1. Where are nutrients primarily absorbed?
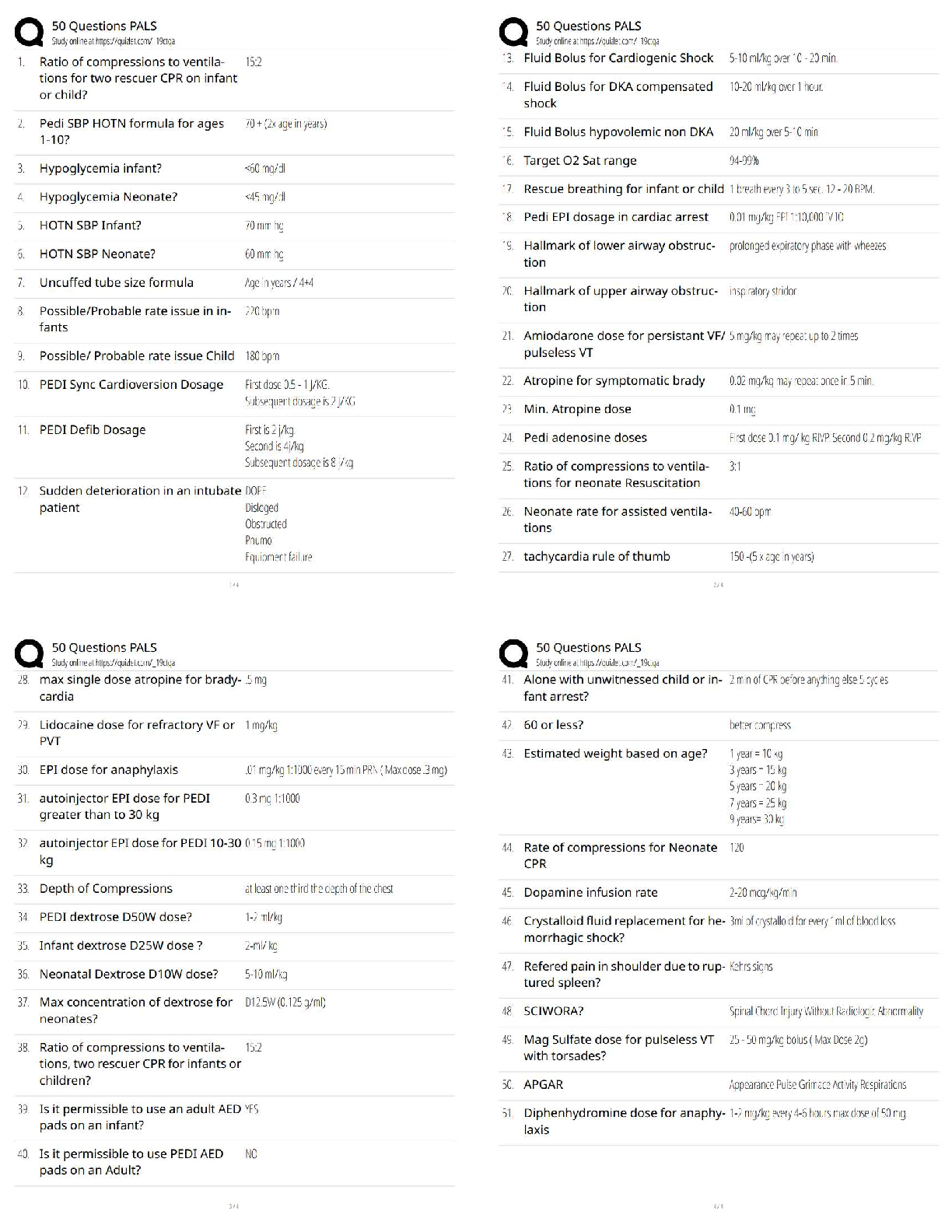
a. Stomach
b. Small intestine
c. Large intestine
d. They are absorbed in each of these sites.
2. Gastric secretions include all the following except
a. Bicarbonate
b. P
...
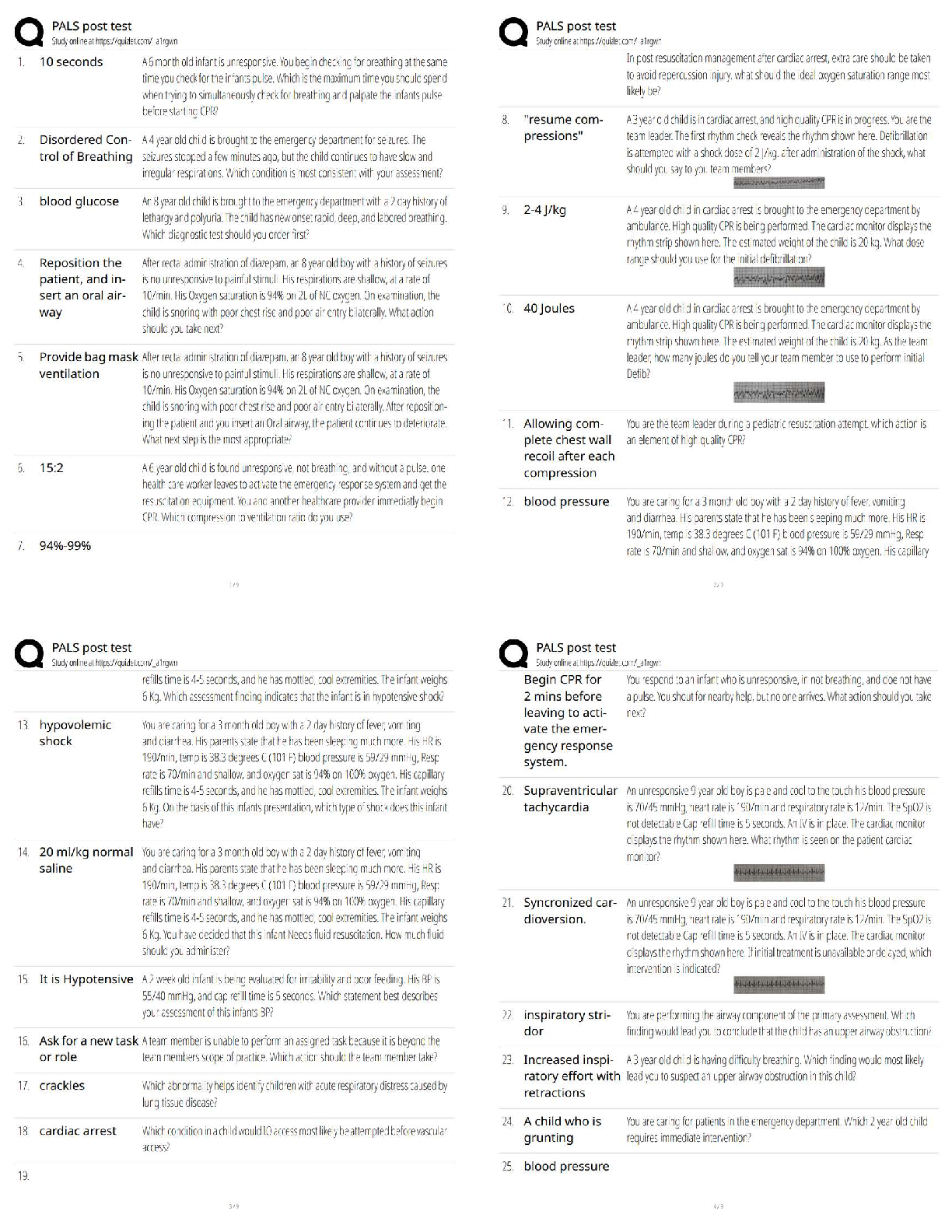
1. Where are nutrients primarily absorbed?
a. Stomach
b. Small intestine
c. Large intestine
d. They are absorbed in each of these sites.
2. Gastric secretions include all the following except
a. Bicarbonate
b. Pepsin
c. Hydrochloric acid
d. Mucus
3. What is the most common cause of chronic gastritis?
a. Excessive alcohol intake
b. Stress response
c. Helicobacter pylori
d. Pernicious anemia
4. Treatment for acute gastritis associated with stress response includes which of the following?
a. Antacids
b. Sucralfate
c. Beta-blockers
d. Foods containing lactose
5. What is the most significant factor in the development of gastric ulcers?
a. NSAIDs
b. H. pylori
c. Excess gastric acid
d. Spicy foods
6. Factors that protect the gastric mucosa include all the following except
a. Mucus
b. Prostaglandins
c. Pepsin
d. Bicarbonate
7. How does H. pylori, a bacterium, cause ulcers?
a. It increases production of gastric acid.
b. It causes an inflammatory response that destroys tissue.
c. It directly erodes sites in the mucosal wall.
d. All of the above.
8. What is the underlying pathology experienced by people with irritable bowel syndrome?
a. Changes in mucous cell structure
b. Excessive gastric secretions
c. Hypersensitive responses to ordinary stimuli
d. Impaired colonic reflexes
9. Which of the following statements about the relationship of IBS and psychiatric disorders is correct?
a. People with IBS have poor coping skills.
b. Women who have been sexually or physically abused may also have IBS.
c. Anxiety and depression cause IBS.
d. People with IBS often have psychiatric histories.
10. Jane S., 24, comes to the emergency room complaining of abdominal pain and bloody stools since yesterday afternoon. This has never happened to her before, and she is very alarmed. While talking with her, she remembers that her aunt and grandmother both had similar complaints at times. She says neither of them ever ate fresh fruit for that reason. She has no fever but complains that she constantly feels as if she is going to have a bowel movement regardless of how often she goes. What do you suspect she has?
a. Ulcerative colitis
b. Irritable bowel disease
c. Crohn’s disease
d. Infectious diarrhea
11. Pharmacological management of Crohn’s disease may include the use of which of the following?
a. Steroids
b. Antibiotics
c. Antidiarrheals
d. All of the above
12. What is thought to cause diverticulitis?
a. Genetics
b. Infection
c. Environmental factors
d. Diet
13. Which of the following is a complication of diverticulitis?
a. Abscess formation
b. Peritonitis
c. Local inflammation
d. All of the above
14. An intestinal obstruction usually results in which of the following?
a. Massive fluid and electrolyte imbalances
b. Life-threatening peritonitis
c. Bowel infarction
d. All of the above
15. Which of the following is not associated with a bacterial gastroenteritis?
a. Others who have shared the same food and water source are ill with similar symptoms.
b. The source of contamination is unwashed surfaces or undercooked food.
c. Individuals become ill within 12 hours of ingesting the contaminated product.
d. It is highly contagious and spreads rapidly among children and the elderly.
16. Diarrhea is always accompanied by an increase in the water content of the stools. All of the following are responsible for this except
a. Increased fluid ingestion
b. Increased fluid secretion
c. Decreased fluid absorption
d. Alteration in bowel motility
17. Adenocarcinoma of the esophagus is associated with which of the following?
a. Gastritis
b. Iron excess
c. Alcoholism
d. Barrett’s esophagus
18. From what do colorectal cancers most often arise?
a. Ulcerated tissue
b. Adenomas
c. Lipomas
d. Diverticula
19. The liver receives blood from two sources, each with a different pressure gradient. This becomes important when the liver is not functioning properly. Which of the following is correct?
a. Hepatic artery under high pressure; portal vein under low pressure
b. Hepatic artery under moderately high pressure; portal vein under low pressure
c. Mesenteric artery under high pressure; mesenteric vein under low pressure
d. Mesenteric artery under moderately high pressure; mesenteric vein under low pressure
20. What do alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase measure?
a. Pancreatic damage
b. Hepatic damage
c. Hepatitis antibodies
d. Gallstones
21. Jeanette tells you that several friends with whom she shared a beach house for 2 weeks a month ago have recently been diagnosed with hepatitis. She says she has been vaccinated against hepatitis and was not sexually active with anyone in this group. She asks if she is likely to get hepatitis too. How do you respond?
a. No, the vaccination will protect you.
b. No, not if you did not have unprotected sex.
c. Possibly, the source may be from shellfish or poor hand washing.
d. Possibly, but it has been a month and if you have not contracted it already, it’s unlikely that you will.
22. Anitha and Vivic are a married couple. Both have hepatitis B and are now carriers of the disease. Which of the following statements about hepatitis B is true?
a. Carriers cannot infect others if they are not having symptoms themselves.
b. They probably infected each other.
c. Their children will not be affected by their illness.
d. They are both at risk for developing cirrhosis and carcinoma of the liver.
23. Cirrhosis may be caused by which of the following?
a. Alcohol
b. Hepatitis
c. Obstruction
d. All of the above
24. Esophageal varicosities are a result of which of the following?
a. Ascites
b. Portal hypertension
c. Hepatic encephalopathy
d. Metabolic dysfunction
25. Elevated levels of which substance produce hepatic encephalopathy?
a. Nitrates
b. Glucose
c. Ammonia
d. Albumin
26. Pancreatitis is commonly associated with which chronic disease?
a. Multiple sclerosis
b. Alcoholism
c. Rheumatoid arthritis
d. Diabetes
27. How are fatty foods digested after surgical resection for cholecystitis?
a. By bile flowing directly from the liver into the duodenum
b. By bile stored in the pancreatic ducts into the duodenum
c. Fatty foods must be avoided to remain comfortable
d. By dietary supplements or bile enzymes taken by mouth to digest fatty foods
28. A patient with a nasogastric tube is at increased risk for
a. Chronic gastritis
b. H. pylori
c. B12 deficiency
d. Stress-induced gastric ulcer
29. Altered bowel habits, bloating, and abdominal pain that occur when a person’s stress level is increased are characteristic of
a. Crohn’s’ disease
b. IBS
c. Ulcerative colitis
d. Diverticulosis
30. H. pylori produce release of urease. This enzyme is necessary for
a. Inhibition of ammonia production that decreases gastric acid
b. Prevention of formation of adenocarcinomas
c. Inhibition of cytokinin production
d. Formation of B12
31. Clinical manifestations of diverticulitis include
a. Left lower quadrant pain
b. Constipation
c. Leukocytosis
d. All of the above
32. Signs and symptoms of ulcerative colitis include all of the following except
a. Periumbilical pain
b. Relief with defecation
c. Bloody diarrhea
d. Weight loss
33. Your patient was recently diagnosed with celiac sprue. Which of the following foods would you tell her to avoid?
a. Rice
b. Wheat flour
c. Nuts
d. Fiber
[Show More]












.png)
.png)
.png)