1. Know bone marrow/stem cell differentiation: Cells further differentiated from myeloid stem cells (all that apply)
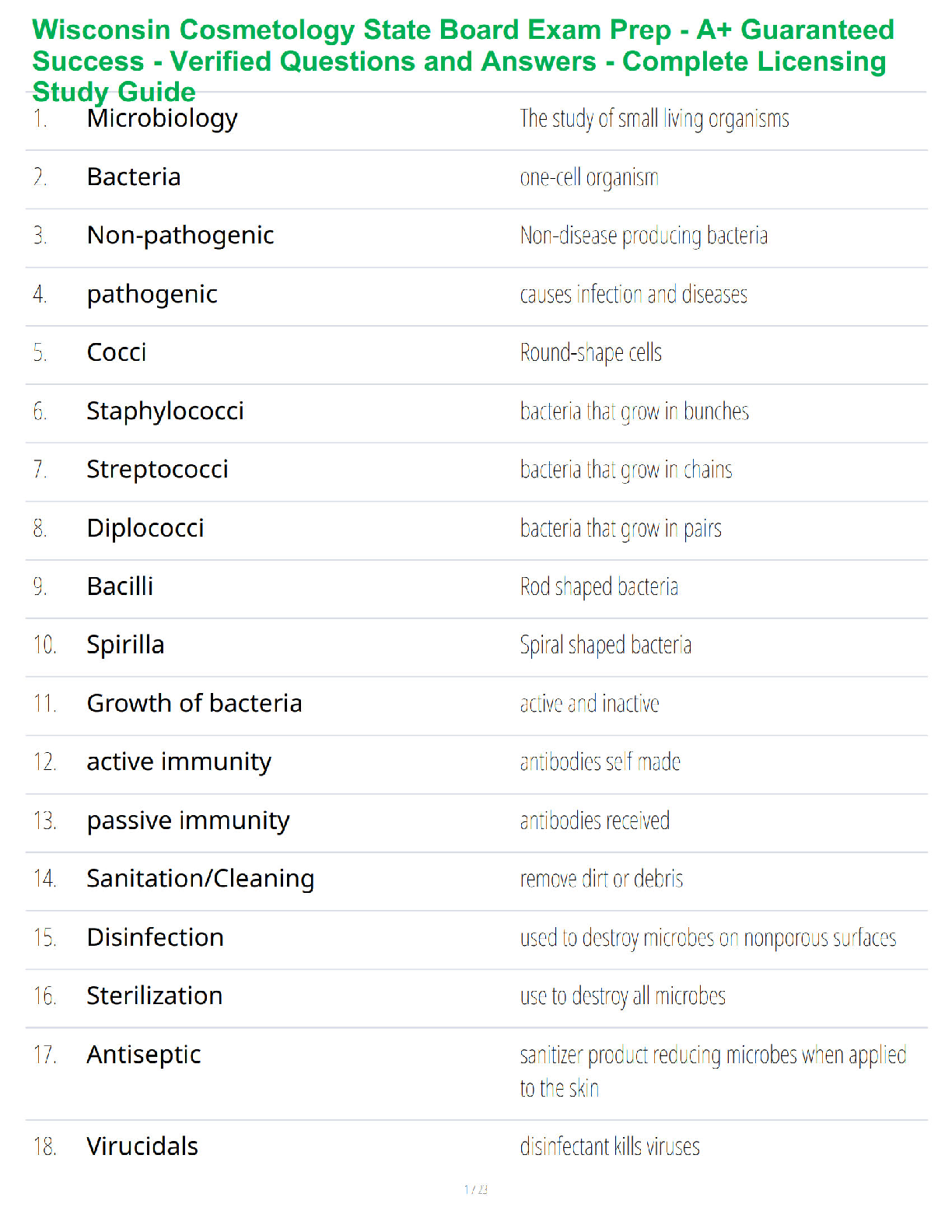
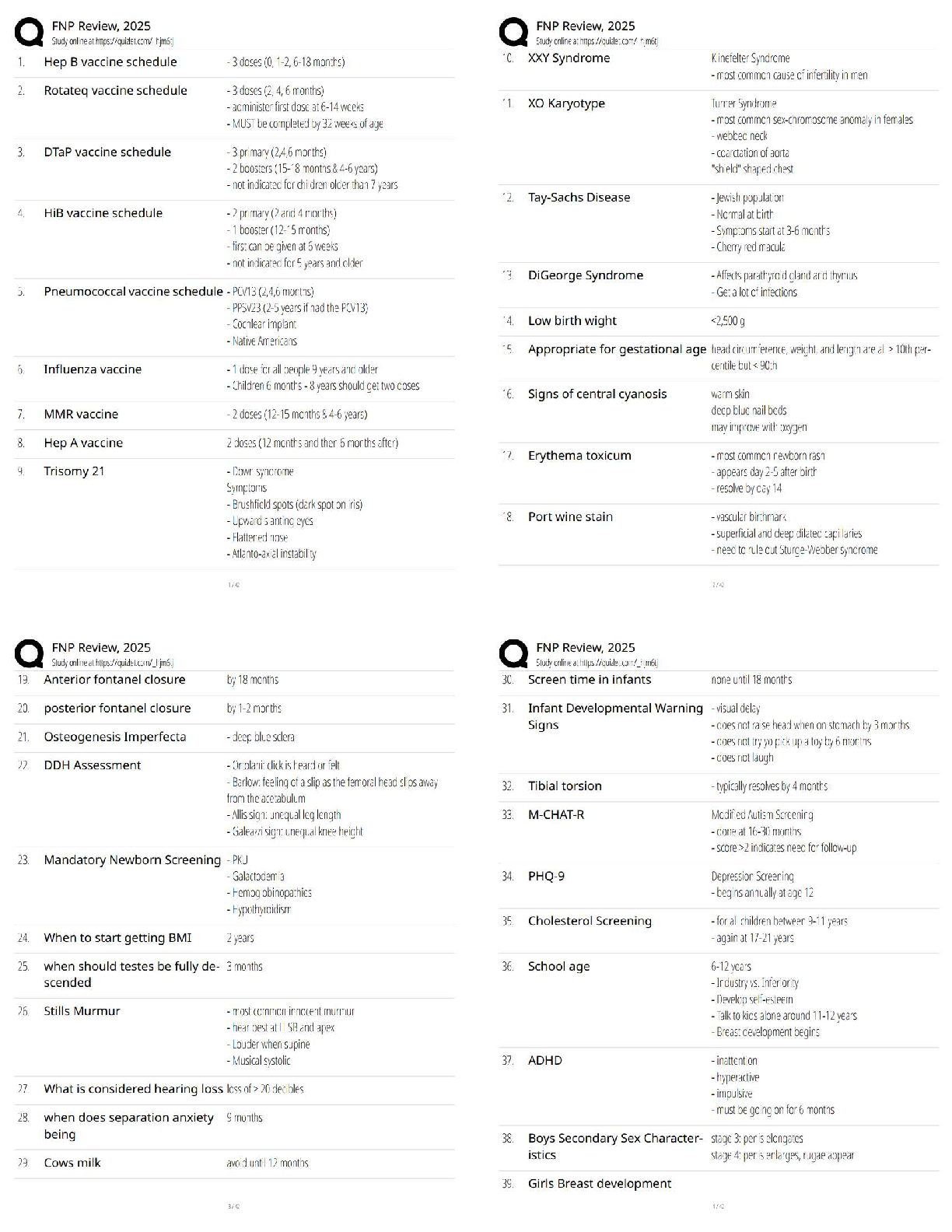
NUR 2212Homestead Campus Study Guide Test # 3
1. Know bone marrow/stem cell differentiation: Cells
...
1. Know bone marrow/stem cell differentiation: Cells further differentiated from myeloid stem cells (all that apply)
NUR 2212Homestead Campus Study Guide Test # 3
1. Know bone marrow/stem cell differentiation: Cells further differentiated from myeloid stem cells (all that apply)
Through the process of hematopoiesis, stem cells differentiate into either myeloid or lymphoid stem cells. Into what do myeloid stem cells further differentiate? Select all that apply.
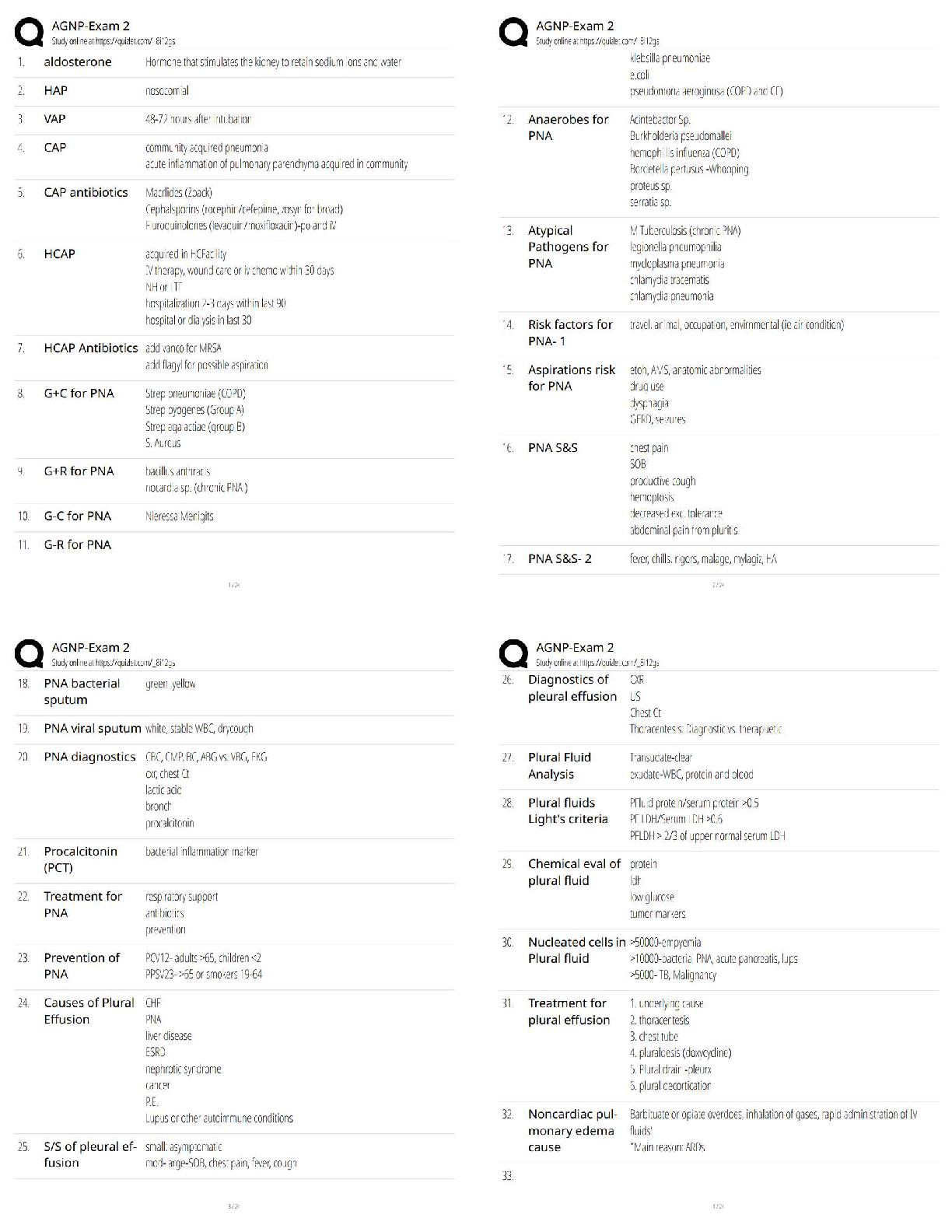
2. Know autologous blood donation: Advantages
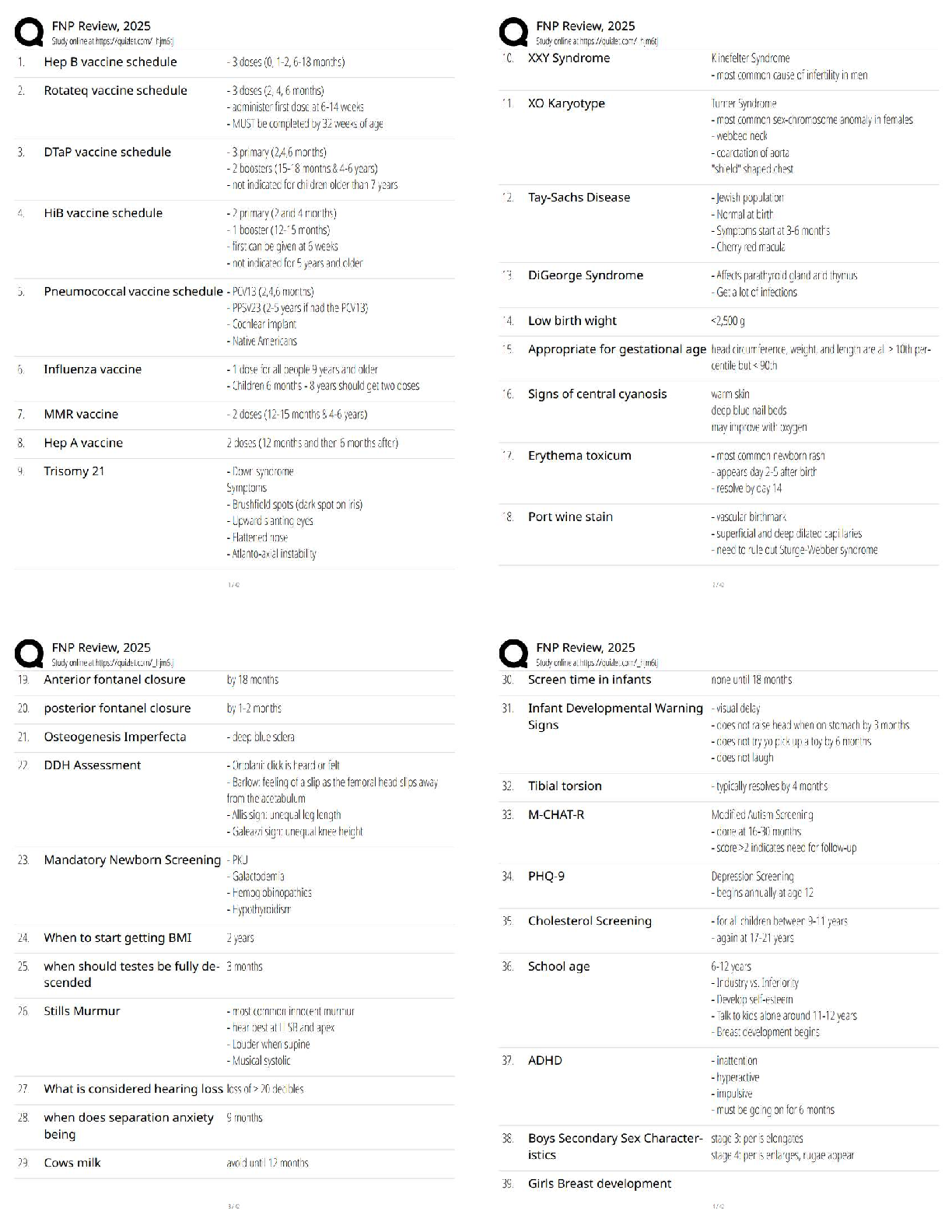
Autologous blood donation= patient’s own blood that has been collected for future
A patient undergoing a hip replacement has autologous blood on standby if a transfusion is needed. What is the primary advantage of autologous transfusions?
B) Prevention of viral infections from another person’s blood
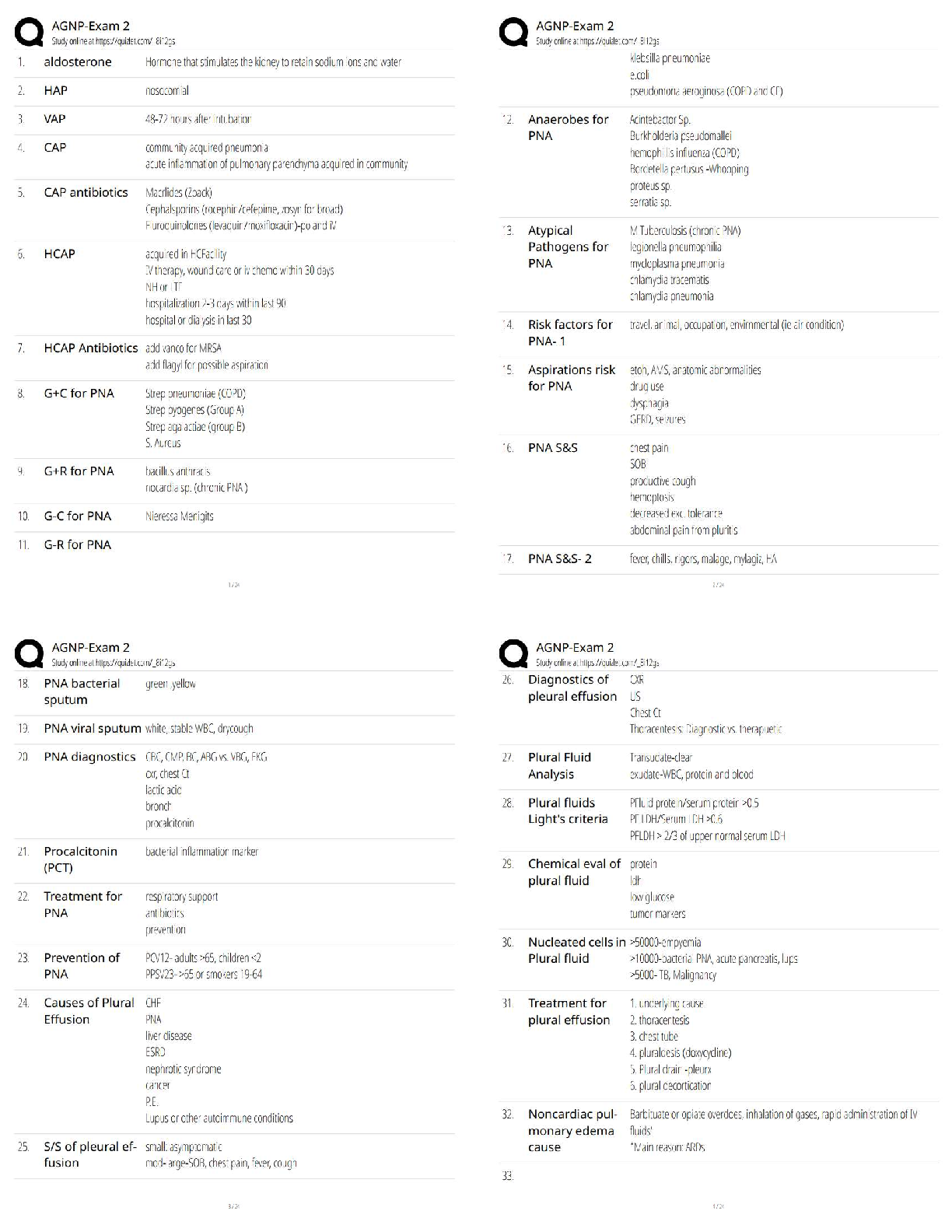
Which of the following circumstances would most clearly warrant autologous blood donation?
C) The patient has elective surgery pending.
3. Know bone marrow/stem cell differentiation: Cells further differentiated from lymphoid stem cells
T, B lymphocytes, plasma cells or natural killer cells/ cytokines
A patient has been diagnosed with a lymphoid stem cell defect. This patient has the potential for a problem involving which of the following?
A) Plasma cells
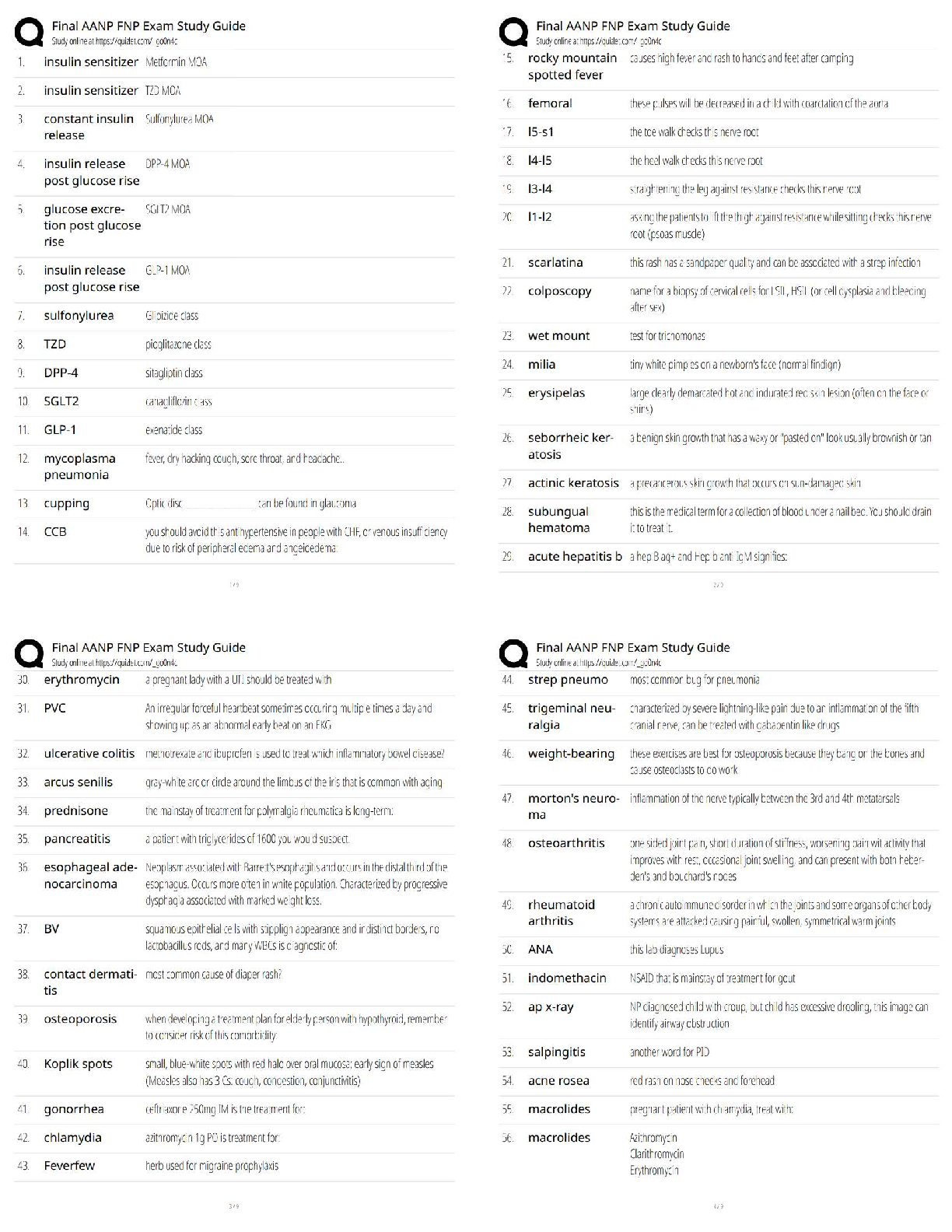
a defect in the lymphoid stem cell can cause problems with T or B lymphocytes, plasma cells (a more differentiated form of B lymphocyte), or natural killer (NK) cells.
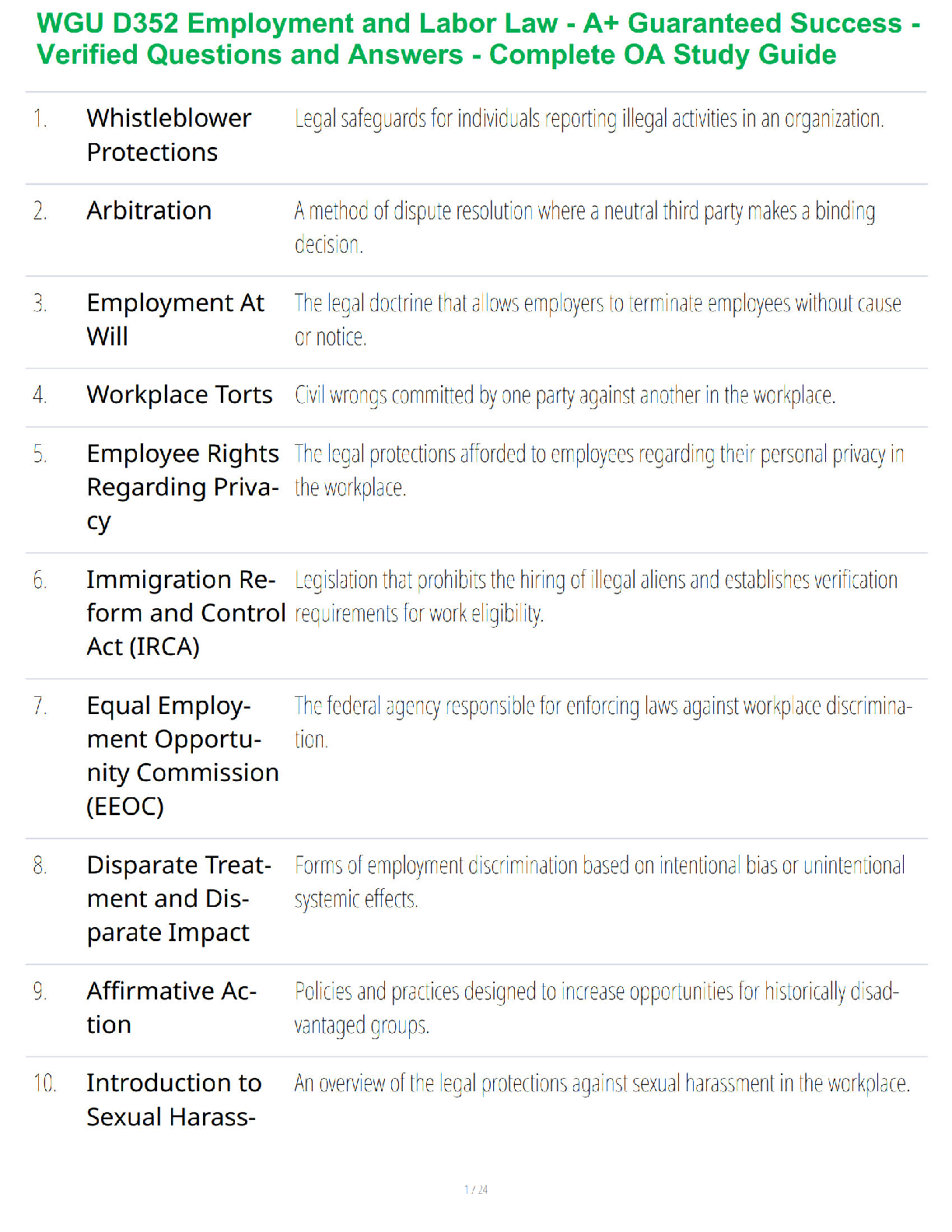
4. Know structure of erythrocytes (red blood cells)
The nurse is describing normal RBC physiology to a patient who has a diagnosis of anemia. The nurse should explain that the RBCs consist primarily of which of the following?
5. Know physiological process for RBCs formation: How is initiated?
A patient with a hematologic disorder asks the nurse how the body forms blood cells. The nurse should describe a process that takes place where?
6. Know common causes of iron efficiency anemia in adults: laboratory tests to detect causes
An older adult client is exhibiting many of the characteristic signs and symptoms of iron deficiency. In addition to a complete blood count, what diagnostic assessment should the nurse anticipate?
A low serum iron level, a low ferritin level, and symptoms of pica are associated with iron deficiency anemia. TIBC may also be elevated. None of the other anemias are associated with pica.
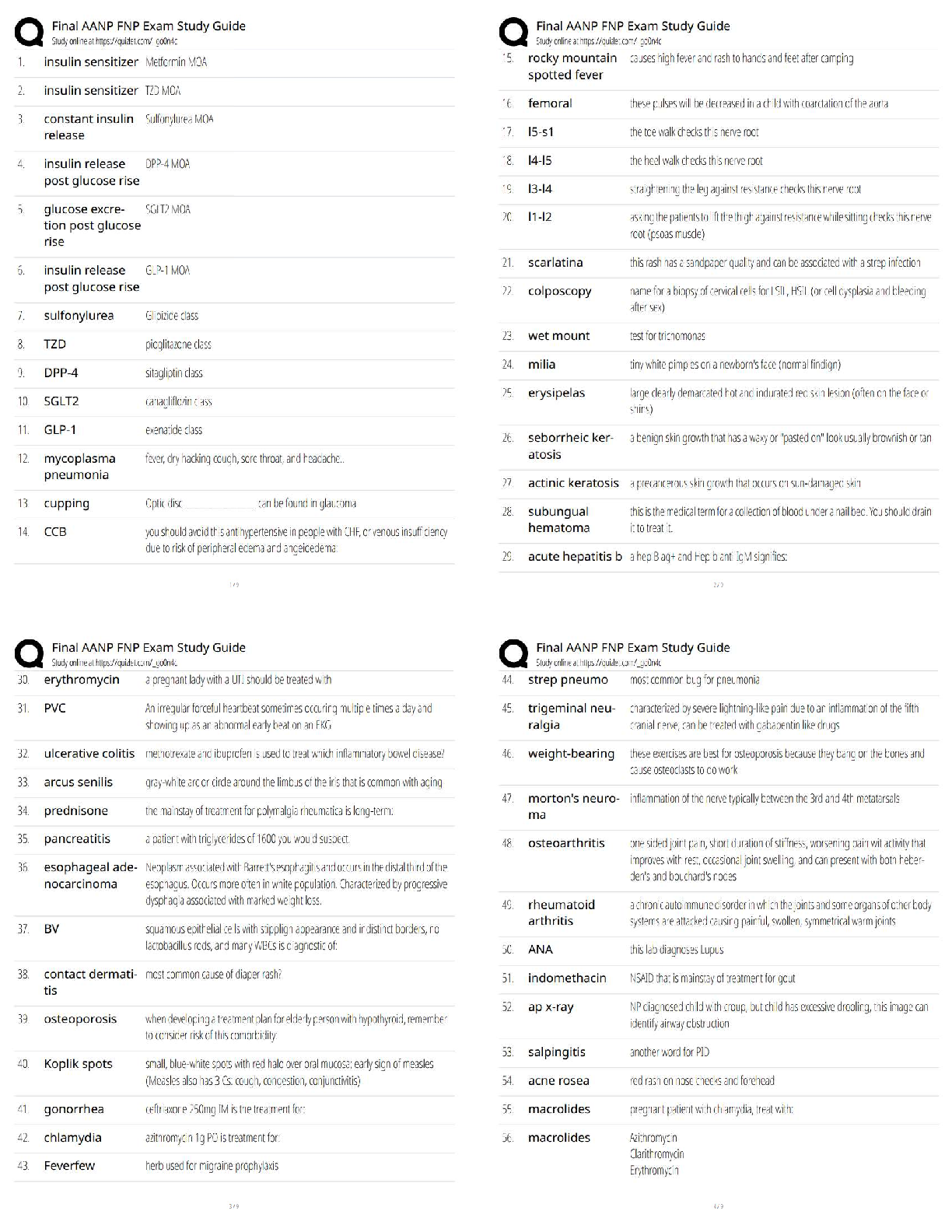
7. Know further differentiation of B- Lymphocyte: What are plasma cells and their function
A nurse is educating a patient about the role of B lymphocytes. The nurse’s description will include which of the following physiologic processes?
D) Antibody production
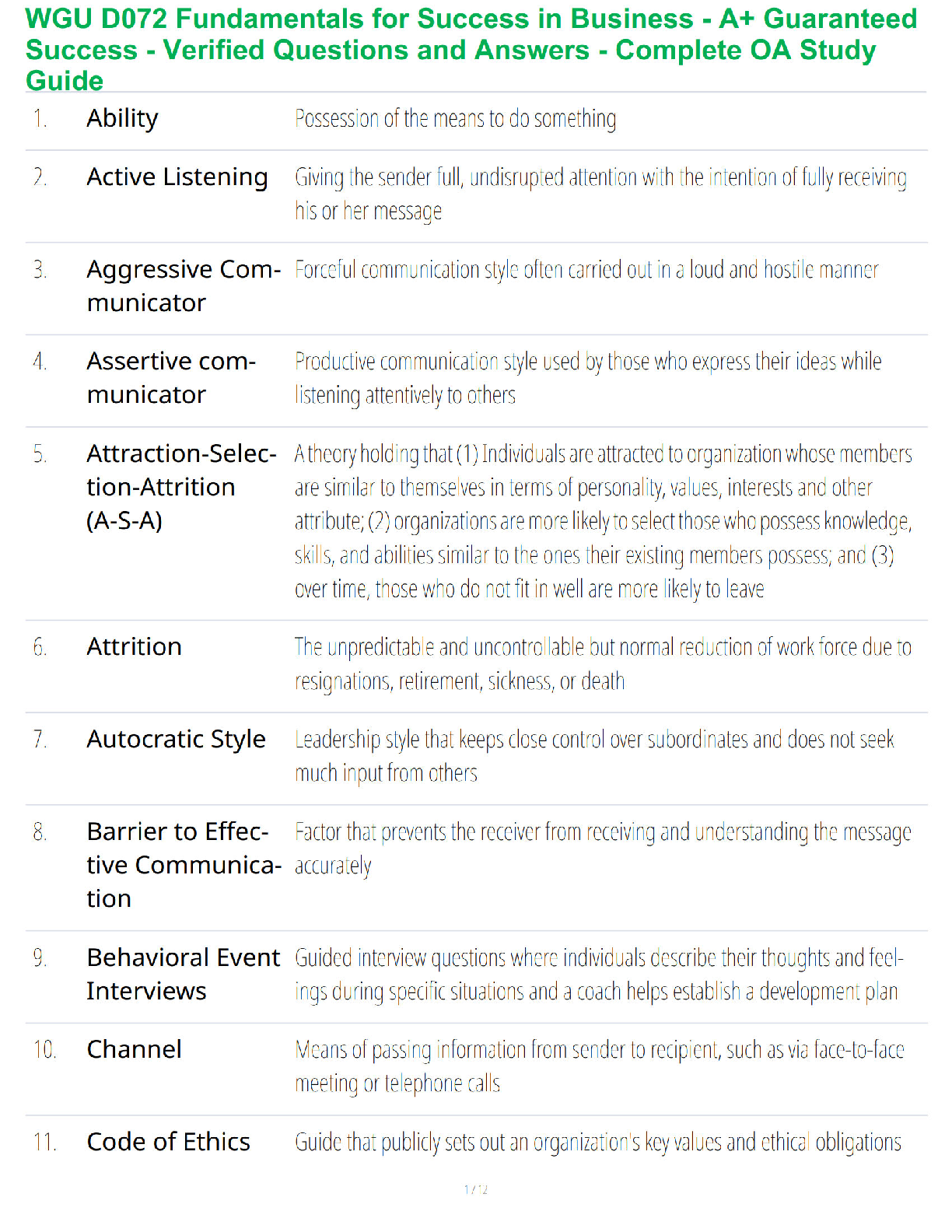
8. Know spleen function: Priority nursing considerations after splenectomy. Think of possible consequences after surgery. Discharge education to patient
A patient is scheduled for a splenectomy. During discharge education, what teaching point should the nurse prioritize?
B) The need to report any signs or symptoms of infection promptly
9. Know process of hemostasis after a cut
An individual has accidentally cut his hand, immediately initiating the process of hemostasis. Following vasoconstriction, what event in the process of hemostasis will take place?
10. Know therapeutic phlebotomy: indications
The nurse’s brief review of a patient’s electronic health record indicates that the patient regularly undergoes therapeutic phlebotomy. Which of the following rationales for this procedure is most plausible?
11. Know nursing actions during the transfusion of packed red blood cells: Preprocedure, during procedure, and postprocedure
Before:
A patient’s low hemoglobin level has necessitated transfusion of PRBCs. Prior to administration, what action should the nurse perform?
C)Assess the patient’s vital signs to establish baselines.
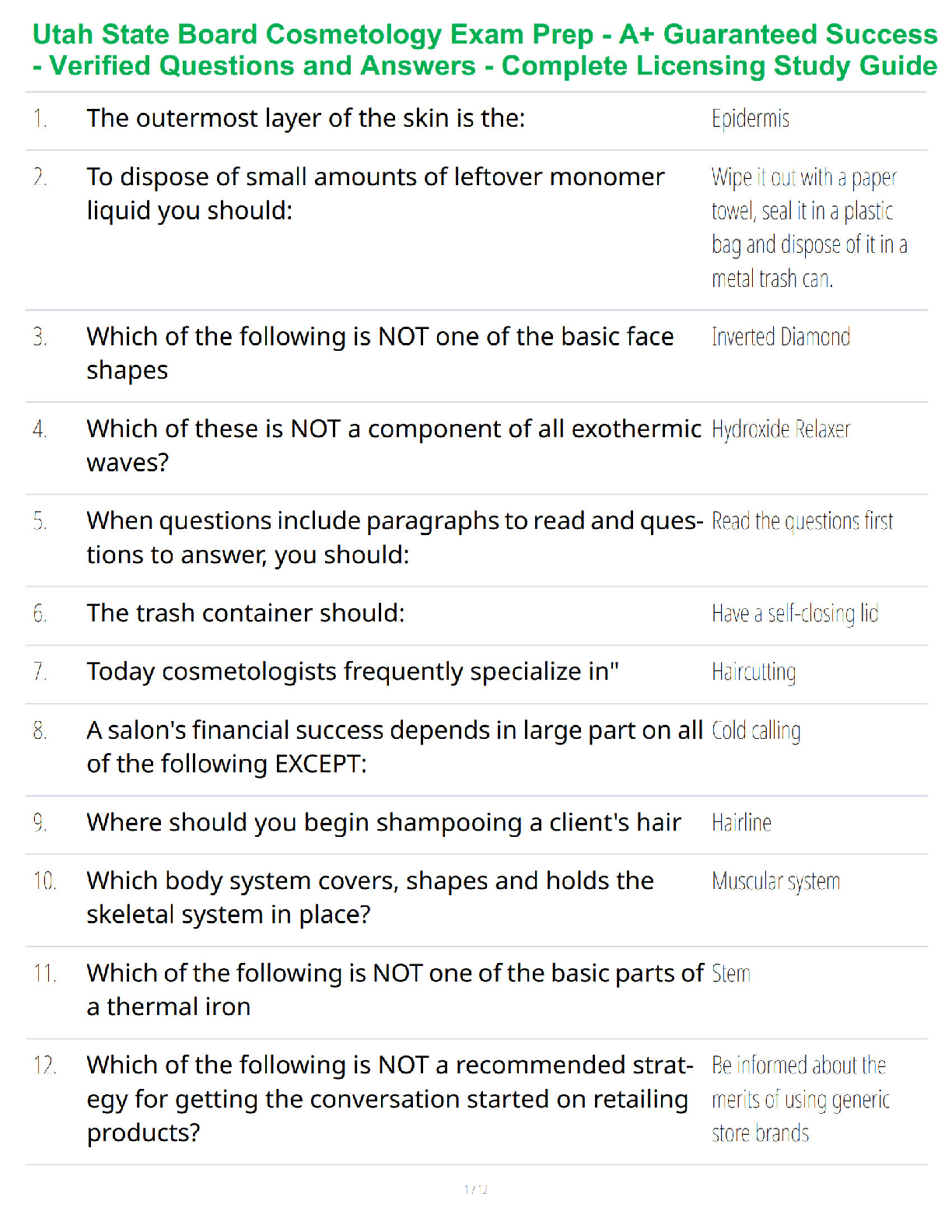
During:
The nurse caring for a patient receiving a transfusion notes that 15 minutes after the infusion of packed red blood cells (PRBCs) has begun, the patient is having difficulty breathing and complains of severe chest tightness. What is the most appropriate initial action for the nurse to take?
A patient on the medical unit is receiving a unit of PRBCs. Difficult IV access has necessitated a slow infusion rate and the nurse notes that the infusion began 4 hours ago. What is the nurse’s most appropriate action?
B) Discontinue the remainder of the PRBC transfusion and inform the physician.
12. Know nursing action when transfusion of packed red blood cells exceeds more than 4 hours: its rationale
A patient on the medical unit is receiving a unit of PRBCs. Difficult IV access has necessitated a slow infusion rate and the nurse notes that the infusion began 4 hours ago. What is the nurse’s most appropriate action?
B) Discontinue the remainder of the PRBC transfusion and inform the physician.
13. Know etiology of acute hemolytic reaction
A patient is being treated in the ICU after a medical error resulted in an acute hemolytic transfusion reaction. What was the etiology of this patient’s adverse reaction?
14. Know measures of preventing acute hemolytic reaction
An interdisciplinary team has been commissioned to create policies and procedures aimed at preventing acute hemolytic transfusion reactions. What action has the greatest potential to reduce the risk of this transfusion reaction?
15. Know assessment of transfusion-associated circulatory overload (TACO): S/S
A patient is receiving a blood transfusion and complains of a new onset of slight dyspnea. The nurse’s rapid assessment reveals bilateral lung crackles and elevated BP. What is the nurse’s most appropriate action?
A) Slow the infusion rate and monitor the patient closely.
16. Know complications of long-term transfusion therapy
Complications include: iron overload, infection, and transfusion reaction
Manifested by: HF, endocrine failure (diabetes, hypothyroidism etc.)/ hepatitis B or C, CMV/ and sensitization, febrile reactions (respectively)
D) Iron overload
17. Know priority nursing management for transfusion reactions
A patient is receiving the first of two ordered units of PRBCs. Shortly after the initiation of the transfusion, the patient complains of chills and experiences a sharp increase in temperature. What is the nurse’s priority action?
18. Know transfusion of platelets or fresh-frozen plasma: speed of infusion for each type of transfusion
The nurse is preparing to administer a unit of platelets to an adult patient. When administering this blood product, which of the following actions should the nurse perform?
A) Administer the platelets as rapidly as the patient can tolerate.
19. Know autologous donation
Which of the following circumstances would most clearly warrant autologous blood donation?
20. Know blood components commonly used in transfusion therapy (factor VIII, IX): indications and consideration
A patient’s electronic health record states that the patient receives regular transfusions of factor IX. The nurse would be justified in suspecting that this patient has what diagnosis?
B)Hemophilia
VIII
2) A young man with a diagnosis of hemophilia A has been brought to emergency department after suffering a workplace accident resulting in bleeding. Rapid assessment has revealed the source of the patient’s bleeding and established that his vital signs are stable. What should be the nurse’s next action?
A nurse is providing education to a patient with iron deficiency anemia who has been prescribed iron supplements. What should the nurse include in health education?
21. Know S/S of megaloblastic anemias
The nurse is assessing a new patient with complaints of overwhelming fatigue and a sore tongue that is visibly smooth and beefy red. This patient is demonstrating signs and symptoms associated with what form of what hematologic disorder?
22. Know consequences of decreased erythropoietin production in kidney injury
A patient with renal failure has decreased erythropoietin production. Upon analysis of the patient’s complete blood count, the nurse will expect which of the following results?
23. Know pica: Type of anemia related to it
A patient comes to the clinic complaining of fatigue and the health interview is suggestive of pica. Laboratory findings reveal a low serum iron level and a low ferritin level. With what would the nurse suspect that the patient will be diagnosed?
24. Know CBC findings in hemolytic anemia
A patient comes into the clinic complaining of fatigue. Blood work shows an increased bilirubin concentration and an increased reticulocyte count. What would the nurse suspect the patient has?
25. Know normal level of platelets: S/S of decreased values
A patient’s blood work reveals a platelet level of 17,000/mm3. When inspecting the patient’s integumentary system, what finding would be most consistent with this platelet level?
26. Know nursing diagnoses for patients diagnosed with iron deficiency anemia
An adult patient has been diagnosed with iron-deficiency anemia. What nursing diagnosis is most likely to apply to this patient’s health status?
27. Know iron containing foods
A woman who is in her third trimester of pregnancy has been experiencing an exacerbation of iron-deficiency anemia in recent weeks. When providing the patient with nutritional guidelines and meal suggestions, what foods would be most likely to increase the woman’s iron stores?
28. Know treatment of anemia related to end-stage kidney injury
A patient with poorly controlled diabetes has developed end-stage renal failure and consequent anemia. When reviewing this patient’s treatment plan, the nurse should anticipate the use of what drug?
29. Know sickle cell anemia: Nursing diagnosis for patients experiencing a vaso-occlusive crisis
A nurse is planning the care of a patient with a diagnosis of sickle cell disease who has been admitted for the treatment of an acute vaso-occlusive crisis. What nursing diagnosis should the nurse prioritize in the patient’s plan of care?
30. Know measures to prevent crises in patients suffering from sickle cell anemia
The medical nurse is aware that patients with sickle cell anemia benefit from understanding what situations can precipitate a sickle cell crisis. When teaching a patient with sickle cell anemia about strategies to prevent crises, what measures should the nurse recommend?
31. Know secondary polycythemia: etiological factors
A patient’s electronic health record notes that he has previously undergone treatment for secondary polycythemia. How should this aspect of the patient’s history guide the nurse’s subsequent assessment?
32. Know quantitative and qualitative platelet defects: etiological factors
A client with several chronic health problems has been newly diagnosed with a qualitative platelet defect. What component of the patient’s previous medication regimen may have contributed to the development of this disorder?
33. Know medication antidotes: warfarin toxicity
patient with a history of atrial fibrillation has contacted the clinic saying that she has accidentally overdosed on her prescribed warfarin (Coumadin). The nurse should recognize the possible need for what antidote?
34. Know causes of death in patients suffering from leukemia
A nurse is caring for a patient who has a diagnosis of acute leukemia. What assessment most directly addresses the most common cause of death among patients with leukemia?
35. Know priority nursing diagnosis for leukemic patient during the induction phase of chemotherapy
A nursing student is caring for a patient with acute myeloid leukemia who is preparing to undergo induction therapy. In preparing a plan of care for this patient, the student should assign the highest priority to which nursing diagnoses?
36. Know acute myeloid leukemia treatment: type of medication used during induction phase
One medical management of AML is to achieve remission by the Aggressive administration of chemotherapy, called induction therapy, which usually requires
37. Know priority nursing intervention during the induction phase of chemotherapy
A patient with a diagnosis of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is being treated with induction therapy on the oncology unit. What nursing action should be prioritized in the patient’s care plan?
38. Know S/S of a leukemic patient with low platelets
A nurse is caring for a patient who has been diagnosed with leukemia. The nurse’s most recent assessment reveals the presence of ecchymoseson the patient’s sacral area and petechiae in her forearms. In addition to informing the patient’s primary care provider, the nurse should perform what action?
39. Know Hodgkin lymphoma: diagnostic findings in CBC
An adult patient’s abnormal complete blood count (CBC) and physical assessment have prompted the primary care provider to order a diagnostic workup for Hodgkin lymphoma. The presence of what assessment finding is considered diagnostic of the disease?
40. Math question calculating IV drip rate: Example type: 500 mL over 2 hrs. Drip factor: 10 gtt/mL (3 questions)
41. Math question calculating infusion time: Example type: 2000 ml to infuse at a rate 100ml/hr – how long will it take to complete infusion? (4 questions)
42. Know pernicious anemia: S/S, treatment
Red smooth tongue, low B12 in pernicious anemia leads to large and oval shaped RBC’s
Numbness of hands/feet paresthesia
43. Know offspring % for parents that are carriers of sickle cell traits
4. A 25 year-old pregnant female and her partner both have sickle cell trait. What is the percentage that their offspring will develop sickle cell anemia?*
44. Know risk factors for sickle cell crisis (all that apply)
A 14 year-old female has sickle cell anemia. Which factors below can increase the patient’s risk for developing sickle cell crisis?
45. Know management of sickle cell crisis (all that apply)
A 6 year-old is admitted with sickle cell crisis. The patient has a FACE scale rating of 10 and the following vital signs: HR 115, BP 120/82, RR 18, oxygen saturation 91%, temperature 101.4’F. Select all the appropriate nursing interventions for this patient at
H. Remove restrictive clothing or objects from the patient
The answers are A, B, E, G, and H. When a patient is in sickle cell crisis, the abnormal RBCs are sickling and sticking together, which blocks blood flow. To help alleviate the RBCs from clumping together and sickling, oxygen and hydration are priority. This will help dilute the blood (hence decrease the sticking of RBCs) and help supply oxygen to the RBCs (remember abnormal RBCs with hemoglobin S are very sensitive to low oxygen levels and will sickle when there is low oxygen)
[Show More]












.png)
.png)
.png)