MULTIPLE CHOICE
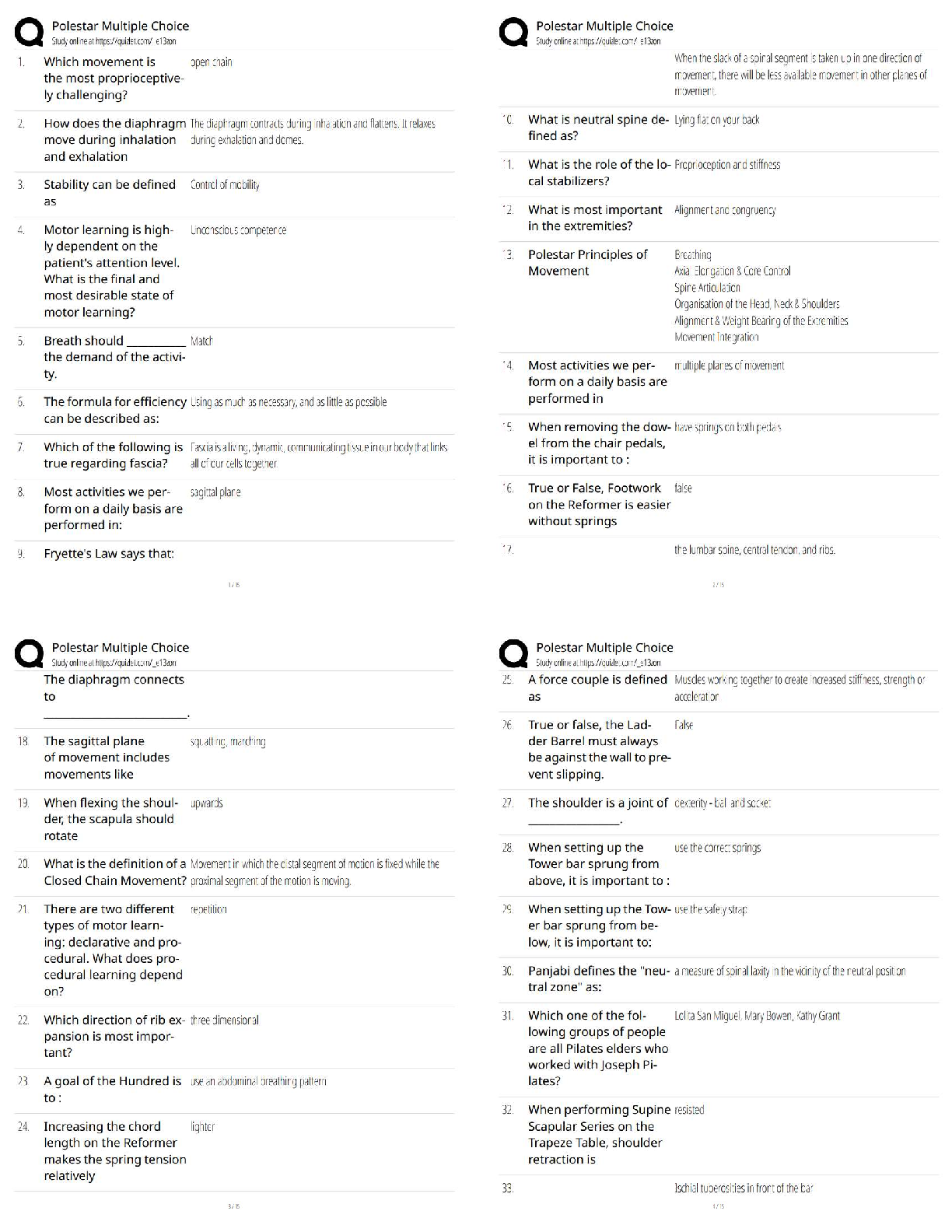
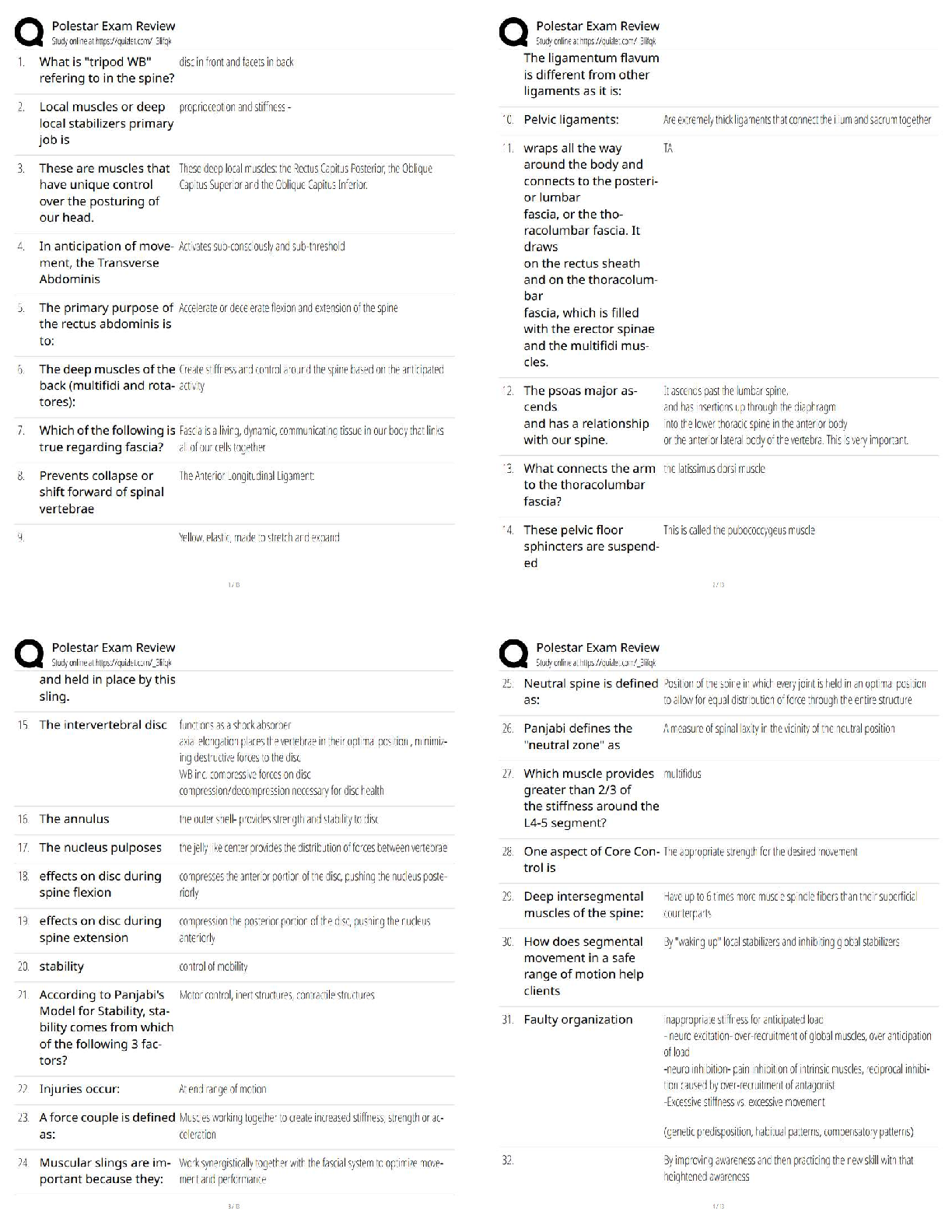
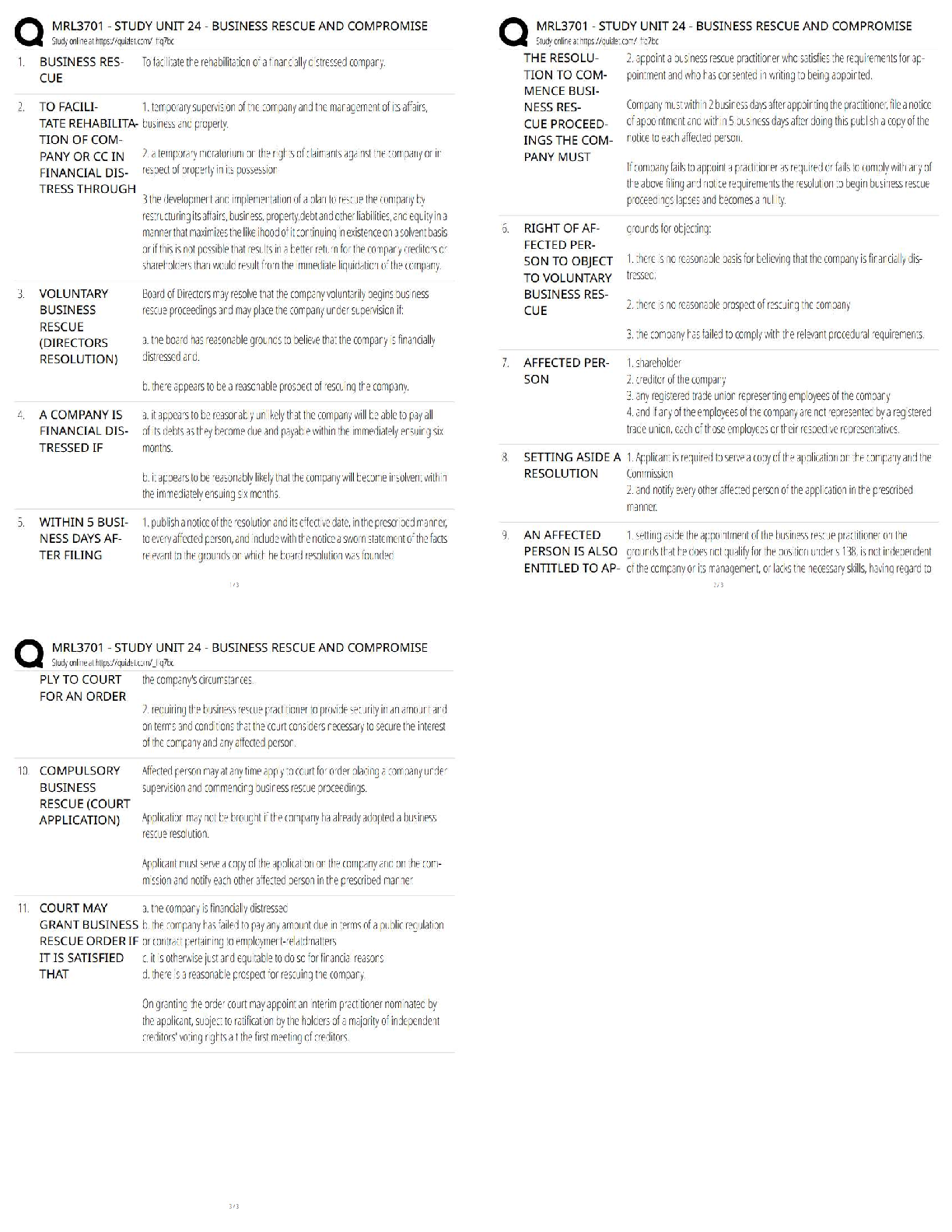
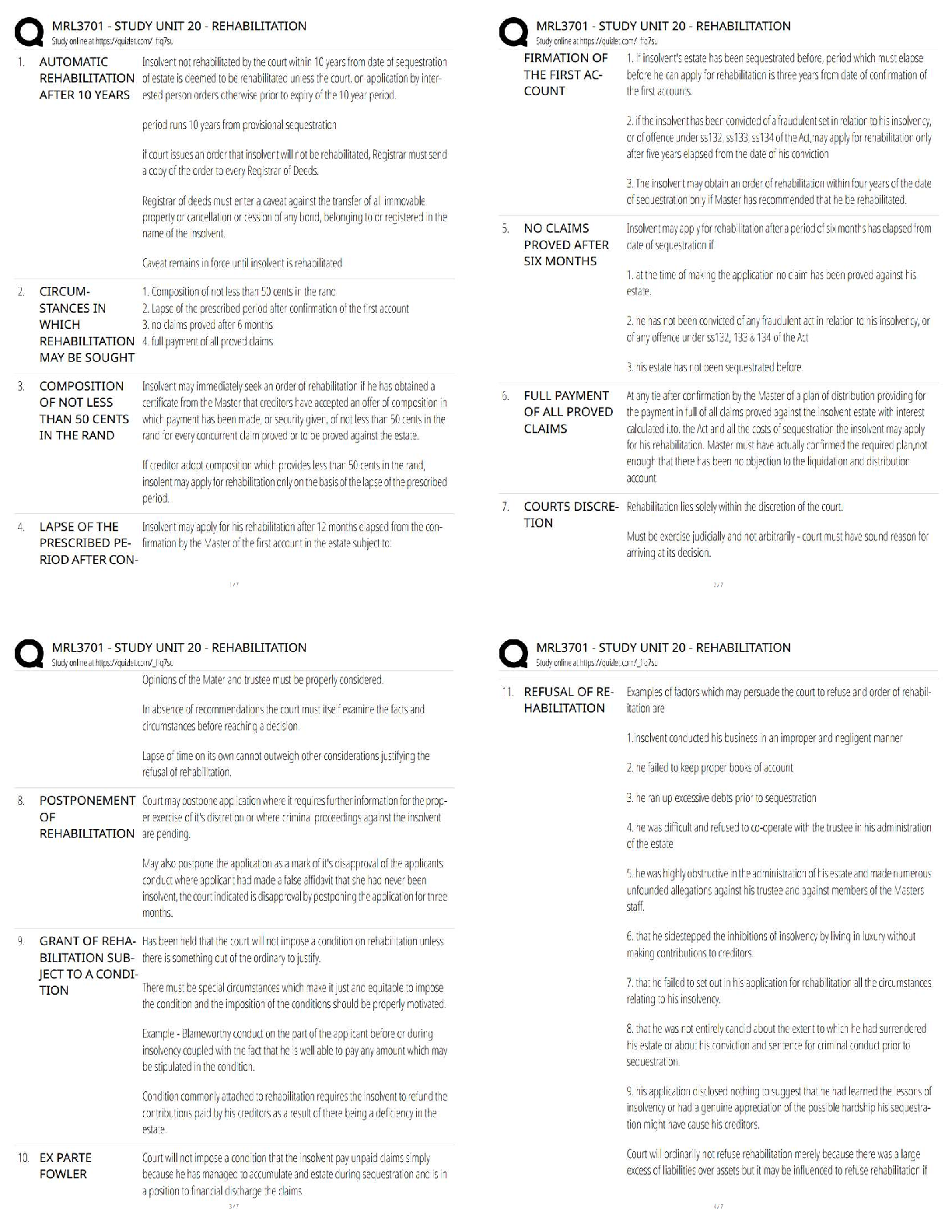
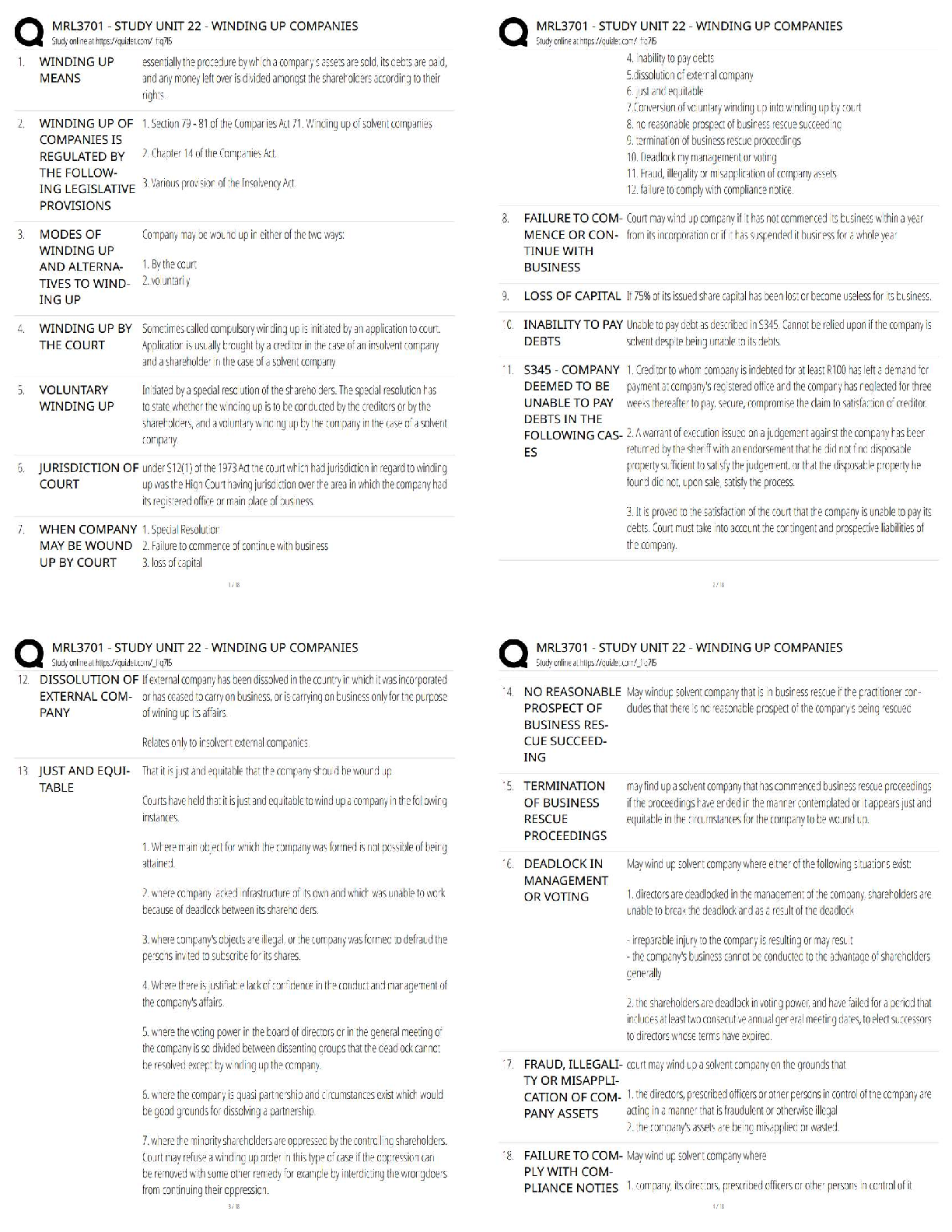
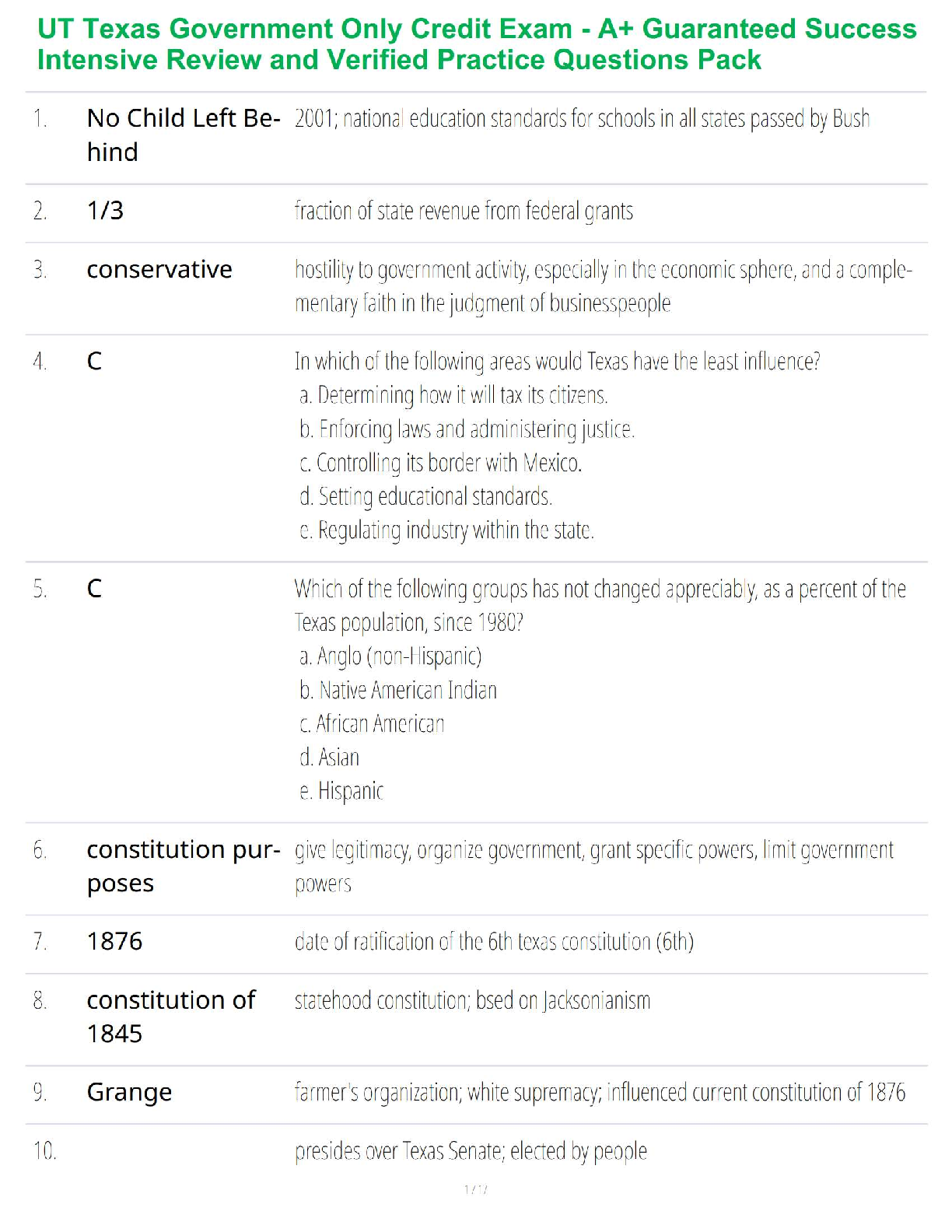
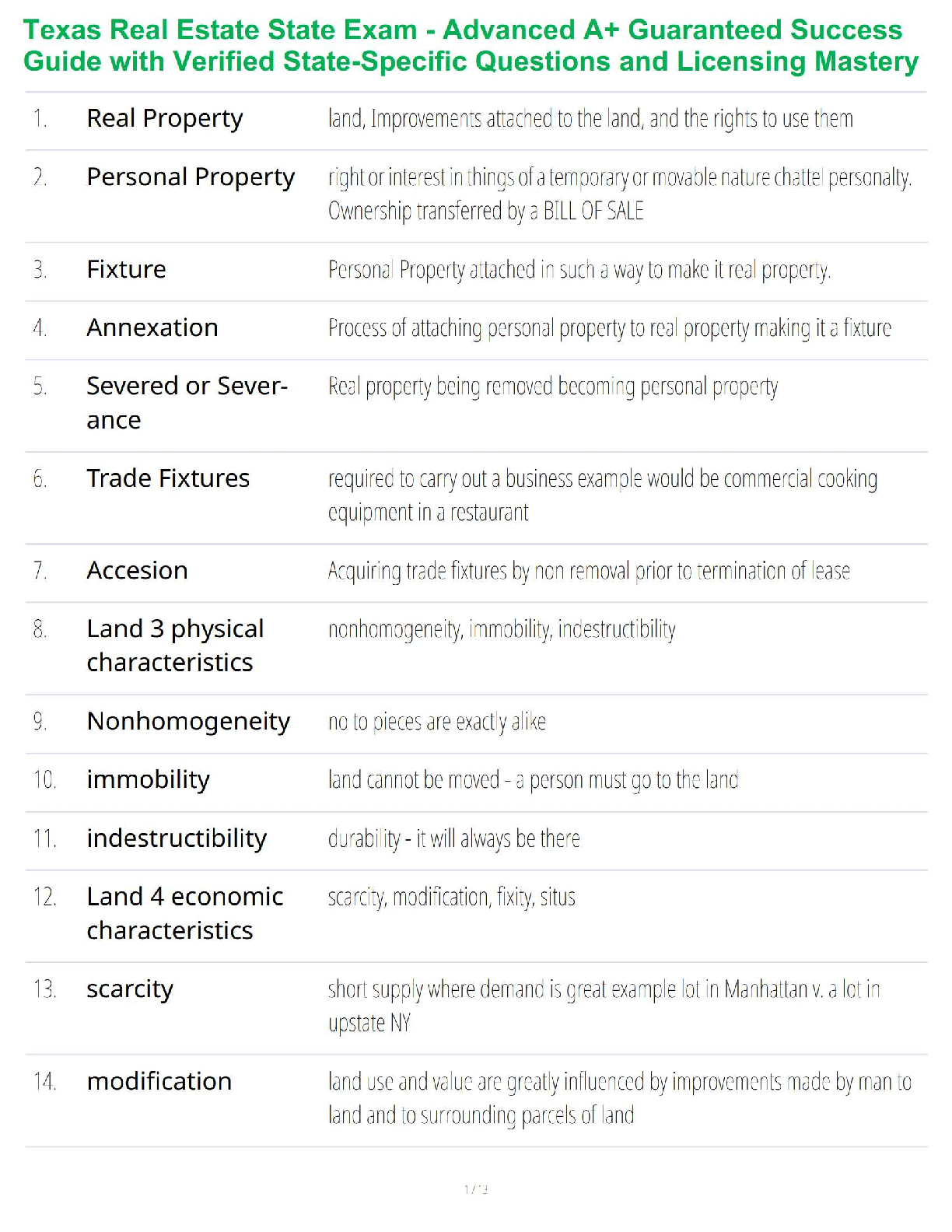
1. In the isolation of nucleic acids from blood samples, a step is typically performed to separate large molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids, from smaller molecules such as salts. Which type
...
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. In the isolation of nucleic acids from blood samples, a step is typically performed to separate large molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids, from smaller molecules such as salts. Which type of separation mechanism would best be suited for this task?
a. Ion exchange
b. Affinity
c. Partition
d. Size-exclusion
2. The type of separation mechanism for chromatography that involves, as one example, use of immunologic principles is _____ chromatography.
a. ion exchange
b. affinity
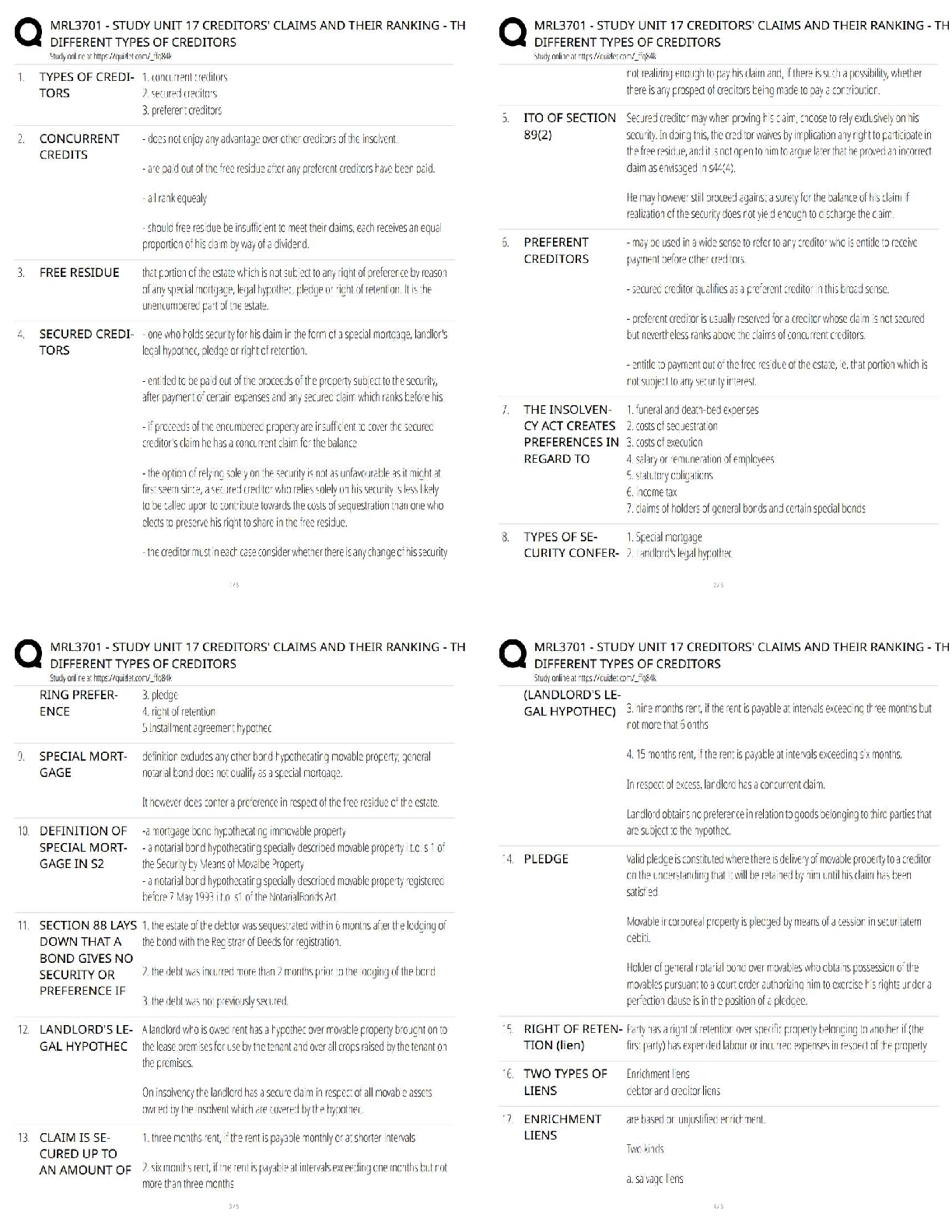
c. partition
d. adsorption
3. In the thin layer chromatography procedure for drug screening, the retention factor (Rf) value for a compound is given by the:
a. ratio of distance moved by the unknown solute to distance moved by the solvent in the mobile phase.
b. rate of movement of the mobile phase through the adsorbent compared with standards and controls.
c. measurement in centimeters of the distance the solute moved in the mobile phase from the point of application.
d. distance moved by the mobile phase front from the point of application compared with a control.
4. A toxicology screen is set up using thin layer chromatographic plates. Four positive controls/standards are used with the following distance of migration from application point results: Std A = 8 cm; Std B = 15 cm; Std C = 22. The acetone solvent front moved 35 cm. After processing an unknown sample, a solute had a migration distance of 16 cm. What are the retention factors (Rf) of standards A, B, and C?
a. 8, 15, 22
b. 8, 12, 18
c. 4.4, 2.3, 1.5
d. 0.23, 0.43, 0.63
5. A toxicology screen is set up using thin layer chromatographic plates. Four positive controls/standards are used with the following distance of migration from application point results: Std A = 8 cm; Std B = 15 cm; Std C = 22. The acetone solvent front moved 35 cm. After processing an unknown sample, a solute had a migration distance of 16 cm. What is the Rf of the unknown solute?
a. 0.23
b. 0.45
c. 1.94
d. 16
6. A measure of peak separation in a chromatographic method that equals the difference in retention time for two components divided by the average of their peak widths is the definition of:
a. retention factor.
b. derivatization.
c. resolution.
d. affinity.
7. Examine the following HPLC chromatograms, both of which were obtained from the same sample:
A B
Which chromatogram has the best resolution because of increased separation or chromatographic efficiency?
a. Chromatogram A
b. Chromatogram B
8. Which one of the following improvements could be made to increase the chromatographic (separation) efficiency of a poorly resolved HPLC separation?
a. Using a shorter column
b. Changing the composition of the mobile phase
c. Using smaller particles in the stationary phase
d. Increasing the dead volume
9. In HPLC, analyte detectors can consist of fluorometers, photometers, and electrochemical detectors. An electrochemical detector measures an electroactive analyte by:
a. monitoring the current that is generated by oxidation or reduction reaction under a constant potential voltage and that is proportional to the concentration of analyte.
b. measuring an electrical potential difference between two electrodes.
c. measuring the radiant energy given off when the chemical bonds of an element are dissociated and the element is placed in a ground or atomic state.
d. measuring both an alteration in enzyme level and a redox reaction at a potentiometric ion-specific electrode.
10. You are preparing placental tissue for separation and isolation of a specific enzyme. The enzyme has a negative charge, so you want to use chromatography to perform your task. Which one of the following chromatographic separation mechanisms would be most useful?
a. Ion-exchange
b. Partition
c. Affinity
d. Adsorption
11. A type of detector used in GC that is universal in its detection of compounds but has low sensitivity compared with other detectors is a(n) _____ detector.
a. flame ionization
b. thermal conductance
c. electron capture
d. photoionization
12. In partition chromatography, separation is based on:
a. hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions.
b. the molecular size of solutes in a solution and the size of the pores on the beads.
c. the ability of one component immobilized on a stationary phase to capture specific molecules in the mobile phase.
d. the differences in the relative solubility of compounds between the stationary and mobile phases.
13. In clinical applications using gas chromatography, which one of the following column temperature techniques will cause the more volatile analytes to elute first and therefore produce the best separation of complex mixtures of analytes with a range of volatilities?
a. Isothermal operation
b. Refrigerator (4° to 8° C) temperature operation
c. Temperature programmed operation
d. Room temperature operation
14. What component of an HPLC introduces an aliquot of sample into the column and how is this introduction accomplished with the high pressure in the flow path?
a. A syringe is used with a flexible tip placed into the flow path.
b. A flame ionizes the sample and sprays it into the column.
c. A flexible septum is coated with sample and placed in the column.
d. A fixed-loop injector with a switching valve moves the sample into the flow path.
15. Some analytes must be derivatized to increase their column retention or detectability. Derivatization means:
a. altering the chemical structure of the analyte to an isomeric form to increase detection and specificity.
b. adding fluorescent labels or combining the analyte with chiral reagents or other chemicals to increase detectability.
c. removing dissolved gases in the solvent to produce a clear chromatogram.
d. using multiple detectors to assist in identification.
TRUE/FALSE
1. Thin layer chromatography is a type of planar chromatography with separation based on the principles of partition chromatography.
2. In column chromatography, analytes are identified by their retention times.
[Show More]












.png)
.png)
.png)