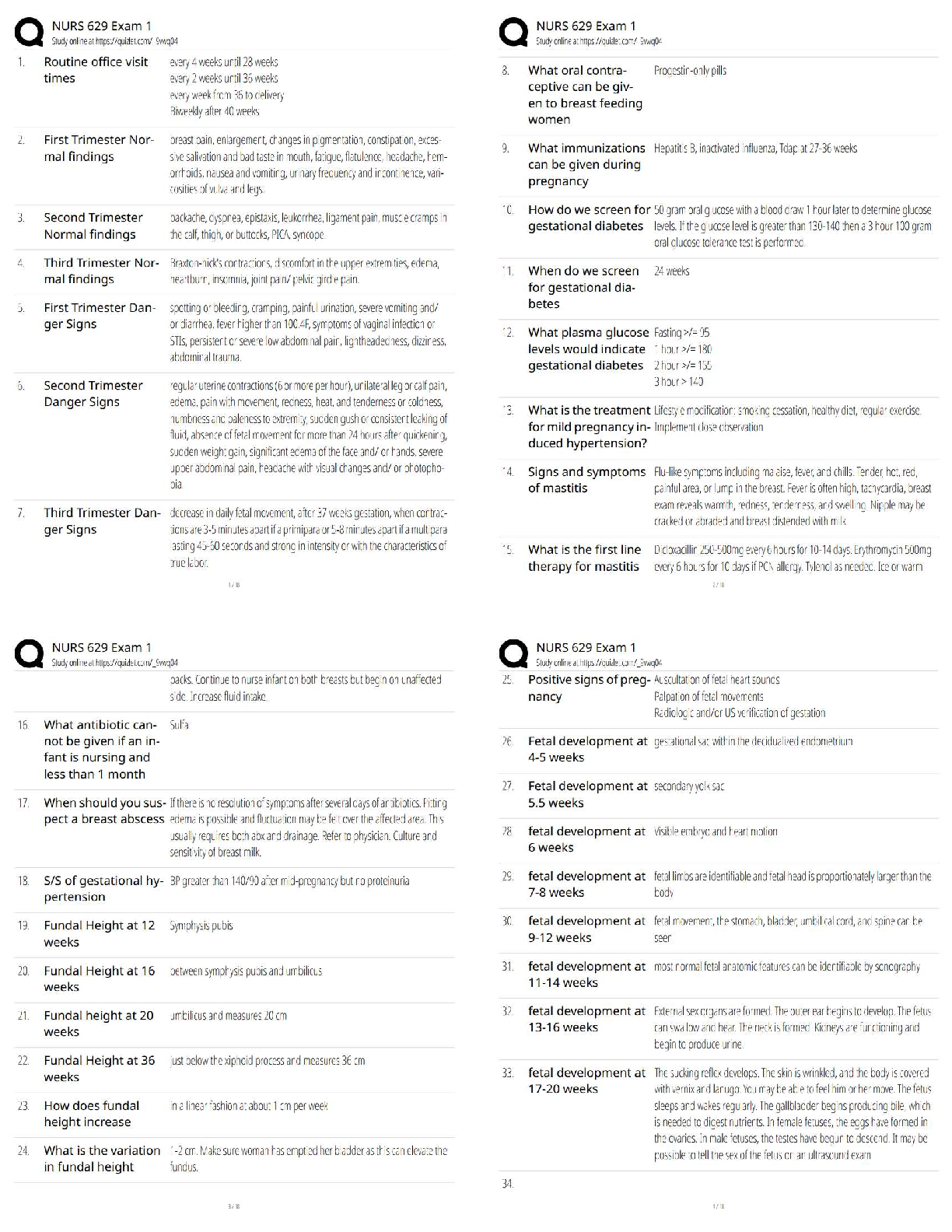
4. Reverse osmosis is:
a. the process of vaporizing and condensing a liquid to purify or concentrate a substance or to separate a volatile substance from less volatile substances.
b. a process by which water is forced through a semipermeable membrane that acts as a molecular filter.
c. a process that removes ions to produce mineral-free deionized water.
d. a process used to convert a liquid or a volatile solid into vapor.
5. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health of the CDC distributes a document that specifies how U.S. clinical laboratories should handle infectious agents. This document is referred to as:
a. the Chemical Hygiene Plan.
b. the Exposure Control Plan.
c. HAZMAT.
d. Universal Precautions.
6. A highly purified chemical that is directly weighed or measured to produce a solution whose concentration is exactly known is referred to as a:
a. calibrator.
b. primary reference material.
c. secondary standard.
d. working solution.
7. Chemicals with the designation _____ are suitable for use in most clinical chemistry laboratory analyses.
a. technical grade
b. analytical reagent grade
c. USP (United States Pharmacopeia)
d. NF (National Formulary)
8. What is the molarity (mol/L) of a solution containing 25 g of H2SO4 (MW= 98 g) in 150 mL of deionized water?
a. 1.7 mol/L
b. 0.59 mol/L
c. 0.002 mol/L
d. 16.3 mol/L
9. How many grams of NaCl (MW = 58.5 g) are required to prepare 250 mL of a 6 mol/L solution of NaCl?
a. 87.75 g
b. 58.5 g
c. 585 g
d. 877.5 g
10. What is the normality of a solution containing 20 g of H2SO4 (MW = 98) in 500 mL of buffer?
a. 8.2 N
b. 2.8 N
c. 0.82 N
d. 176.8 N
11. Universal Precautions:
a. consist of shipping standards that divide potentially infectious specimens or substances into risk groups.
b. state that only HIV, hepatitis, and sexually transmitted disease-positive specimens should be considered and handled as infectious material.
c. state that hand washing is only necessary before entering a clinical laboratory.
d. consist of guidelines that in part necessitate the wearing of barrier protection when handling potentially infectious material.
12. You have seen another laboratorian collecting blood from a patient without using any barrier protection. What safety mandate is this employee ignoring?
a. Chemical hygiene plan
b. Universal Precautions
c. Clinical laboratory plan
d. Tuberculosis exposure plan
13. The one technical aspect of a clinical laboratory that has received considerable attention in the need for ergonomic design to decrease musculoskeletal stress would be:
a. pipetting.
b. chair design.
c. lighting.
d. flooring.
14. Regarding centrifugation, what is the formula for calculating relative centrifugal force (RCF)?
a. RCF = 1.118 r (in cm) rpm2
b. RCF = 1.118 105 r (in cm) rpm2
c. RCF = 1.118 105 r2 (in cm) rpm
d. RCF = 1.118 r (in inches) rpm2
15. Fifty milligrams (mg) per 1000 mL is equal to:
a. 0.005 g/mL.
b. 0.050 g/mL.
c. 0.050 g/L.
d. 0.50 mg/mL.
16. What is the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) recommendation for the most appropriate RCF and time for centrifugation of blood samples to obtain sufficient separation of cellular and liquid components?
a. 2000 g for 20 min
b. 1200 g for 10 min
c. 500 g for 10 min
d. 100 g for 15 min
17. The class of fire that involves flammable liquids and gases is class and the recommended extinguisher agent is:
a. A; water.
b. B; water.
c. B; dry chemical or carbon dioxide.
d. C; Halon 1211 foam.
18. The type of pipette that is a piece of glass tubing drawn out to a tip and graduated uniformly along its length and is used for reagent measurement is referred to as a:
a. transfer pipette.
b. volumetric pipette.
c. micropipette.
d. measuring pipette.
19. The increased use of electronic health record (EHR) systems has amplified the need for standardized communication between EHR and other systems. The newest universal code system that has standardized terms for all kinds of laboratory observations and measurements and includes a code number, a long formal name, a shorter name, and synonyms is referred to as the:
a. Occupational Safety and Health Act.
b. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute system.
c. Logical Observation Identifier Names and Codes system.
d. National Fire Protection Association system.
TRUE/FALSE
1. The maximum amount of working volume of a flammable solvent allowed outside a storage cabinet is 1 gallon per room.
[Show More]











.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)