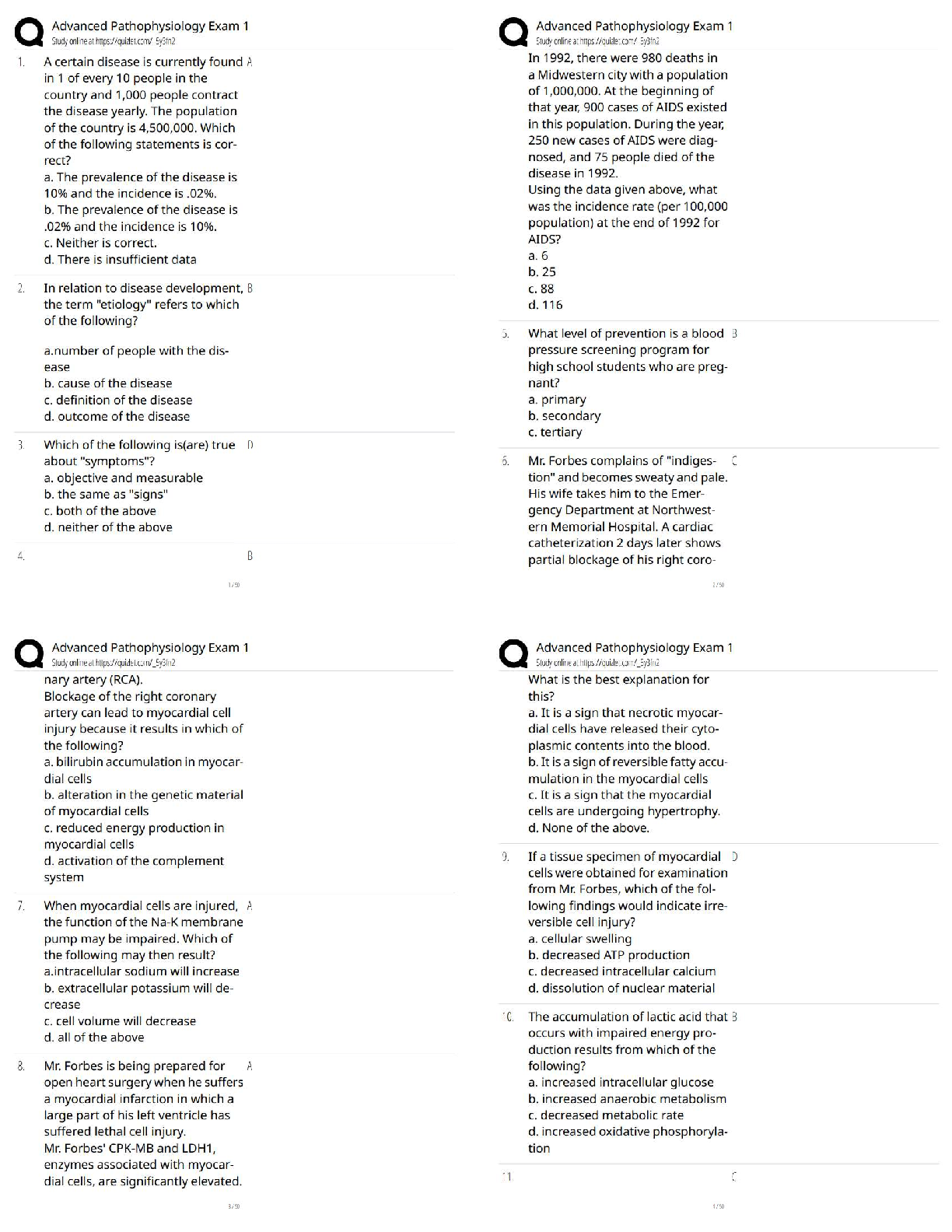
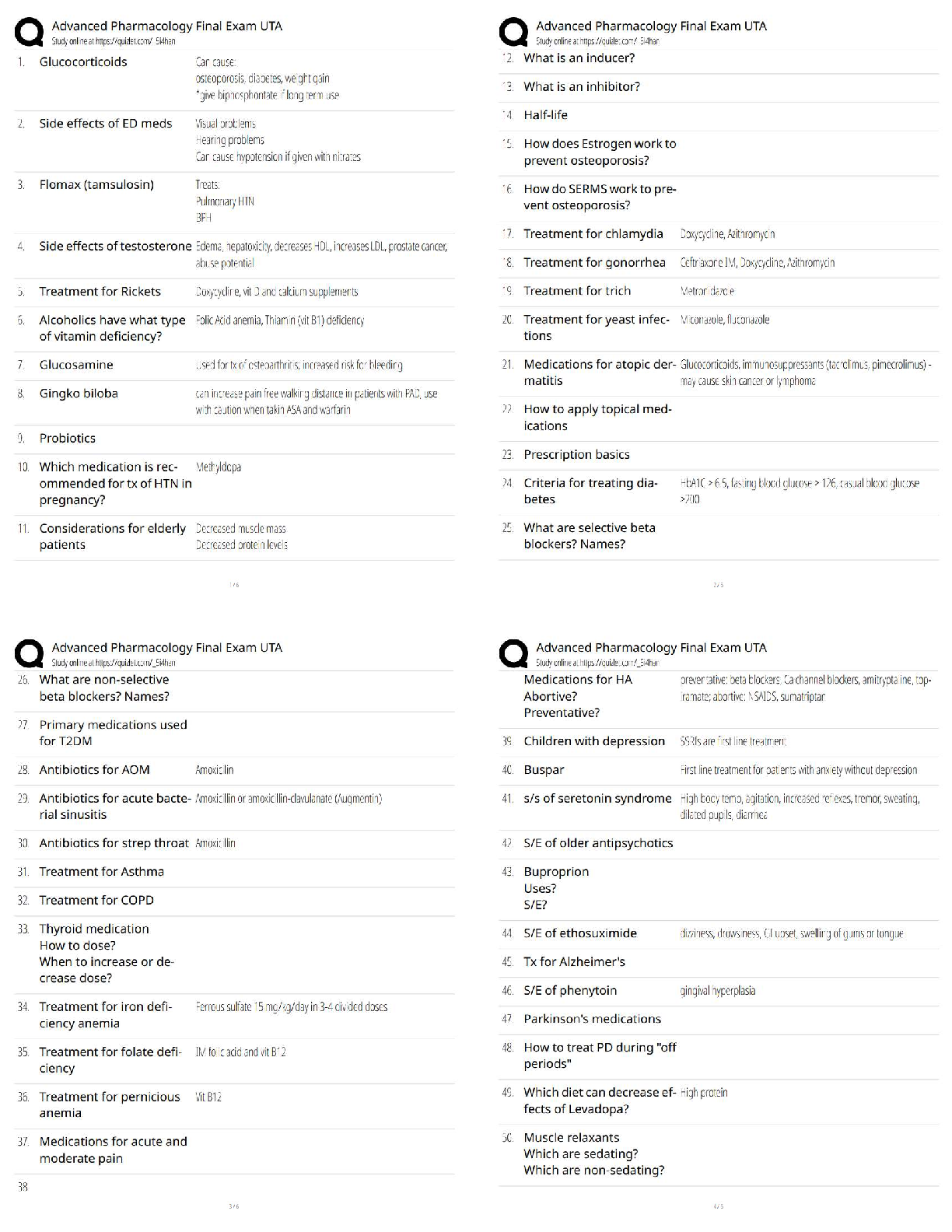
1. HEMATOLOGY 2Hematology 2 Evolve
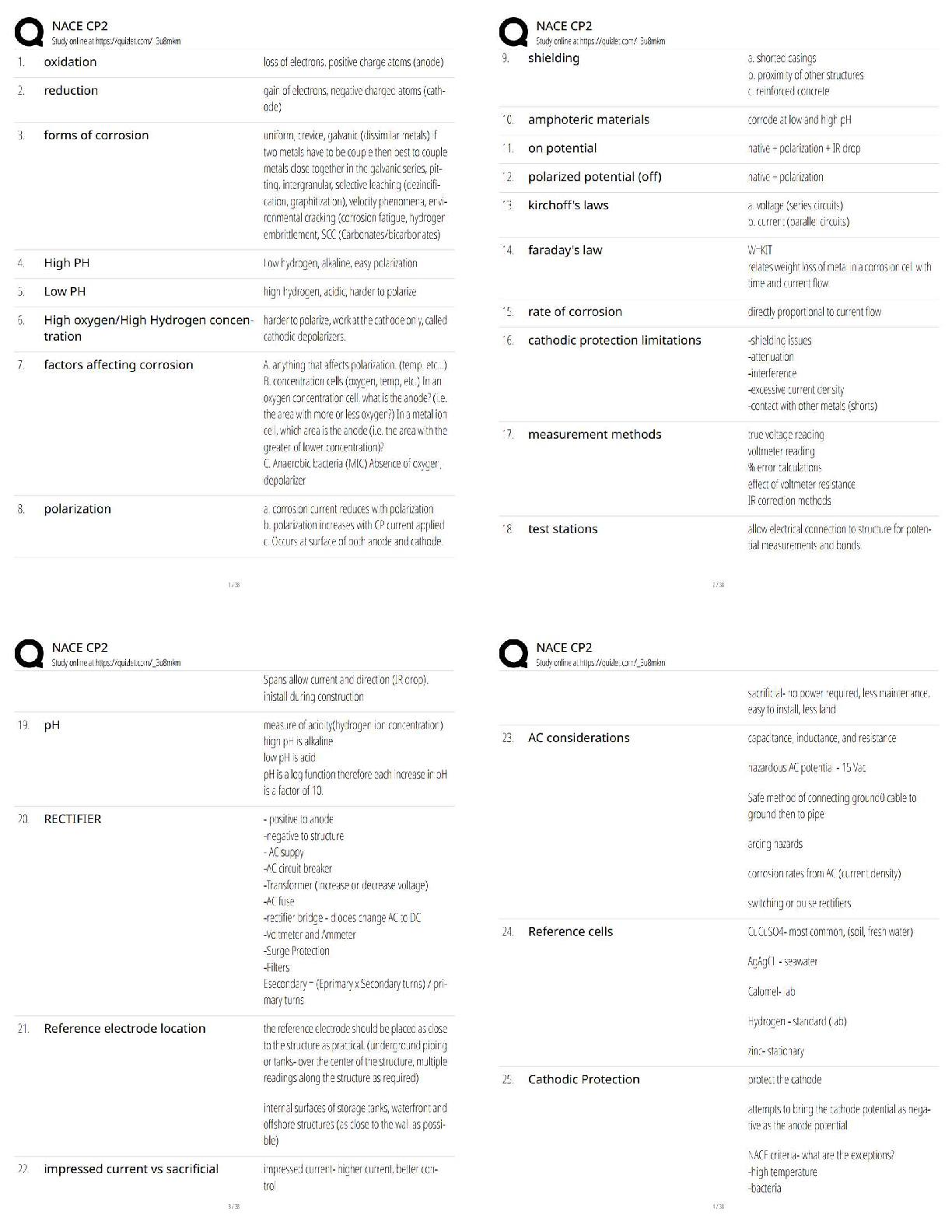
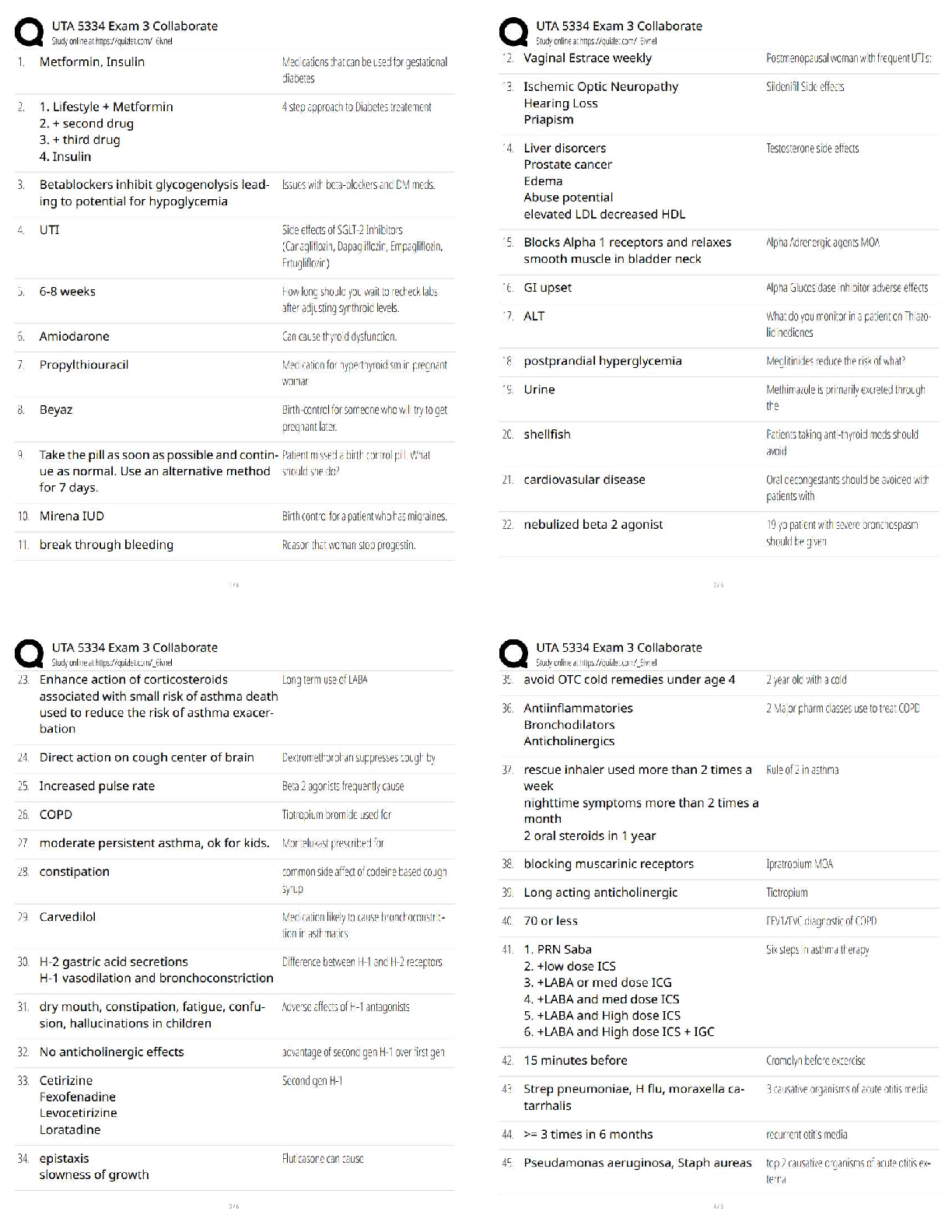
2.
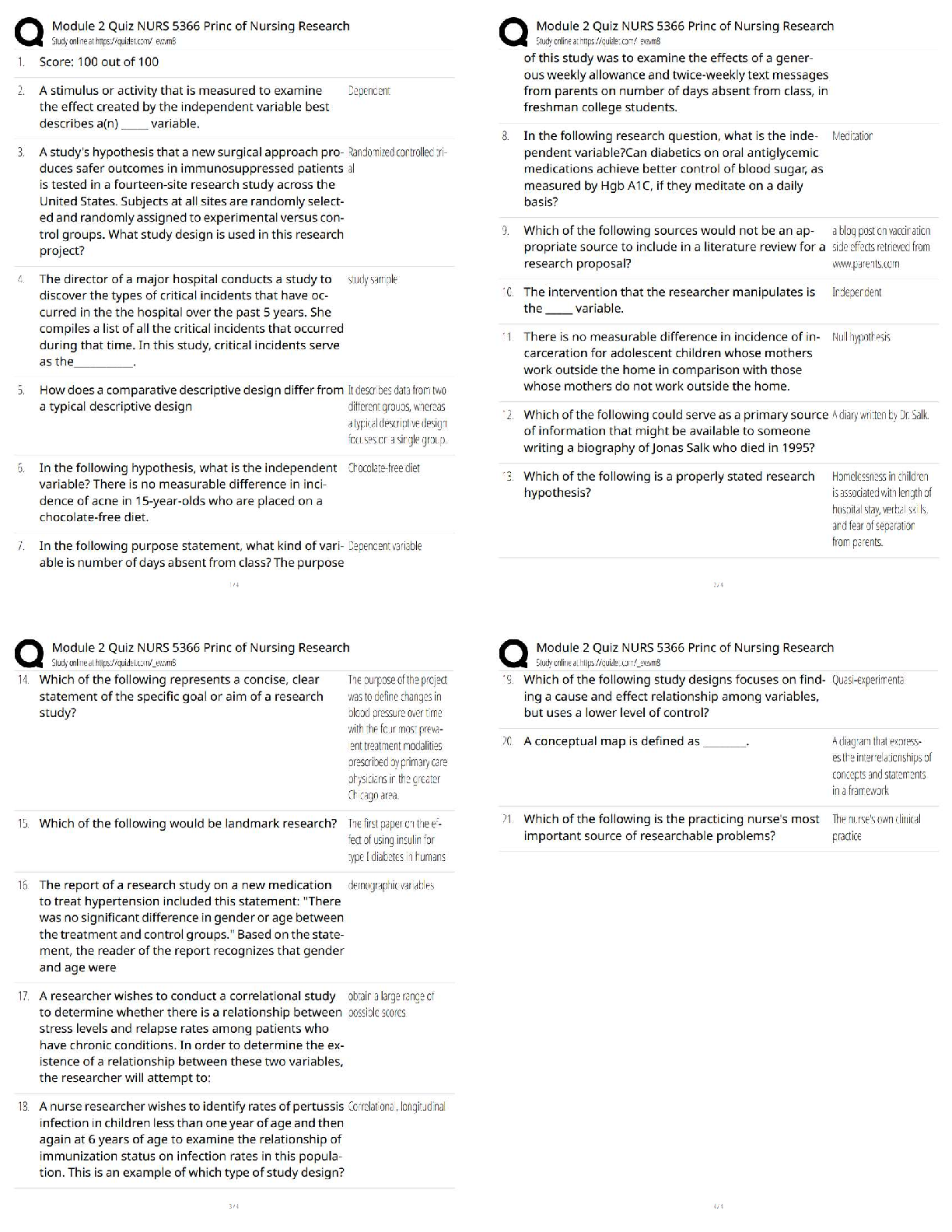
3. Cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) 0.2 mg intramuscularly (IM) is prescribed for a client with pernicious anemia. A vial of the drug labeled "1 mL = 100 mcg" is available. How many m
...
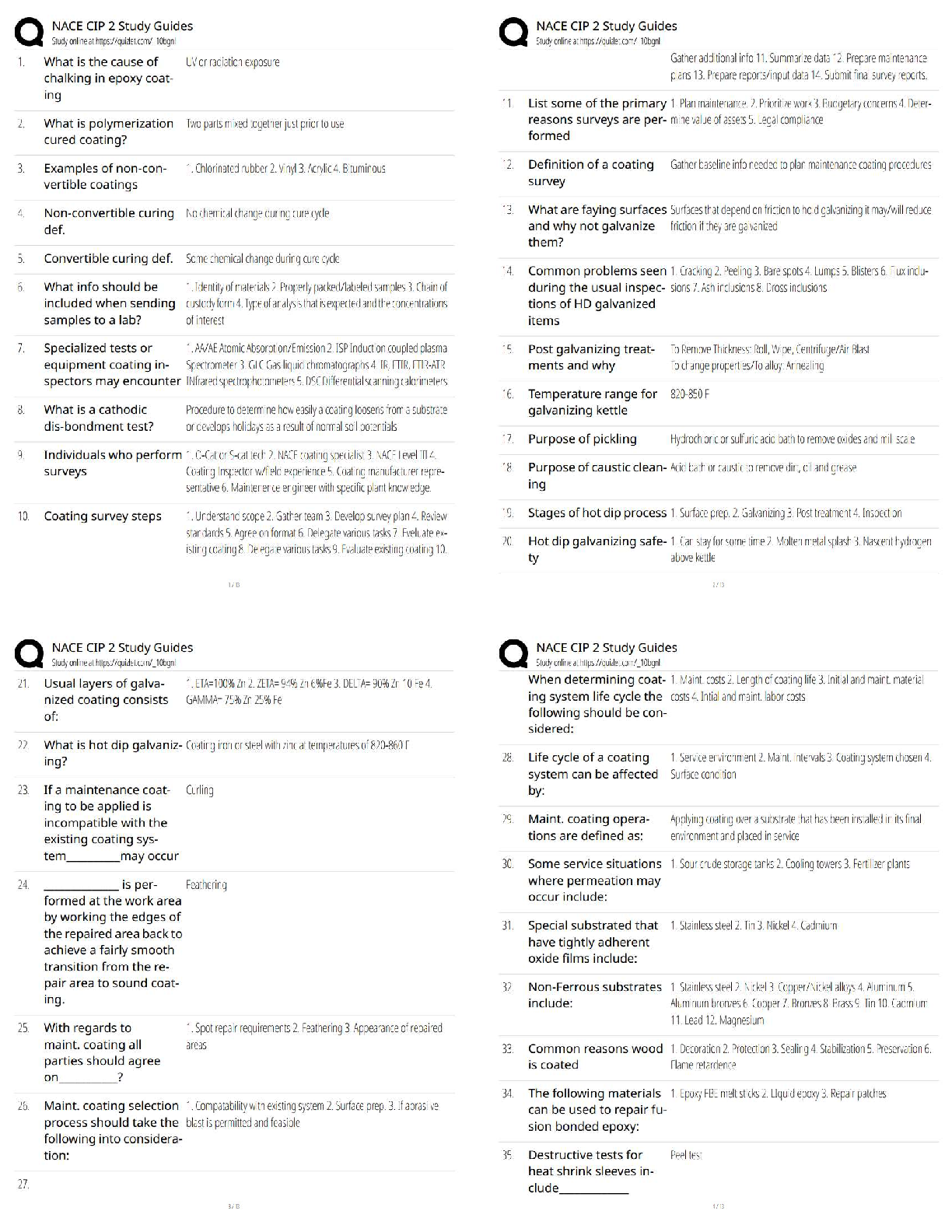
1. HEMATOLOGY 2Hematology 2 Evolve
2.
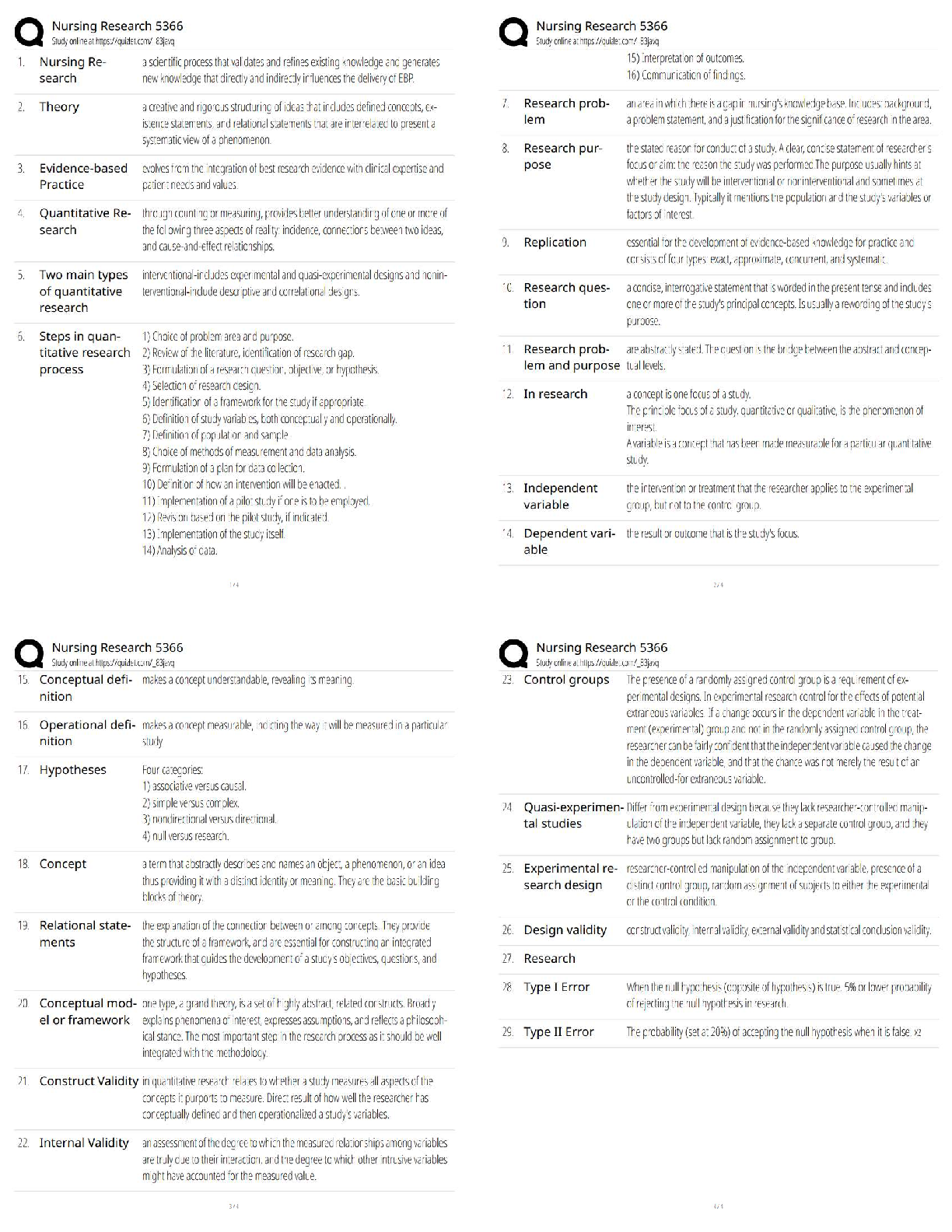
3. Cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) 0.2 mg intramuscularly (IM) is prescribed for a client with pernicious anemia. A vial of the drug labeled "1 mL = 100 mcg" is available. How many milliliters should the nurse administer? Bottom of Form
20.
A healthcare provider prescribes 0.2 mg of cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) intramuscularly for a client with pernicious anemia. A vial of the drug labeled 100 mcg = 1 mL is available. How much solution should the nurse administer?
21.
A client with chronic kidney disease is admitted to the hospital with severe infection and anemia. The client is depressed and irritable. The client’s spouse asks the nurse about the anticipated plan of care. Which is an appropriate nursing response?
1
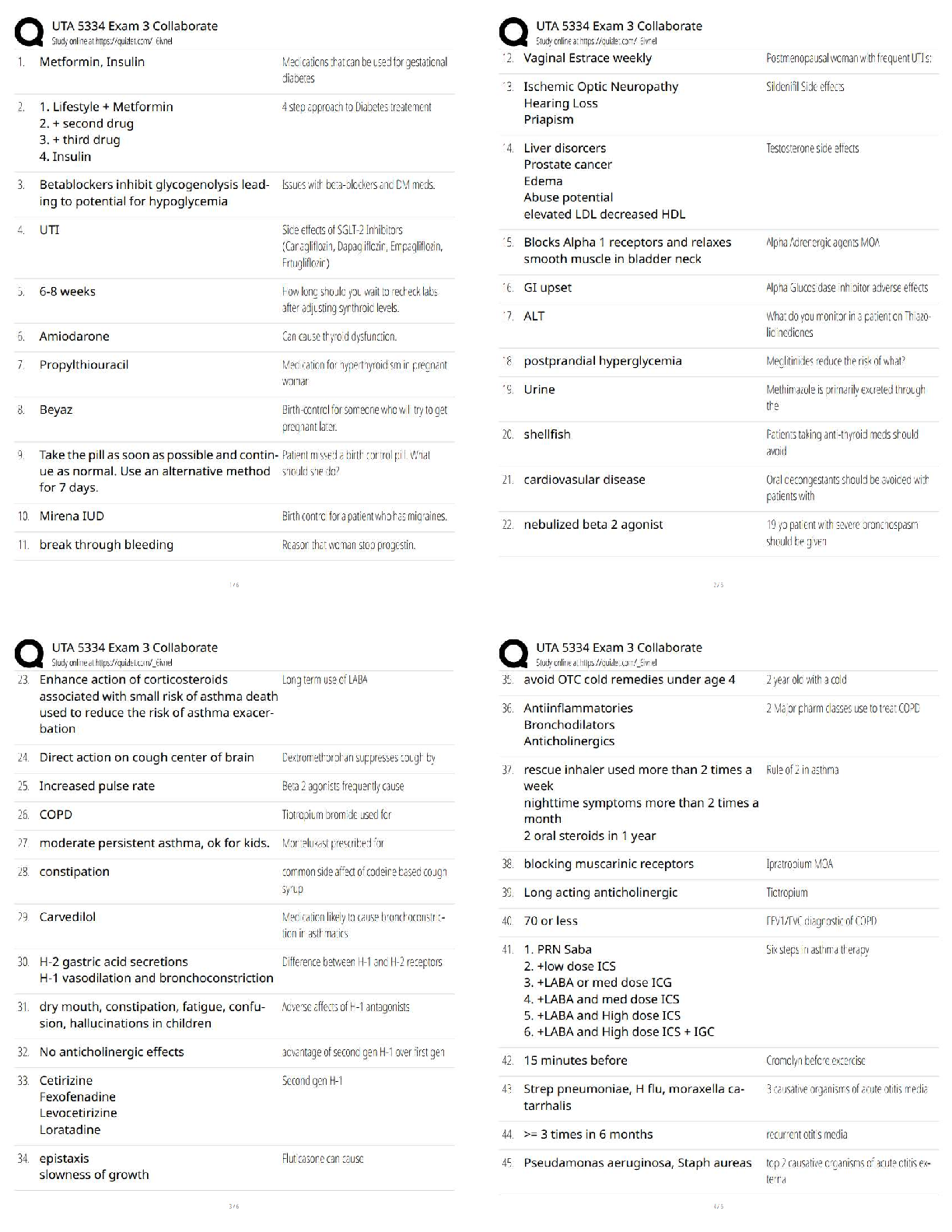
"The staff will provide total care, because the infection causes severe fatigue."
2
"Mood elevators will be prescribed to improve depression and irritability."
3 "Vitamin B12 will be prescribed for the anemia, and the stools will be dark."
4 "The intake of meat, eggs, and cheese will be restricted so the kidneys can clear the body of waste products."
22.
A client is receiving epoetin for the treatment of anemia associated with chronic renal failure. Which client statement indicates to the nurse that further teaching about this medication is necessary?
1
"I realize it is important to take this medication because it will cure my anemia."
2
"I know many ways to protect myself from injury because I am at risk for seizures."
3
"I recognize that I may still need blood transfusions if my blood values are very low."
4
"I understand that I will still have to take supplemental iron therapy with this medication."
23.
A client with a diagnosis of anemia is receiving packed red blood cells. What is the most important action by the nurse when administering the transfusion?
1
Warning the client about the possibility of fluid overload
2
Monitoring the client's response, particularly within the first 10 minutes
3
Adjusting the client's transfusion flow rate so that it infuses at a consistent rate during the procedure
4
A client receiving a blood transfusion that was just initiated reports urticaria and difficulty breathing. The heart rate has increased, the blood pressure is falling, and the client is becoming extremely apprehensive. Which type of shock does the nurse suspect the client is experiencing?
1
Septic shock
2
Cardiogenic shock
3
Neurogenic shock
4
Anaphylactic shock
41.
During administration of a whole blood transfusion, the client begins to complain of shortness of breath. The nurse notes the presence of jugular venous distension, bibasilar crackles, and tachycardia. Prioritize the following nursing actions.
1.
Elevate the head of the bed to 45 degrees
2.
Apply oxygen via nasal cannula
3.
Reduce the flow rate of the transfusion
4.
Administer furosemide (Lasix) per provider prescription
5.
Document findings in the client record
42.
A client who is obtunded has a blood pressure of 80/35 mm Hg after a blood transfusion. In an effort to support renal perfusion, the nurse administers dopamine at 2 mcg/kg/min as prescribed. What is the most relevant outcome indicating effectiveness of the medication for this client?
1
A decrease in blood pressure
2
An increase in urinary output
3
A decrease in core temperature
4
A healthcare provider prescribes two units of blood for a client who is bleeding. Which nursing interventions are necessary before the blood transfusion is administered? Select all that apply.
1
Obtain the client's vital signs.
2
Monitor hemoglobin and hematocrit levels.
3
Allow the blood to reach room temperature.
4
Determine typing and crossmatching of blood.
5
Use a Y-type infusion set to initiate 0.9% normal saline.
46.
While caring for a client receiving blood transfusion care, the nurse notices that the client is having an acute hemolytic reaction. What is the priority nursing intervention in this situation?
1
Stop the blood transfusion immediately.
2
Report to the primary healthcare provider.
3
Recheck identifying tags and numbers on the client.
4
Maintain a patent intravenous (IV) line with saline solution.
47.
An elderly adult suffered an injury after falling down in the washroom. The primary healthcare provider performed a surgical procedure on the client and orders a blood transfusion. A family member of the client mentions that blood transfusions are not permitted in their community. What should the nurse do in order to handle the situation?
1
The nurse should wait for the court’s order to give blood to the client.
2
The nurse should proceed with the transfusion in order to save the client’s life.
3
The nurse should inform the primary healthcare provider and not give blood to the client.
4
The nurse should explain to the family member that the client needs this transfusion.
The team leader is making client assignments. Which team member should be assigned a client with a tracheostomy, chest tube, and blood transfusion?
1
Charge nurse
2
Registered nurse (RN)
3
Unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP)
4
Licensed practical nurse/licensed vocational nurse (LPN/LVN)
49.
Ten minutes after the initiation of a blood transfusion, a client reports lumbar pain. What is the next nursing action?
1
Stop the transfusion.
2
Obtain the vital signs.
3
Assess the pain further.
4
Increase the flow of normal saline.
50.
While receiving a blood transfusion, a client develops acute dyspnea, generalized urticaria, a heart rate of 128, and a blood pressure of 70/38. What type of reaction does the nurse conclude that the client probably is experiencing?
1
Panic
2
Pyrogenic
3
Hemolytic
4
Anaphylactic
A nurse is caring for a client who is a victim of trauma and is to receive a blood transfusion. How should the nurse respond when the client expresses fear that acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) may be acquired as a result of the blood transfusion?
1
"The blood is treated with radiation to kill the virus."
2
"The ability to directly identify HIV has eliminated this concern."
3
"Consideration should be given to donating your own blood for transfusion."
While receiving a blood transfusion, a client develops flank pain, chills, and fever. What type of transfusion reaction does the nurse conclude that the client probably is experiencing?
1 Allergic
2 Pyrogenic
3 Hemolytic
4 Anaphylactic
53.
During a blood transfusion a client develops chills and a headache. What is the priority nursing action?
1
Cover the client.
2
Stop the transfusion at once.
3
Decrease the rate of the blood infusion.
4
Notify the healthcare provider immediately.
54.
A blood transfusion of packed cells has been prescribed for a client. The nursing unit is extremely busy. How should the nurse manager delegate for the task of blood administration?
1
Assign a licensed practical nurse (LPN) and a nursing assistant (Canada: continuing care assistant) to verify the blood is , and have the LPN monitor the client 15 minutes after hanging the product.
2
Have two registered nurses ascertain that the client identification and blood product are with no discrepancies, hang the blood, and check in 15 minutes.
3
Have all identification verified by registered nurses, then have the registered nurse hang the product and monitor the client, staying with the client during the initial 15 minutes.
4
Have the product and name band verified by a registered nurse, hang, and monitor every hour until infused within a 10-hour period or discontinued.
55.
A blood transfusion of packed cells has been prescribed for a client with leukemia. The nurse will complete the following steps in what order?
1.
Check primary healthcare provider’s prescription.
2.
Obtain vital signs and history of transfusions.
3.
Ascertain that intravenous catheter size is 18 or 20 gauge.
4.
Change main line solution to normal saline.
5.
Check client identification before hanging unit of blood.
56.
A blood transfusion of packed cells has been prescribed for a client. The client shows signs of hemolytic reaction. Place the appropriate nursing actions in order.
1.
Stop the transfusion.
2.
Change the intravenous (IV) administration set.
3.
Run 0.9% normal saline at a rapid rate.
4.
Notify the primary healthcare provider and blood bank.
57.
While receiving a blood transfusion, the client suddenly shouts, "I feel like someone is lowering a heavy weight on my chest. I feel like I’m going to die!" Which actions are priority?
1
Administer nitroglycerin and aspirin.
2
Slow the rate and monitor the vital signs.
3
Stop the transfusion and administer normal saline.
4
Ask the client to further describe the feeling and rate the pain.
58.
A blood transfusion is initiated after a client has emergency surgery. What should the nurse do first when the client develops fever, chills, and low back pain?
1
Stop the blood and infuse saline
2
Administer the prescribed antipyretic
3
Obtain a prescription for an antihistamine
4
Slow the rate of the transfusion and inform the blood bank
60.
79.
Laboratory results of a client’s blood after chemotherapy indicate bone marrow depression. What should the nurse encourage the client to do? Select all that apply.
1
Use a soft toothbrush.
2
Sleep with the head of the bed elevated.
3
Increase activity levels and take frequent walks.
4
Drink more citrus juices and eat more citrus fruits.
5
Read the ingredients in over-the-counter drugs before taking them.
91.
A healthcare provider prescribes supplemental oral iron therapy for a child with iron-deficiency anemia. What side effect will the nurse tell the parents to anticipate?
1
Bloody stool
2
Orange urine
3
Greenish-black stool
4
Staining of the mouth
39.
A prescribed blood transfusion of packed red blood cells was started five minutes ago. Now the client is complaining of chest pain, flank pain, difficulty breathing, and chills. The blood pressure has dropped from 140/88 to 110/60 mm Hg, temperature is 100.8° F (38.2° C), and the client seems less alert. What should the nurse suspect?
1
Urticarial reaction
2
Hemolytic reaction
3
Circulatory overload
In4
Anaphylactic reaction
.
43.
A client with a gastric hemorrhage is scheduled to receive two units of whole blood. List the nurse’s activities in the order that they should be performed when administering a blood transfusion.
1.
Verify that a type and crossmatch blood sample has been sent to the lab.
In
2.
Ask another nurse to check the blood identification at the client’s bedside.
In
3.
Obtain venous access, preferably with a 19-gauge needle or larger.
In
4.
Prime the blood infusion set tubing with normal saline at the bedside.
5.
Run the blood at a slower rate during the first 10 minutes of the transfusion.
A client is diagnosed with esophageal varices and is admitted to the hospital. The healthcare provider prescribes a blood transfusion. Place the following nursing actions in the order.
1. Check the client’s vital signs.
3. Establish intravenous access with IV normal saline.
2. Verify the blood product with another nurse against the client's identification (ID) bracelet.
4. Monitor the client’s vital signs and status according to agency policy.
59.
A nurse is reviewing the laboratory report of an infant with tetralogy of Fallot that indicates an increased red blood cell (RBC) count. What does the nurse identify as the cause of the polycythemia?
1 Low blood pressure
2 Diminished iron level
3 Tissue oxygen needs
4 Hypertrophic cardiac muscle
[Show More]










.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)