Medicine Year 1 University of Manchester Questions and Correct Answer Keys. With Justification for Correct Answers
Document Content and Description Below
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Sample/practice exam 2017, questions and answers
Medicine Year 1 (University of Manchester)
Questions and Correct Answer Keys
MSCAA Practice Paper 1 2020
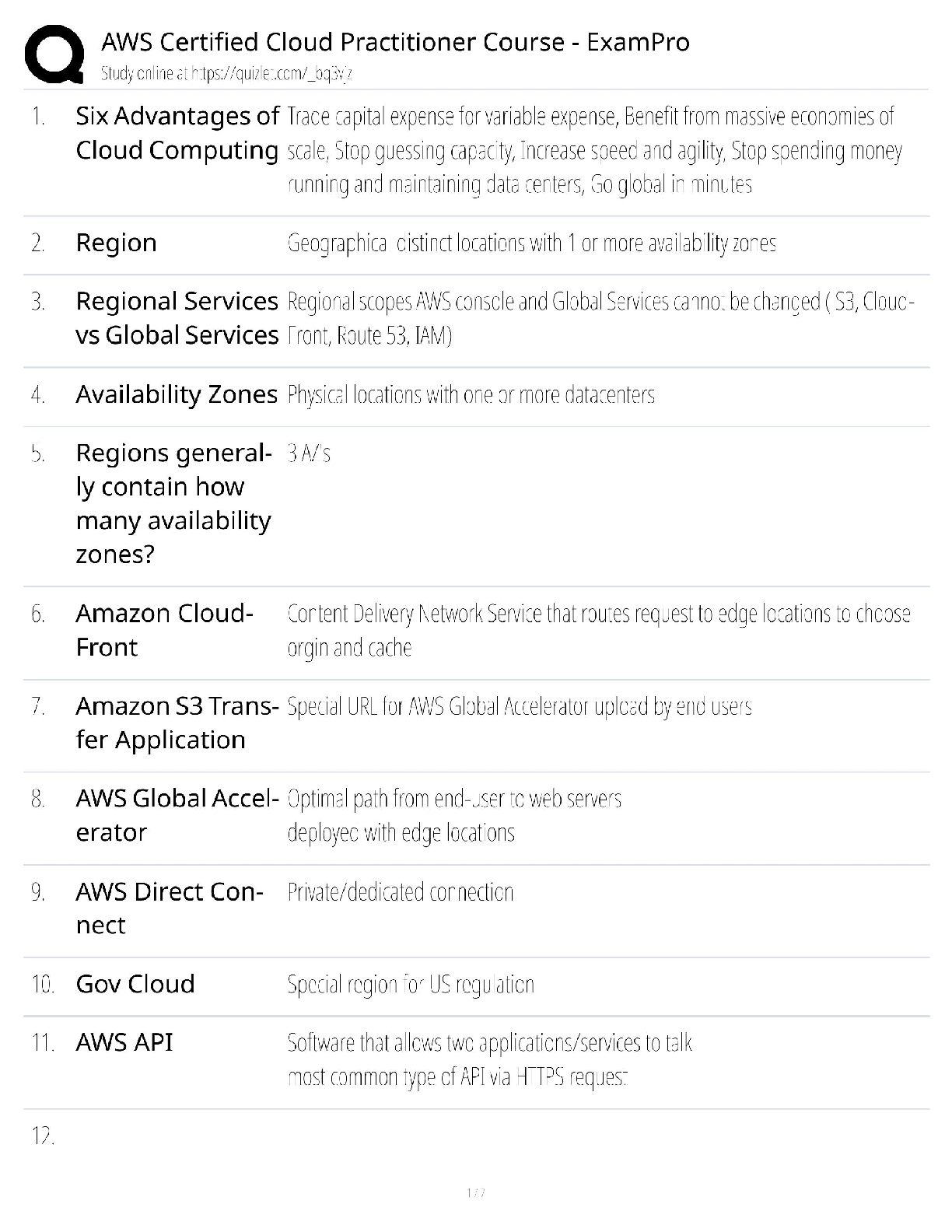
1. A 67 year old w
...
oman suddenly loses the vision in her left eye. She is in good
health with no history of eye disease and is not taking any medication.
Her right eye is normal. The left has vision reduced to hand movements only.
The left pupil reacts sluggishly to light. Her fundal photograph is shown (see
image).
Which is the cause of her sudden loss of vision?
A. Branch retinal artery occlusion
B. Branch retinal vein occlusion
C. Central retinal artery occlusion
D. Central retinal vein occlusion
E. Cilioretinal vein occlusion
Which is the most appropriate treatment?
A. Amitriptyline
B. Haloperidol
C. Immediate release carbidopa-levodopa
D. Lorazepam
E. Risperidone
Which is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Lumbar disc prolapse
B. Mechanical back pain
C. Osteomalacia
D. Osteoporotic vertebral collapse
E. Spinal cord compression
Correct Answer: E
3. A 78 year old woman has back pain and bilateral leg weakness. She had
surgery for breast cancer 14 years ago. She had a minor fall at home a few
days ago.
She has weakness of hip flexion bilaterally.
2. A 78 year old man develops increasing confusion on the ward at night. He is
wandering around naked asking for his wife, shouting, and threatening staff
and patients. He was admitted this morning with 1 week of productive cough
and temperature. He has a history of idiopathic Parkinson's disease.
His temperature is 37.6°C, pulse rate 100 bpm, BP 132/71 mmHg and oxygen
saturation 95% breathing air. His capillary blood glucose is 5 mmol/L.
Attempts to calm him with nursing measures do not improve the situation, and
he begins hitting staff.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
4. A 28 year old man is investigated for polyuria and polydipsia. He has bipolar disorder
for which he has taken lithium for 2 years.
Initial investigations:
Sodium 145 mmol/L (135–146)
Potassium 3.9 mmol/L (3.5–5.3)
Serum osmolality 296 mOsmol/kg (285–295)
Urinary osmolality 356 mOsmol/kg (350–1000)
Fasting glucose 5.8 mmol/L (3.0–6.0)
Serum lithium 0.75 mmol/L (0.5–1.2)
Which is the most useful diagnostic investigation?
A. 24-h urinary cortisol test
B. Glucose tolerance test
C. Serum corrected calcium
D. Short Synacthen test
E. Water deprivation test
for
correct answer
It is essential to exclude hypercalcaemia due to hyperparathyroidism before progressing
to a water deprivation test.
Which is the most appropriate long-term plan for secondary stroke prevention?
A. Apixaban
B. Aspirin
C. Aspirin and dipyridamole
D. Clopidogrel
E. Ticagrelor
5. A 65 year old woman had a stroke 2 weeks ago causing right arm weakness
and dysphasia. CT scan of head showed a left parietal lobe infarct. Her
medication since the stroke includes aspirin and simvastatin.
Her pulse rate is 82 bpm and irregular.
Investigations:
ECG: atrial fibrillation, rate 68 bpm.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
6. A 49 year old man has 3 days of cough and fever. He undergoes
haemodialysis three times per week.
His temperature is 38.6°C, pulse rate 90 bpm, BP 122/80 mmHg, respiratory rate 30
breaths per minute and oxygen saturation 95% breathing 15 L/min oxygen via a
non-rebreather mask. His JVP is 4 cm above the sternal angle. He has inspiratory
crackles in the right mid and lower zone and left upper zone. His blood capillary
glucose is 12 mmol/L.
Investigations:
Sodium
Potassium
Urea
Creatinine 131 mmol/L
5.7 mmol/L
16.7 mmol/L
327 μmol/L (135–146)
(3.5–5.3)
(2.5–7.8)
(60–120)
Chext X-ray: see image
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 7 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most appropriate initial treatment?
A. Haemodialysis
B. Intravenous 10 mL 10% calcium gluconate
C. Intravenous 1000 mL 0.9% sodium chloride over 1 h
D. Intravenous co-amoxiclav and clarithromycin
E. Intravenous furosemide
Which is the most appropriate treatment to give before the scan?
A. Intravenous 0.9% sodium chloride infusion
B. Intravenous acetylcysteine
C. Intravenous furosemide infusion
D. Intravenous hydrocortisone
E. Intravenous mannitol
7. A 67 year old man is due to have a CT scan of chest, abdomen and pelvis
with intravenous contrast as assessment for possible lymphoma. He had a
renal transplant 5 years ago. His medication includes prednisolone, tacrolimus
and lisninopril.
His BP is 131/86 mmHg.
Investigations:
Urea 12.9 mmol/L
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
longer used as no evidence of benefit.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most likely cause for her acute kidney injury?
A. Glomerulonephritis
B. Hypovolaemia
C. Renal arterial emboli
D. Rhabdomyolysis
E. Ureteric ob
A 76 year old woman has become increasingly confused over the past 2 weeks. She
has a history of hypertension and cardiac failure. She is taking
bendroflumethiazide, doxazosin, amlodipine, ramipril and atenolol.
Her BP is 108/71 mmHg.
Investigations:struction
9.
Sodium 121 mmol/L (135–146)
Potassium 3.5 mmol/L (3.5–5.3)
Urea 10.0 mmol/L (2.5–7.8)
Urinalysis: glucose negative, ketones negative, blood 2+, protein 1+,
leucocytes positive (catheter sample).
She has passed 60 mL of urine over the past 2 hours.
(135–146)
(3.5–5.3)
(2.5–7.8)
(60–120)
Creatine kinase 870 U/L (25–175)
8. A 78 year old woman is admitted after been found collapsed at home. She
has been lying on the floor overnight. She has a history of hypertension and
takes amlodipine.
Her temperature is 35.8°C, pulse rate 88 bpm and irregular, and BP 102/60
mmHg.
Investigations:
Sodium 136 mmol/L
Potassium 5.8 mmol/L
Urea 20.9 mmol/L
Creatinine 180 μmol/L
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Creatinine 105 µmol/L (60–120)
Which medication is most likely to be responsible for her presentation?
A. Amlodipine
B. Atenolol
C. Bendroflumethiazide
D. Doxazosin
E. Ramipril.
Which is the most appropriate next investigation?
A. Cervical spine X-ray
B. CT angiography
C. CT scan of chest
D. CT scan of neck
E. MR scan of brain
Full blood count and clotting screen are normal.
Chest X-ray lung fields clear; left sided 4th rib fracture
10. A 92 year old woman has severe neck, chest and back pain and tingling in her
left hand following a mechanical fall. She has bruising around her right eye.
Investigations:
CT scan of head
right orbital fracture no intracranial injury or bleed, mild small vessel disease;
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
B. Sinus arrhythmia
C. Sinus tachycardia
D. Supraventricular premature beats
E. Supraventricular tachycardia
Which is the most likely causative organism?
A. Corynebacterium species
B. Enterococcus species
C. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
D. Staphylococcus aureus
E. Streptococcus pyogenes
12. A 64 year old woman develops an acutely painful right knee 3 weeks after a
prosthetic right knee replacement. Her temperature is 38.2°C and pulse rate
103 bpm. Her right knee is inflamed, with serous fluid discharging from the
lower end of the wound.
11. A 24 year old woman attends her GP with 2 months of intermittent
palpitations. She describes the episodes as feeling as if the heart stops for a
second followed by a pounding sensation. She reports episodes two to
three times per week lasting 5–10 minutes, most commonly when she is
going to sleep. She is otherwise well. She has been taking the combined
oral contraceptive pill for 2 years.
Her pulse rate is 68 bpm and BP 108/71 mmHg. Her heart sounds are normal.
Investigations:
ECG: sinus rhythm, rate 70 bpm.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Candida is also very uncommon.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
13. A 52 year old man has 3 months of fatigue. He has a history of ulcerative
colitis and takes mesalazine. He drinks 20 units of alcohol per week.
His temperature is 36.8°C and pulse rate 80 bpm. He has 3 cm
hepatomegaly.
Investigations:
Ultrasound scan of abdomen: bile duct wall thickening and dilatation
Albumin
ALT 36 g/L
65 IU/L (35–50)
(10–50)
ALP 580 IU/L (25–115)
Bilirubin 18 µmol/L (<17)
γGT 230 IU/L (9–40)
Which is the most appropriate next diagnostic investigation?
A. CT scan of abdomen
B. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
C. Liver biopsy
D. MR cholangiopancreatography
E. Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Adenoma
B. Carcinoma
C. Hamartoma
D. Sarcoidosis
E. Tuberculosis
Which is the most appropriate next management option?
A. Continuous positive airway pressure
B. Invasive ventilation
C. Nasal high flow oxygen
D. Nasopharyngeal airway
E. Non-invasive ventilation
15. A 65 year old woman has an infective exacerbation of COPD.
Her temperature is 37.8°C, pulse rate 108 bpm, BP 100/75mmHg,
respiratory rate 26 breaths per minute and oxygen saturation 88% breathing
15 L/minute oxygen via a non-rebreather mask. She is alert.
Investigations:
Arterial blood gas on 15 L/min oxygen
pH 7.28 (7.35–7.45)
PO2 7.2 kPa (11–15)
PCO2 8.9 kPa (4.6–6.4)
Bicarbonate 31.3 mmol/L (22–30)
Lactate 1.2 mmol/L (1–2)
14. A 60 year old woman has 6 weeks of a cough productive of blood streaked
sputum.
Investigations:
CT scan of chest: mass in left lower lobe
Needle biopsy: nuclei that are enlarged, hyperchromatic and pleomorphic
Which is the most likely explanation for the ECG findings?
A. Aortic dissection
B. Hyperkalaemia
C. Myocardial infarction
D. Pericarditis
E. Pulmonary embolism
16. A 79 year old man attends the Emergency Department with 2 hours of chest
pain and lightheadedness.
His ECG is shown (see image).
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Myocardial infarction
B. Pancreatitis
C. Pneumonia
D. Pulmonary embolus
E. Subphrenic abscess
17. A 50 year old woman has acute onset of shortness of breath. She
underwent a laparoscopic cholecystectomy 10 days ago.
Her temperature is 37.4°C, pulse rate 104 bpm, BP 122/80 mmHg, respiratory
rate 24 breaths per minute and oxygen saturation 94% breathing air. Her
chest is clear. She has minimal tenderness over the right hypochondrium.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 19 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which further investigation will help to establish the diagnosis?
A. Chest X-ray
B. ECG
C. Nasal swabs
D. Transoesophageal echocardiogram
E. Urine dipstick analysis
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate 55 mm/hr (<20)
Blood cultures are awaited.
15 × 109/L (3.0–10.0)
Investigations:
White cell count
18. A 39 year old man has had fever, chills and generalised weakness for
1 month. He has a history of systolic heart murmur. He is an intravenous drug
user.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 20 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most appropriate immediate management plan?
A. Admit and observe for 24 h
B. CT scan of head
C. Discharge with head injury instructions
D. Refer to neurosurgeon
E. X-ray of skull
19. A 16 year old girl presents to the Emergency Department after an episode
of loss of consciousness following a fall. She had consumed an excessive
amount of alcohol at a party before the fall.
She has a dirty scalp wound and cannot remember recent events. Her pulse
rate is 68 bpm, BP 110/80 mmHg and oxygen saturation 98% breathing
air. She opens her eyes to command and is confused. Her capillary blood
glucose is 6.0 mmol/L.
Her wound is cleaned and sutured.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 21 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most appropriate initial management plan?
A. Botulinum toxin type A injection into bladder wall
B. Oral duloxetine
C. Oral oxybutynin
D. Percutaneous sacral nerve stimulation
E. Topical oestrogen
20. A 47 year old woman has 1 year of increased urinary frequency, urgency and
nocturia. She finds that she leaks urine if she is unable to get to the toilet
promptly. She had three normal pregnancies with no complications.
The perineum appears normal and there is no uterine prolapse. Incontinence
is not provoked by coughing or straining. Urinalysis is negative. A postmicturition ultrasound scan of bladder shows minimal residual urine volume.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 22 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
21. A 72 year old woman has 6 months of mild constipation.
Parathyroid hormone 11.2 pmol/L (1.6–8.5)
Vitamin D 65 nmol/L (>60)
Investigations:
Haemoglobin 110 g/L (115–165)
Creatinine 70 µmol/L (60–120)
Calcium 2.90 mmol/L (2.2–2.6)
Phosphate 0.65 mmol/L (0.8–1.5)
24 h urinary calcium 7 mmol (2–6)
Which is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcaemia
B. Multiple myeloma
C. Primary hyperparathyroidism
D. Tertiary hyperparathyroidism
E. Vitamin D intoxication
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most appropriate treatment?
A. Apixaban
B. Aspirin
C. Diltiazem hydrochloride
D. No treatment
E. Warfarin sodium
22. A 52 year old man visits his GP for health screening. He is well.
His pulse rate is 80 bpm and irregular, and BP 128/84 mmHg.
Investigations:
Sodium 136 mmol/L (135–146)
(3.5–5.3)
(2.5–7.8)
(60–120)
Potassium 3.9 mmol/L
Urea 4.9 mmol/L
Creatinine 80 μmol/L
HbA1c 40 mmol/mol (20–42)
Thyroid function tests are normal.
ECG shows atrial fibrillation, 76 bpm.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 24 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most appropriate initial management option?
A. Anterior pack
B. Antihypertensive medication
C. Cautery
D. Cryotherapy
E. Ice pack
23. An 80 year old man presents to the Emergency Department with 2 hours
of epistaxis that has not stopped despite compression. He has a history of
hypertension.
A bleeding site is visible in the anterior nasal cavity. His BP is 160/95 mmHg.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 25 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most appropriate initial management?
A. Give intravenous piperacillin with tazobactam
B. Give Microlax ® enema
C. Insert a nasogastric tube
D. Start regular intravenous morphine
E. Take to theatre for laparotomy
24. A 65 year old man has abdominal distension and vomiting 48 hours after a
sigmoid colectomy with primary anastomosis for bowel cancer. He has not
passed any flatus for 24 hours. He is taking regular paracetamol and as
required intravenous morphine.
His abdomen is distended with tenderness over the wound but no rebound or
guarding. There are no bowel sounds.
His temperature is 37.6°C, pulse rate 96 bpm and BP 122/85 mmHg.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 26 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Genital herpes
B. Gonorrhoea
C. HIV seroconversion
D. Lymphogranuloma venereum
E. Secondary syphilis
25. A 23 year old man attends the sexual health clinic with a painful swelling in
his groin and pain when opening his bowels. He had unprotected anal sex
with a new male partner 4 weeks ago.
He has a perianal ulcer and tender inguinal lymphadenopathy.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 27 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most likely cause of his acute deterioration?
A. Acute myocardial infarction
B. Diaphragmatic hernia
C. Lobar pneumonia
D. Pneumothorax
E. Pulmonary embolus
26. A 63 year old man with COPD has had an increase in cough for 2 days.
He now has pain of sudden onset in the right side of his chest radiating to
the right shoulder, and increasing breathlessness.
Chest X-ray: see image.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 28 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
From which artery is the bleeding most likely to be arising?
A. Gastroduodenal artery
B. Left gastric artery
C. Short gastric artery
D. Splenic artery
E. Superior mesenteric artery
27. A 25 year old man presents to the Emergency Department after vomiting a
large quantity of blood.
At endoscopy, a deep ulcer is identified in the posterior wall at the junction of
the first and second parts of the duodenum. There is a bleeding vessel in the
base.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 29 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Androgen secreting tumour
B. Cushing's syndrome
C. Polycystic ovary syndrome
D. Premature ovarian failure
E. Prolactinoma
(1–11)
(2–8)
(0.2–2.9)
(<50)
(100–500)
Cortisol post 1 mg dexamethasone 40 nmol/L
Prolactin 425 U/L
15 U/L (follicular)
6 U/L (follicular)
3.5 nmol/L
Investigations:
LH (pre-menopausal female)
FSH
Testosterone
28. A 27 year old woman has a long history of irregular menstruation. She does
not take any medication. Her BMI is 29.4 kg/m2.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 30 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which antibody test is most likely to diagnose the underlying cause?
A. Anti-gastric parietal cell
B. Antimitochondrial
C. Antinuclear
D. Anti-smooth muscle
E. Anti-tissue transglutaminase
29. A 30 year old woman attends 3 months after a diagnosis of iron deficiency
anaemia. She was advised to take oral iron supplements and has been
taking these regularly. She has some looseness of her stools, and her
periods are scanty on a combined oral contraceptive.
Investigations:
Haemoglobin 92 g/L (115–165)
MCV 70 fL (80–96)
Ferritin 8 µg/L (12–200)
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 31 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which treatment is most appropriate to preserve neurological function?
A. Chemotherapy
B. External beam radiotherapy
C. Intravenous bisphosphonates
D. Radiation brachytherapy
E. Surgical decompression of the spinal cord
.
30. A 75 year old man is admitted with weakness in his legs. He has a squamous
cell lung cancer treated by radiotherapy 18 months previously.
He is cachetic. He has 4 out of 5 power in hip flexion and knee flexion
bilaterally. Sensation and reflexes are normal, and sphincter function is
preserved. His BMI is 17 kg/m2. MR scan of spine shows destructive bony
lesions of T12 and L2–L4 vertebral body.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 32 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Essential hypertension
B. Glucocorticoid excess
C. Phaeochromocytoma
D. Primary hyperaldosteronism
E. Primary hypoadrenalism
31. A 34 year old woman has headaches for 3 months. Her mother
developed hypertension at the age of 38 years.
Her BP is 180/92 mmHg. Otherwise, examination, including fundoscopy, is
normal.
Investigations:
Sodium 136 mmol/L (135–146)
Potassium 3.3 mmol/L (3.5–5.3)
Chloride 97 mmol/L (95–106)
Urea 4.0 mmol/L (2.5–7.8)
Creatinine 94 µmol/L (60–120)
Plasma aldosterone:renin ratio 50 (<25)
Cortisol (9am) 307 nmol/L (200–700)
Urinalysis is normal.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 33 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most likely cause of his haematuria?
A. Alport's nephropathy
B. Drug reaction
C. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
D. IgA nephropathy
E. Postinfectious glomerulonephritis
IgA characteristically causes visible haematuria a few days after URTI (post-infectious
GN has lag time of around 2 weeks before haematuria occurs and would be a less benign
presentation if associated with visible haematuria).
32. A 20 year old man has 2 days of visible haematuria. Three days before the
haematuria started, he developed tonsillitis and was treated with
phenoxymethylpenicillin. He has no significant medical history.
His BP is 112/54 mmHg.
Investigations:
Urea 3.2 mmol/L (2.5–7.8)
Creatinine 61 µmol/L (60–120)
Urinalysis: glucose negative, ketones negative, blood 3+, protein 3+, nitrites
negative, leucocytes negative.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 34 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Cholecystitis
B. Chronic pancreatitis
C. Duodenal ulcer
D. Gastric ulcer
E. Gastric carcinoma
Duodenal ulcers tend to be made worse with stress and the pain is often worse at night
radiating into the back - it is relieved by eating and patients tend to put weight on - in
contrast to a gastric ulcer which is made worse with eating and people often lose weight.
33. A 38 year old man has 2 months of epigastric pain that radiates into his back.
It is worse at night and sometimes wakes him up. It is better after eating. He
has been very busy at work. He occasionally misses lunch, which worsens the
pain. He has not lost weight. He smokes 10 cigarettes per day and drinks two
bottles of wine per week.
Examination is normal.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 35 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which clinical feature is most specific for inflammatory back pain?
A. Improvement with activity
B. Nocturnal pain
C. Radiation to leg
D. Stiffness during the day
E. Young age
Inflammatory back pain (IBP) is typically improved with activity and not relieved by rest,
as opposed to mechanical pain which is worse with activity and is relieved by rest. IBP
can wake the patient in the early hours of the morning and sacroilieitis can radiate to the
thigh, but these features are much less specific. Morning stiffness is specific for
inflammatory back pain but not persistent daytime stiffness. IBP can occur at any age
although mechanical pain is less common in young people.
34. A 26 year old woman has 12 months of back pain, located in the low
lumbosacral region. She has intermittent bilateral thigh pain. The back pain
disturbs her sleep. The pain is improved by activity but not relieved by
resting. She finds it difficult to bend down during the day to pick things up
from the floor.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 36 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the best initial treatment for his acute knee pain and swelling?
A. Arthroscopic joint washout
B. Intravenous flucloxacillin
C. Oral allopurinol
D. Oral naproxen
E. Oral prednisolone
Correct Answer: E
The presentation is likely due to an acute attack of gout. Although infection is not
completely excluded at this stage it is less likely as G stain is negative and there are
several positive features of gout in the history. IA or oral steroids, colchicine or
NSAIDs are all effective treatments for acute gout. NSAIDs are contraindicated in
CKD of this stage. Allopurinol will not help the acute attack.
35. A 68 year old man has a swollen tender knee for 3 days and cannot weight
bear. He has had previous episodes of big toe swelling. He has a history of
chronic kidney disease stage 4.
Investigations:
Fluid analysis of knee aspirate:
White cell count 55 000/mL, 95% neutrophils
Gram stain negative
Copious 10 μm intracellular needle shaped crystals
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 37 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most appropriate additional intravenous treatment?
A. 500 mL 0.9% sodium chloride over 15 min
B. 500 mL Hartmann's solution over 15 min
C. Dopamine hydrochloride
D. Furosemide
E. Noradrenaline/norepinephrine
Correct Answer: E
Description of adequate (if not over) hydration. Needs vasoconstriction.
36. An 18 year old man is in the intensive care unit with septic shock as a result of
a compound fracture of his leg. His urine output has been <30 mL for the past
2 hours.
His pulse rate is 125 bpm, BP 85/40 mmHg and JVP 4 cm above the sternal
angle. There are basal crackles on auscultation of the chest.
Investigations:
ECG shows sinus rhythm, 125 bpm.
He is being treated with intravenous 0.9% sodium chloride at 125 mL/h and
antibiotics.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 38 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most appropriate next step in management?
A. MR scan of shoulder
B. Refer for orthopaedic opinion
C. Refer for physiotherapy
D. Ultrasound scan of shoulder
E. X-ray of shoulder
Clinically the diagnosis is right supraspinatus tendinopathy and no further investigation is
required to confirm the diagnosis. Most cases can be managed in primary care and a
referral to orthopaedics is not required. The most appropriate management is either
general advise and home exercises or referral to a physiotherapist.
37. A 34 year old man has pain in his right shoulder and upper arm for 6 weeks
that worsens when elevating his arm above his head. He does not recall any
injury.
There is no deformity, tenderness or reduced range of movement. There is
pain on abduction of the right shoulder that is worse with the arm in internal
rotation and when abduction is resisted. He is treated with ibuprofen.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 39 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most suitable initial treatment?
A. Diamorphine hydrochloride
B. Glycopyrronium
C. Hyoscine hydrobromide
D. Midazolam
E. Mirtazapine
Terminal restlessness is a common and distressing condition that requires active
management: important knowledge for FY doctors. The diagnosis of dying has already
been made and reversible causes of her deterioration will thus have been considered and
excluded: NICE guidelines indicate that terminal restlessness should be managed with
Midazolam by prn subcutaneous injections / continuous subcutaneous infusion via a
syringe driver.
38. A 65 year old woman with advanced carcinoma of the breast with cerebral
and liver metastases is rapidly deteriorating and is recognised to be
dying. She becomes confused and agitated.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 40 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
In which part of the brain are changes most likely to be found in early Alzheimer’s
disease?
A. Basal ganglia
B. Frontal lobe
C. Medulla oblongata
D. Parietal lobe
E. Temporal lobe
Correct Answer: E
39. A 80 year old man has progressive memory loss over 2 years.
He scores 20/30 on the Montreal Cognitive Assessment, and he requires an
MR scan of brain.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 41 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most appropriate immediate management option?
A. Activated charcoal
B. Intravenous amiodarone hydrochloride
C. Intravenous atropine sulfate
D. Intravenous magnesium
E. Intravenous sodium bicarbonate
Correct Answer: E
Bicarbonate is the treatment of the choice in patients with prolonged QRS complexes
following a tricyclic antidepressant overdose.
40. A 43 year old woman is admitted to hospital with an overdose of amitriptyline
hydrochloride taken 4 hours previously. She has a history of chronic
headache.
Her pulse rate is 105 bpm and BP 95/40 mmHg. She is drowsy and her pupils
are dilated. ECG shows significant QRS prolongation.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 42 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most appropriate method for providing analgesia during the early
postoperative period?
A. Epidural anaesthesia
B. Intramuscular opioid
C. Oral non-steroidal analgesia
D. Patient controlled intravenous analgesia
E. Spinal anaesthesia
This is because for major abdominal surgery in respiratory disease opioid, by whatever
route, should be avoided. Epidural is best because it can be topped up and titrated; spinal
anaesthesia cannot. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation has been used for postoperative pain, but trial results are contradictory. Intramuscular injection is difficult to
titrate.
41. A 76 year old man undergoes an abdominoperineal resection for a low
rectal carcinoma. He has a history of severe COPD and hypertension.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 43 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which type of study design is being used?
A. Case–control study
B. Case series
C. Cohort study
D. Cross-sectional study
E. Ecological study
42. A researcher is seeking to examine whether long-term mobile phone use is
linked to acoustic neuroma risk. The information on mobile phone usage is
collected from participants with acoustic neuroma and a comparable group
of participants without acoustic neuroma, selected from the general practice
register.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 44 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which type of antihypertensive is most appropriate?
A. ACE inhibitor
B. Alpha blocker
C. Beta blocker
D. Calcium channel blocker
E. Thiazide-like diuretic
There is good evidence for renal function protection in diabetic nephropathy with ACE-1
in addition to its hypertensive properties.
eGFR 43 mL/min/1.73 m2 (>60)
(<3.5)
Investigations:
Urinary albumin: creatinine ratio 42 mg/mmol
43. A 56 year old woman has home blood pressure readings averaging 160/90
mmHg.
Hypertension is confirmed on 24 hour ambulatory monitoring. She has type 1
diabetes mellitus.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 45 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which investigation is most likely to confirm the diagnosis?
A. Blood cultures
B. Bronchoscopy
C. Echocardiography
D. High resolution CT scan of chest
E. Induced sputum for microscopy and culture
This is because the patient has pulmonary fibrosis as a complication from amiodarone
therapy. This classically does not cause clubbing. Patients present with cough and
dyspnoea. Fever and reactive blood changes (raised WCC, ESR) are not uncommon. An
HRCT would confirm changes of interstitial lung disease. Blood cultures are indicated but
this is unlikely to be an infective cause. Bronchoscopy is not indicated. The features are
not those of heart failure so an echo will not confirm the diagnosis. An induced sputum is
not indicated at this stage.
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate 65 mm/hr (<20)
Chest X-ray shows bilateral reticular opacities in both bases.
14.0 × 109/L (3.0–10.0)
141 g/L (130–175)
Investigations:
Haemoglobin
White cell count
44. A 70 year old man has dry cough and breathlessness on exertion for the past
3 months. He has lost 4 kg is weight. He has a history of ischaemic heart
disease and atrial fibrillation. He takes warfarin sodium, ramipril and
amiodarone hydrochloride. He is a never smoker.
His temperature is 37.5°C, pulse rate 70 bpm, respiratory rate 18 breaths per
minute and oxygen saturation 91% breathing air. He has fine bibasal
inspiratory crackles. There is no finger clubbing.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 46 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Delirium tremens
B. Fluoxetine overdose
C. Hepatic encephalopathy
D. Korsakoff's psychosis
E. Wernicke's encephalopathy
The patient has typical features of delerium tremens with confusion, visual hallucinations,
tachycardia and pyrexia on the background of heavy alcohol use. This normally occurs on
reduction or abstinence, which may not be clear from the history.
45. A 31 year old woman is admitted with 24 hours of confusion. She is having
visual hallucinations of snakes and mice on the floor. Her partner says that
she often drinks 80 units of alcohol per week. He has not seen her for the past
week. She has a history of depression and takes fluoxetine. Her temperature
is 37.6°C, pulse rate 100 bpm and BP 162/98 mmHg. She is disorientated in
time and place. She has no focal neurological deficit.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 47 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which mechanism best explains the development of hyponatraemia?
A. Increased sodium secretion in the distal tubule
B. Increased water absorption in the collecting duct
C. Increased water ingestion
D. Reduced cortisol secretion
E. Reduced sodium reabsorption in the proximal tubule
The picture is of syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion with hyponatraemia and
inappropriately concentrated urine. ADH stimulates synthesis of aquaporin-2 in the apical
membrane of the collecting duct which promotes water absorption. This leads to a
dilutional hyponatraemia.
(135–146)
(3.5–5.3)
(2.5–7.8)
(60–120)
(285–295)
Urine osmolality 585 mOsmol/kg (100–1000)
46. A 61 year old woman is admitted with 2 days of confusion. She has a history
of hypertension and takes nifedipine. She smokes 20 cigarettes per day. She
is confused but has no focal neurological deficit. Her pulse rate is 75 bpm, BP
139/87 mmHg and JVP 2 cm above the sternal angle.
Investigations:
Sodium 117 mmol/L
Potassium 4.2 mmol/L
Urea 1.9 mmol/L
Creatinine 57 μmol/L
Serum osmolality 252 mOsmol/kg
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 48 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most appropriate next step in management?
A. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
B. Lumbar puncture
C. MR scan of brain
D. Refer to outpatient headache clinic
E. Start amlodipine
This is because APKD is associated with subarachnoid haemorrage. A lumbar puncture
should be performed. MRA would be reasonable, but not MRI.
47. A 43 year old woman has a sudden severe headache that started 24 hours
ago. She has a history of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
Her temperature is 36.8°C, pulse rate 92 bpm and BP 140/100 mmHg.
Neurological examination is normal. CT scan of head is normal.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 49 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which is the most appropriate therapeutic change?
A. Start co-codamol
B. Start ibuprofen
C. Start prednisolone
D. Stop bisoprolol
E. Stop simvastatin
Classical PMR history, presentation and raised inflammatory markers.
(130–175)
(3.0–10.0)
(150–400)
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate 105 mm/hr (<20)
125 g/L
7.8 × 109/L
391 × 109/L
Investigations:
Haemoglobin
White cell count
Platelets
48. A 74 year old man has progressively worsening muscle aches that are now
causing him to struggle to get up from a chair or raise his arms above his
head. He has a history of oesophageal cancer treated surgically and
ischaemic heart disease. He is taking bisoprolol, clopidogrel, ramipril and
simvastatin.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 50 of 51
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Which additional investigation is most likely to confirm the diagnosis?
A. Creatine kinase
B. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
C. Serum 25-OH cholecalciferol
D. Ultrasound scan of neck
E. X-ray of thoracic and lumbar spine
The clinical features suggest osteomalacia. She has hypocalcaemia and proximal muscle
weakness. The low serum calcium is not adequately explained by CKD. Serum vitamin
D would establish the diagnosis. 24 hour urinary calcium is sometimes performed in
primary hyperparathyroidism but not in a secondary case such as this. The presentation
is not one of myositis and this is unlikely to be significantly elevated.
Ultrasound of neck is another primary hyperparathyroidism test. The lumbar spine X-ray
is most likely to show osteopenia but does not give diagnostic features (unlike in
children).
(2.5–7.8)
(60–120)
(2.2–2.6)
(>60)
(25–115)
(1.6–8.5)
Alkaline phosphatase 230 IU/L
Parathyroid hormone 14.5 pmol/L
7.8 mmol/L
122 μmol/L
2.1 mmol/L
41 mL/min/1.73 m2
Investigations:
Urea
Creatinine
Calcium
eGFR
49. A 59 year old woman has 6 months of pain affecting her hips and lower back.
She is Libyan and has lived in the UK for 10 years. She has chronic kidney
disease stage 3 and hypertension. She is taking lisinopril and
simvastatin. She has weakness of hip flexion bilaterally. There is no muscle or
bony tenderness.
lOMoAR cPSD|784381
Page 51 of 51
[Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 83 pages


.png)







.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)