Financial Accounting > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Appendix 13C Income Taxes and the Net Present Value Method: Answer Key Provided at the end. (All)
Appendix 13C Income Taxes and the Net Present Value Method: Answer Key Provided at the end.
Document Content and Description Below
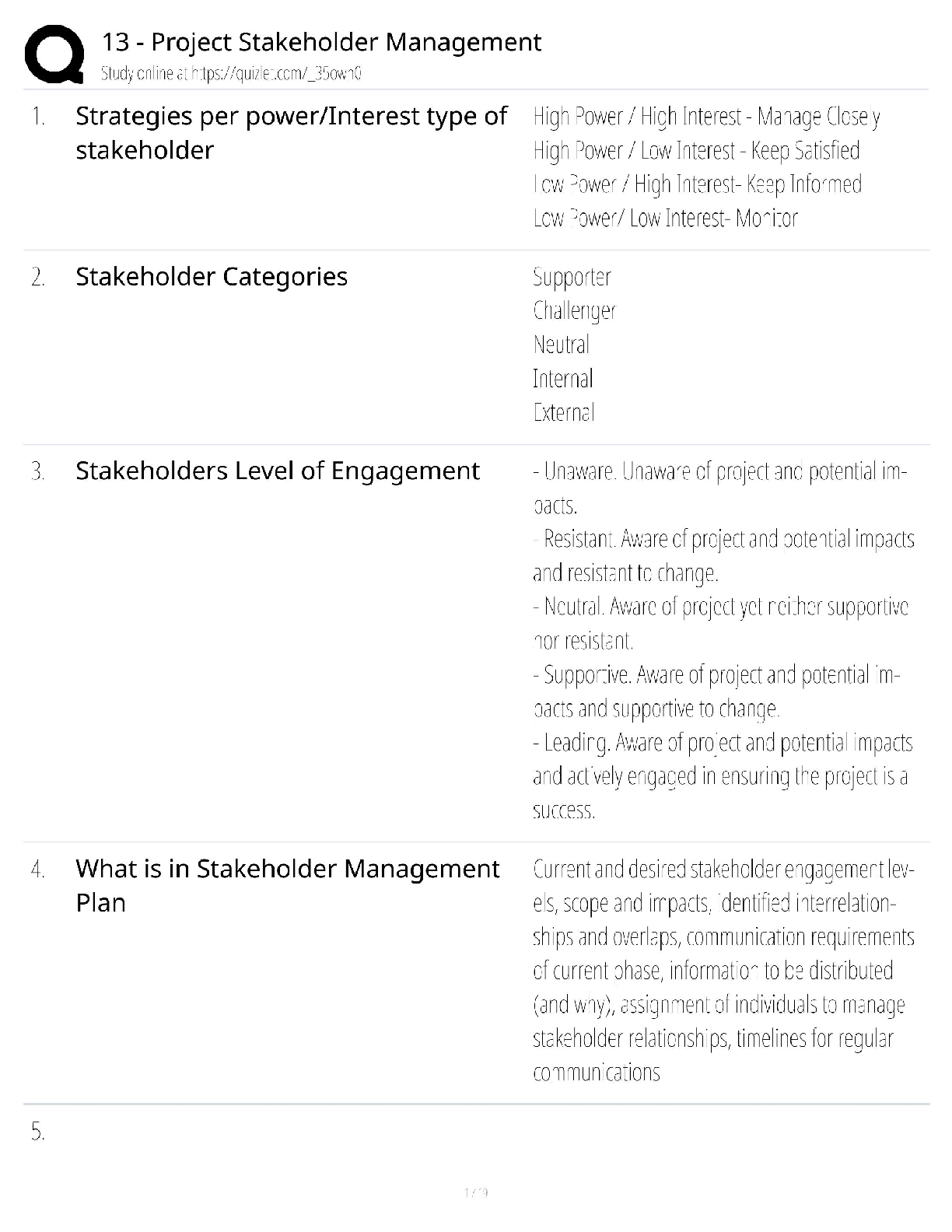
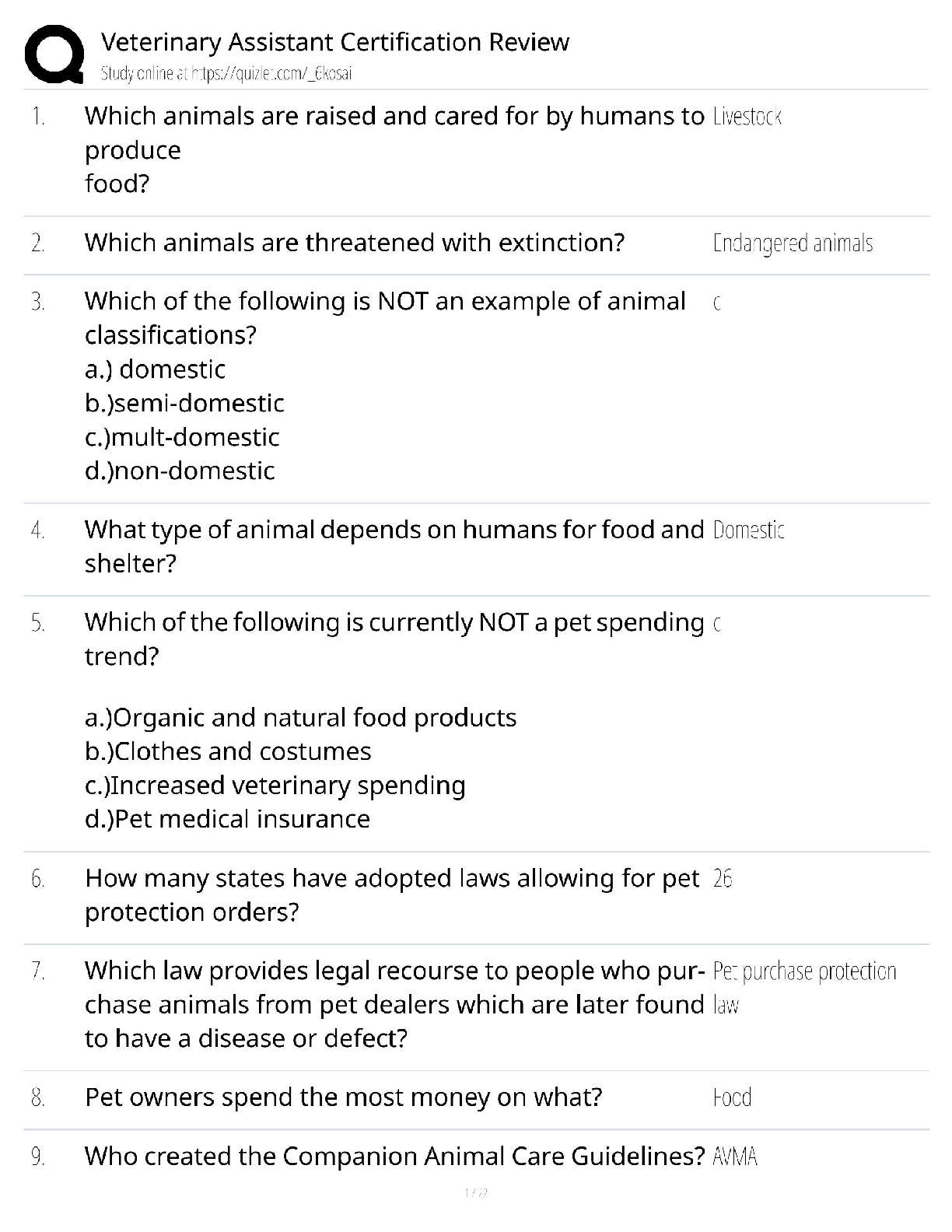
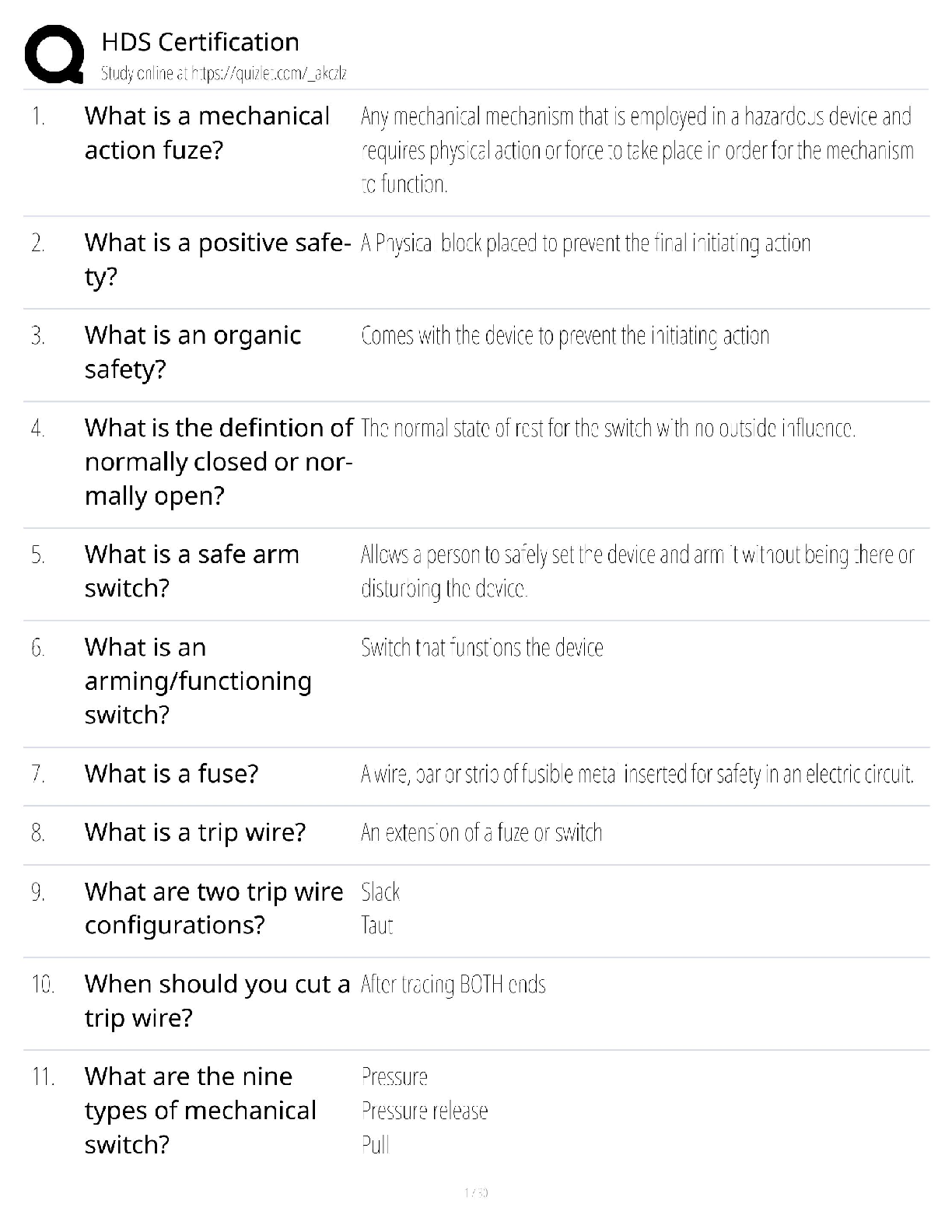
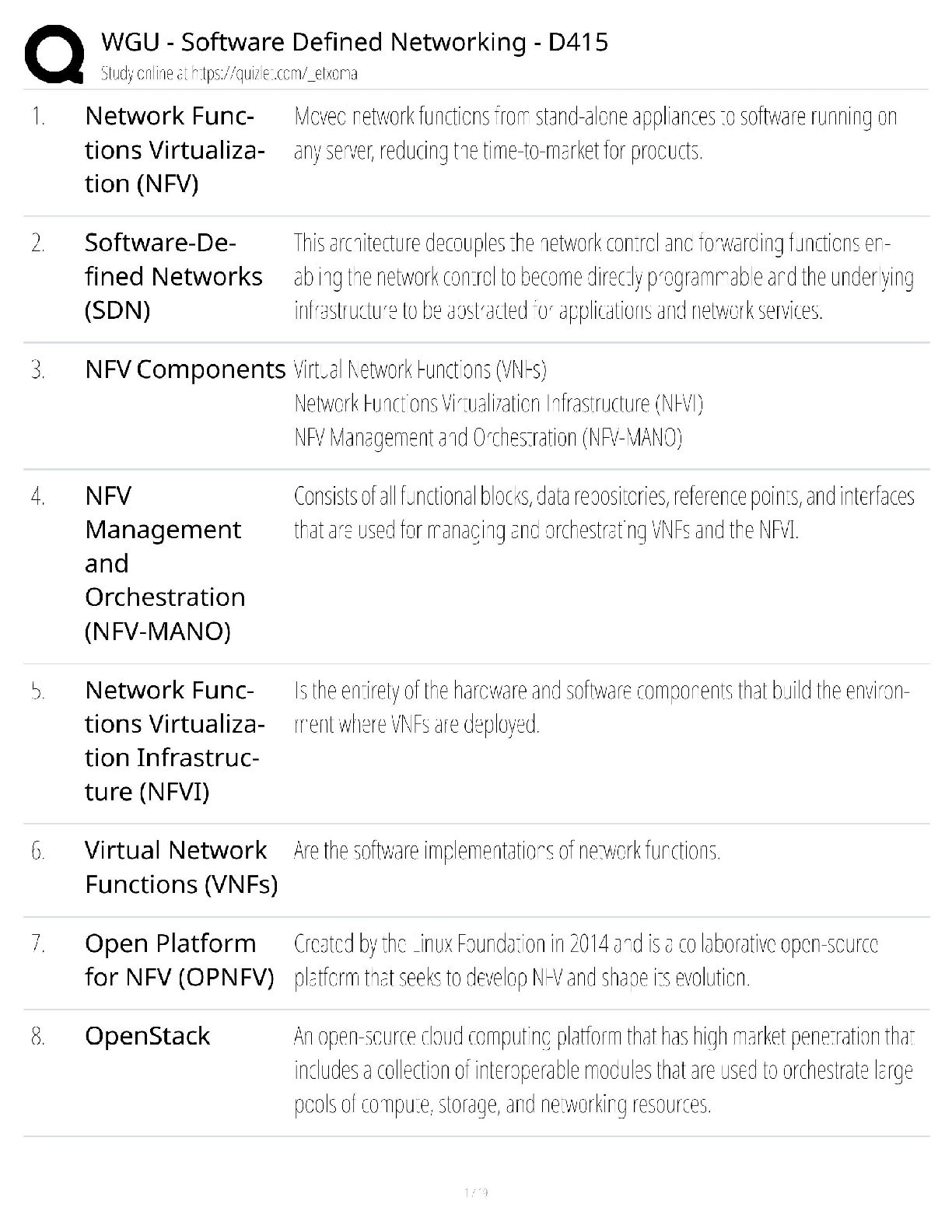
Appendix 13C Income Taxes and the Net Present Value Method True / False Questions 1. Unless the organization is tax-exempt, income taxes should be considered when using net present value analysi ... s to make capital budgeting decisions. True False 2. A capital budgeting project's incremental net income computation for purposes of determining incremental tax expense does not include immediate cash outflows for initial investments in equipment. True False 3. The release of working capital at the end of an investment project is not a taxable cash inflow. True False 4. The investment in working capital at the start of an investment project can not be deducted from revenues when computing taxable income. True False 5. Under the simplifying assumptions made in the text, to calculate the amount of income tax expense associated with an investment project, first calculate the incremental net income earned during each year of the project and then multiply each year's incremental net income by the tax rate. True False Multiple Choice Questions 6. In capital budgeting computations, discounted cash flow methods: A. automatically provide for recovery of initial investment. B. can't be used unless cash flows are uniform from year to year. C. assume that all cash flows occur at the beginning of a period. D. ignore all cash flows after the payback period. 7. Gayheart Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that would require investing $80,000 in equipment with an expected life of 4 years and zero salvage value. The annual incremental sales would be $260,000 and the annual incremental cash operating expenses would be $190,000. The company's income tax rate is 30%. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 2 is: A. $50,000 B. $55,000 C. $70,000 D. $34,000 8. Freiman Corporation is considering investing in a project that would have a 4 year expected useful life. The company would need to invest $160,000 in equipment that will have zero salvage value at the end of the project. Annual incremental sales would be $390,000 and annual cash operating expenses would be $270,000. In year 3 the company would have to incur one-time renovation expenses of $70,000. Working capital in the amount of $10,000 would be required. The working capital would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. The income tax expense in year 2 is: A. $24,000 B. $21,000 C. $36,000 D. $3,000 9. Bourret Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The net present value of the project is closest to: A. $27,928 B. $67,928 C. $49,000 D. $44,020 10. Milliner Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment; the annual depreciation expense will be $60,000. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The net present value of the project is closest to: A. $112,824 B. $352,824 C. $193,380 D. $175,500 11. Bosell Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The income tax rate is 30%. The after-tax discount rate is 14%. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment; the annual depreciation expense will be $60,000. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The net present value of the project is closest to: A. $142,950 B. $320,499 C. $80,499 D. $196,000 12. Jessel Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The net present value of the project is closest to: A. $382,320 B. $227,039 C. $220,209 D. $364,000 13. Blier Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. The income tax expense in year 2 is: A. $17,500 B. $3,500 C. $35,000 D. $21,000 14. Darnold Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The equipment will have a 4 year expected life and zero salvage value. The company's income tax rate is 35% and the after-tax discount rate is 9%. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment; the annual depreciation expense will be $10,000. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The net present value of the project is closest to: A. $74,497 B. $57,170 C. $34,497 D. $52,000 15. Kellog Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that would have a useful life of 4 years and would involve investing $160,000 in equipment that would have zero salvage value at the end of the project. Annual incremental sales would be $390,000 and annual cash operating expenses would be $260,000. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Its income tax rate is 35%. The income tax expense in year 2 is: A. $7,000 B. $45,500 C. $31,500 D. $24,500 16. Broxterman Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 3 is: A. $89,000 B. $56,500 C. $60,000 D. $39,000 17. The following information concerning a proposed capital budgeting project has been provided by Wick Corporation: The expected life of the project is 4 years. The income tax rate is 35%. The after-tax discount rate is 14%. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment and the annual depreciation expense would be $60,000. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The net present value of the project is closest to: A. $101,282 B. $224,850 C. $119,042 D. $266,500 18. Alopecia Hair Tonic Corporation is considering an investment project that is expected to generate net cash inflows of $65,000 per year for 4 years. The only initial investment funds required will be a $150,000 increase in working capital. This will be released at the end of the 4 years. Alopecia's after-tax cost of capital is 12% and its tax rate is 30%. The net present value of this investment project is closest to: A. $4,622 B. $59,222 C. $83,584 D. $99,964 19. Lastufka Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project. The project would require an investment of $240,000 in equipment with a 4 year expected life and zero salvage value. The company uses straight-line depreciation and the annual depreciation expense will be $60,000. Annual incremental sales would be $500,000 and annual incremental cash operating expenses would be $390,000. The company's income tax rate is 35% and the after-tax discount rate is 8%. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The net present value of the project is closest to: A. $66,360 B. $306,360 C. $130,000 D. $124,320 20. Rieben Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that would involve investing $120,000 in equipment with an estimated useful life of 4 years and no salvage value at the end of the useful life. Annual incremental sales from the project would be $320,000 and the annual incremental cash operating expenses would be $220,000. A one-time renovation expense of $40,000 would be required in year 3. The company's income tax rate is 30%. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. The income tax expense in year 3 is: A. $9,000 B. $30,000 C. $12,000 D. $21,000 21. Lasater Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company's tax rate is 35%. The company's after-tax discount rate is 15%. The project would require an investment of $10,000 at the beginning of the project. This working capital would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 2 is: A. $62,500 B. $36,500 C. $50,000 D. $80,000 22. Croes Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 3 is: A. $116,000 B. $80,000 C. $74,000 D. $56,000 23. A company anticipates incremental net income (i.e., incremental taxable income) of $50,000 in year 4 of a project. The company's tax rate is 30% and its after-tax discount rate is 12%. The present value of this future cash flow is closest to: A. $22,260 B. $35,000 C. $9,533 D. $15,000 24. The Moab Corporation had sales of $300,000 and expenses of $175,000 last year. All sales were cash sales and all expenses were cash expenses. Moab Corporation's tax rate is 30%. The after- tax net cash inflow at Moab last year was: A. $210,000 B. $37,500 C. $52,500 D. $87,500 25. Lucarell Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. The income tax expense in year 3 is: A. $24,500 B. $14,000 C. $10,500 D. $38,500 26. Sader Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that would require an investment of $160,000 in equipment with a 4 year expected life and zero salvage value. Annual incremental sales will be $420,000 and annual incremental cash operating expenses will be $320,000. The company's income tax rate is 30% and the after-tax discount rate is 8%. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment; the annual depreciation expense will be $40,000. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The net present value of the project is closest to: A. $271,584 B. $111,584 C. $171,200 D. $168,000 27. Santistevan Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The net present value of the project is closest to: A. $58,218 B. $98,370 C. $112,000 D. $36,168 28. Strathman Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. The income tax expense in year 2 is: A. $33,000 B. $48,000 C. $9,000 D. $24,000 29. A company needs an increase in working capital of $20,000 in a project that will last 4 years. The company's tax rate is 30% and its after-tax discount rate is 10%. The present value of the release of the working capital at the end of the project is closest to: A. $6,000 B. $13,660 C. $9,562 D. $14,000 30. Onorato Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 2 is: A. $133,000 B. $160,000 C. $90,000 D. $98,000 31. Wollard Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. The income tax expense in year 3 is: A. $3,000 B. $12,000 C. $18,000 D. $9,000 32. Welti Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment; the annual depreciation expense will be $30,000. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The net present value of the project is closest to: A. $140,000 B. $150,960 C. $220,155 D. $100,155 33. Pulkkinen Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 2 is: A. $70,000 B. $50,000 C. $52,500 D. $39,500 34. Gutshall Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that would involve investing $240,000 in equipment with an estimated useful life of 4 years and no salvage value at the end of the useful life. Annual incremental sales from the project would be $580,000 and the annual incremental cash operating expenses would be $430,000. A one-time renovation expense of $70,000 would be required in year 3. The project would require investing $10,000 of working capital in the project immediately, but this amount would be recovered at the end of the project in 4 years. The company's income tax rate is 30% and its after-tax discount rate is 13%. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. The income tax expense in year 3 is: A. $6,000 B. $45,000 C. $21,000 D. $27,000 35. Leamon Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that would require an investment of $240,000 in equipment with a 4 year useful life and zero salvage value. The annual incremental sales would be $630,000 and the annual incremental cash operating expenses would be $480,000. In addition, there would be a one-time renovation expense in year 3 of $40,000. The company's income tax rate is 35%. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 3 is: A. $92,500 B. $110,000 C. $78,500 D. $118,500 Folino Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that would require investing $120,000 in equipment with an expected life of 4 years and zero salvage value. Annual incremental sales would be $380,000 and annual incremental cash operating expenses would be $300,000. The project would also require an immediate investment in working capital of $10,000 which would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The project would also require a one-time renovation cost of $30,000 in year 3. The company's income tax rate is 35% and its after-tax discount rate is 15%. The company uses straight-line depreciation. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 36. The income tax expense in year 2 is: A. $17,500 B. $7,000 C. $28,000 D. $10,500 37. The income tax expense in year 3 is: A. $28,000 B. $10,500 C. $7,000 D. $17,500 38. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 2 is: A. $62,500 B. $80,000 C. $43,000 D. $50,000 39. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 3 is: A. $32,500 B. $62,500 C. $43,000 D. $50,000 40. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $110,500 B. $35,669 C. $84,460 D. $41,389 Boch Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The working capital would be required immediately and would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 41. The income tax expense in year 2 is: A. $27,000 B. $12,000 C. $126,000 D. $87,000 42. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 2 is: A. $90,000 B. $103,000 C. $27,000 D. $130,000 43. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $255,230 B. $167,777 C. $153,617 D. $252,000 Pont Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company's income tax rate is 30% and its after-tax discount rate is 10%. The working capital would be required immediately and would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 44. The income tax expense in year 2 is: A. $27,000 B. $21,000 C. $39,000 D. $6,000 45. The income tax expense in year 3 is: A. $27,000 B. $6,000 C. $21,000 D. $39,000 46. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 2 is: A. $90,000 B. $54,000 C. $130,000 D. $103,000 47. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 3 is: A. $103,000 B. $33,000 C. $54,000 D. $60,000 48. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $123,268 B. $193,060 C. $109,608 D. $203,000 Glasco Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The working capital would be required immediately and would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 49. The income tax expense in year 2 is: A. $7,000 B. $3,500 C. $10,500 D. $17,500 50. The income tax expense in year 3 is: A. $7,000 B. $17,500 C. $3,500 D. $10,500 51. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $4,258 B. $15,698 C. $65,000 D. $41,080 Lanfranco Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that would require investing $160,000 in equipment with an expected life of 4 years and zero salvage value. Annual incremental sales would be $480,000 and annual incremental cash operating expenses would be $330,000. The project would also require an immediate investment in working capital of $10,000 which would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The project would also require a one-time renovation cost of $100,000 in year 3. The company's income tax rate is 35% and its after-tax discount rate is 6%. The company uses straight-line depreciation. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 52. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 2 is: A. $111,500 B. $150,000 C. $46,500 D. $110,000 53. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 3 is: A. $46,500 B. $11,500 C. $111,500 D. $50,000 54. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $161,748 B. $169,668 C. $221,000 D. $273,670 Dekle Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 55. The income tax expense in year 2 is: A. $111,000 B. $84,000 C. $18,000 D. $9,000 56. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 2 is: A. $72,000 B. $90,000 C. $18,000 D. $60,000 57. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $94,128 B. $214,128 C. $168,000 D. $147,660 Mitton Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that would require investing $160,000 in equipment with an expected life of 4 years and zero salvage value. Annual incremental sales would be $440,000 and annual incremental cash operating expenses would be $320,000. The project would also require a one-time renovation cost of $0 in year 3. The company's income tax rate is 35% and its after-tax discount rate is 12%. The company uses straight-line depreciation. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 58. The income tax expense in year 2 is: A. $14,000 B. $112,000 C. $28,000 D. $154,000 59. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 2 is: A. $92,000 B. $28,000 C. $120,000 D. $80,000 60. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $279,496 B. $119,496 C. $208,000 D. $204,560 Foucault Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company's income tax rate is 35% and its after-tax discount rate is 12%. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 61. The income tax expense in year 2 is: A. $70,000 B. $7,000 C. $42,000 D. $49,000 62. The income tax expense in year 3 is: A. $70,000 B. $42,000 C. $7,000 D. $49,000 63. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 2 is: A. $140,000 B. $200,000 C. $151,000 D. $73,000 64. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 3 is: A. $151,000 B. $73,000 C. $31,000 D. $80,000 65. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $403,202 B. $282,160 C. $163,202 D. $286,000 Skolfield Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that would require investing $280,000 in equipment with an expected life of 4 years and zero salvage value. Annual incremental sales would be $590,000 and annual incremental cash operating expenses would be $470,000. The project would also require an immediate investment in working capital of $20,000 which would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The project would also require a one-time renovation cost of $30,000 in year 3. The company's income tax rate is 30% and its after-tax discount rate is 15%. The company uses straight-line depreciation. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 66. The income tax expense in year 2 is: A. $15,000 B. $6,000 C. $9,000 D. $36,000 67. The income tax expense in year 3 is: A. $6,000 B. $15,000 C. $9,000 D. $36,000 68. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $(2,498) B. $34,420 C. $(13,938) D. $119,000 Trammel Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that would require investing $280,000 in equipment with an expected life of 4 years and zero salvage value. Annual incremental sales would be $650,000 and annual incremental cash operating expenses would be $450,000. The project would also require a one-time renovation cost of $100,000 in year 3. The company's income tax rate is 30% and its after-tax discount rate is 7%. The company uses straight-line depreciation. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 69. The income tax expense in year 2 is: A. $9,000 B. $30,000 C. $39,000 D. $60,000 70. The income tax expense in year 3 is: A. $9,000 B. $30,000 C. $39,000 D. $60,000 71. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $208,187 B. $315,800 C. $488,187 D. $294,000 Credit Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company's income tax rate is 30% and its after-tax discount rate is 15%. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 72. The income tax expense in year 2 is: A. $15,000 B. $6,000 C. $9,000 D. $21,000 73. The income tax expense in year 3 is: A. $21,000 B. $6,000 C. $9,000 D. $15,000 74. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $106,760 B. $147,868 C. $126,000 D. $67,868 Kostka Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that would require investing $160,000 in equipment with an expected life of 4 years and zero salvage value. Annual incremental sales would be $480,000 and annual incremental cash operating expenses would be $330,000. The project would also require an immediate investment in working capital of $20,000 which would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The project would also require a one-time renovation cost of $0 in year 3. The company's income tax rate is 30% and its after-tax discount rate is 9%. The company uses straight-line depreciation. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 75. The income tax expense in year 2 is: A. $144,000 B. $12,000 C. $33,000 D. $99,000 76. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 2 is: A. $110,000 B. $117,000 C. $150,000 D. $33,000 77. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $213,123 B. $198,963 C. $308,000 D. $320,010 Shinabery Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company's income tax rate is 35% and its after-tax discount rate is 9%. The working capital would be required immediately and would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 78. The income tax expense in year 2 is: A. $14,000 B. $3,500 C. $7,000 D. $10,500 79. The income tax expense in year 3 is: A. $3,500 B. $14,000 C. $7,000 D. $10,500 80. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $39,675 B. $68,280 C. $25,515 D. $65,000 Gouker Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 81. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 2 is: A. $90,000 B. $76,000 C. $108,500 D. $140,000 82. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 3 is: A. $58,500 B. $76,000 C. $90,000 D. $108,500 83. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $201,500 B. $319,429 C. $206,110 D. $119,429 Brogden Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company's income tax rate is 30% and its after-tax discount rate is 10%. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 84. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 2 is: A. $137,000 B. $170,000 C. $67,000 D. $110,000 85. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 3 is: A. $70,000 B. $137,000 C. $37,000 D. $67,000 86. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $141,583 B. $223,630 C. $381,583 D. $238,000 Voelkel Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company's income tax rate is 30% and its after-tax discount rate is 7%. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 87. The income tax expense in year 2 is: A. $90,000 B. $12,000 C. $126,000 D. $24,000 88. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 2 is: A. $96,000 B. $24,000 C. $80,000 D. $120,000 89. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $246,440 B. $165,152 C. $325,152 D. $224,000 Erling Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company's income tax rate is 35% and its after-tax discount rate is 15%. The working capital would be required immediately and would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 90. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 2 is: A. $170,000 B. $115,500 C. $240,000 D. $180,500 91. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 3 is: A. $115,500 B. $140,000 C. $80,500 D. $180,500 92. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $331,080 B. $172,738 C. $377,000 D. $184,178 Zangari Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 93. The income tax expense in year 2 is: A. $17,500 B. $52,500 C. $28,000 D. $10,500 94. The income tax expense in year 3 is: A. $28,000 B. $10,500 C. $52,500 D. $17,500 95. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $47,047 B. $115,500 C. $327,047 D. $175,500 Battaglia Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that would require investing $240,000 in equipment with an expected life of 4 years and zero salvage value. Annual incremental sales would be $620,000 and annual incremental cash operating expenses would be $460,000. The project would also require a one-time renovation cost of $80,000 in year 3. The company's income tax rate is 30% and its after-tax discount rate is 7%. The company uses straight-line depreciation. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 96. The income tax expense in year 2 is: A. $24,000 B. $6,000 C. $48,000 D. $30,000 97. The income tax expense in year 3 is: A. $48,000 B. $30,000 C. $6,000 D. $24,000 98. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 2 is: A. $160,000 B. $100,000 C. $130,000 D. $74,000 99. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 3 is: A. $130,000 B. $80,000 C. $74,000 D. $50,000 100. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $224,000 B. $394,614 C. $236,640 D. $154,614 Amel Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The working capital would be required immediately and would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 101. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 2 is: A. $60,000 B. $69,000 C. $43,000 D. $90,000 102. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 3 is: A. $50,000 B. $29,000 C. $69,000 D. $43,000 103. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $41,110 B. $130,000 C. $114,020 D. $60,190 Stack Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that would require investing $80,000 in equipment with an expected life of 4 years and zero salvage value. Annual incremental sales would be $200,000 and annual incremental cash operating expenses would be $150,000. The project would also require a one-time renovation cost of $10,000 in year 3. The company's income tax rate is 35% and its after-tax discount rate is 7%. The company uses straight-line depreciation. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 104. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 2 is: A. $50,000 B. $33,000 C. $30,000 D. $39,500 105. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 3 is: A. $29,500 B. $39,500 C. $33,000 D. $40,000 106. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $48,483 B. $81,190 C. $128,483 D. $71,500 Helfen Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company's income tax rate is 35% and its after-tax discount rate is 13%. The working capital would be required immediately and would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 107. The income tax expense in year 2 is: A. $14,000 B. $77,000 C. $10,500 D. $101,500 108. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 2 is: A. $56,000 B. $70,000 C. $14,000 D. $40,000 109. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $84,310 B. $42,674 C. $36,544 D. $104,000 Prudencio Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 110. The income tax expense in year 2 is: A. $12,000 B. $33,000 C. $21,000 D. $9,000 111. The income tax expense in year 3 is: A. $21,000 B. $12,000 C. $9,000 D. $33,000 112. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 2 is: A. $61,000 B. $70,000 C. $110,000 D. $89,000 113. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 3 is: A. $70,000 B. $49,000 C. $89,000 D. $61,000 114. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $85,282 B. $139,420 C. $245,282 D. $168,000 Starrs Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The working capital would be required immediately and would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. 115. The income tax expense in year 2 is: A. $9,000 B. $15,000 C. $3,000 D. $6,000 116. The income tax expense in year 3 is: A. $9,000 B. $3,000 C. $15,000 D. $6,000 117. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 2 is: A. $41,000 B. $30,000 C. $27,000 D. $50,000 118. The total cash flow net of income taxes in year 3 is: A. $41,000 B. $27,000 C. $21,000 D. $30,000 119. The net present value of the entire project is closest to: A. $48,070 B. $19,983 C. $70,000 D. $25,903 Essay Questions 120. Brodigan Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The expected life of the project and the equipment is 3 years and the equipment has zero salvage value. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment and the depreciation expense on the equipment would be $150,000 per year. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The net annual operating cash inflow is the difference between the incremental sales revenue and incremental cash operating expenses. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 121. Hothan Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The working capital would be required immediately and would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The company uses straight-line depreciation. The depreciation expense will be $60,000 per year. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The income tax rate is 30% and the after-tax discount rate is 15%. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 122. Mota Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The expected life of the project and the equipment is 3 years and the equipment has zero salvage value. The working capital would be required immediately and would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment and the depreciation expense on the equipment would be $210,000 per year. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The income tax rate is 35%. The after-tax discount rate is 15%. The net annual operating cash inflow is the difference between the incremental sales revenue and incremental cash operating expenses. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 123. Corchado Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that involves investing $600,000 in equipment that would have a useful life of 3 years and zero salvage value. The company would also need to invest $30,000 immediately in working capital which would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project in 3 years. The net annual operating cash inflow, which is the difference between the incremental sales revenue and incremental cash operating expenses, would be $310,000 per year. The project would require a one-time renovation expense of $60,000 at the end of year 2. The company uses straight-line depreciation and the depreciation expense on the equipment would be $200,000 per year. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The income tax rate is 35%. The after-tax discount rate is 6%. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 124. Mickolick Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The working capital would be required immediately and would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 125. Shaddock Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that would require investing $80,000 in equipment with a 4 year useful life and zero salvage value. Data concerning that project appear below: The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The company's tax rate is 30% and the after-tax discount rate is 12%. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 126. Ferriman Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that involves investing $600,000 in equipment that would have a useful life of 3 years and zero salvage value. The company would also need to invest $40,000 immediately in working capital which would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project in 3 years. The net annual operating cash inflow, which is the difference between the incremental sales revenue and incremental cash operating expenses, would be $300,000 per year. The company uses straight-line depreciation and the depreciation expense on the equipment would be $200,000 per year. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The income tax rate is 30%. The after-tax discount rate is 10%. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 127. Gloden Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company uses straight-line depreciation. The depreciation expense will be $30,000 per year. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The income tax rate is 35% and the after-tax discount rate is 12%. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 128. Diss Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that involves investing $570,000 in equipment that would have a useful life of 3 years and zero salvage value. The net annual operating cash inflow, which is the difference between the incremental sales revenue and incremental cash operating expenses, would be $290,000 per year. The company uses straight- line depreciation and the depreciation expense on the equipment would be $190,000 per year. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The income tax rate is 30%. The after- tax discount rate is 6%. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 129. Depew Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The expected life of the project and the equipment is 3 years and the equipment has zero salvage value. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment and the depreciation expense on the equipment would be $250,000 per year. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The net annual operating cash inflow is the difference between the incremental sales revenue and incremental cash operating expenses. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 130. Soffer Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The expected life of the project and the equipment is 3 years and the equipment has zero salvage value. The working capital would be required immediately and would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment and the depreciation expense on the equipment would be $190,000 per year. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The net annual operating cash inflow is the difference between the incremental sales revenue and incremental cash operating expenses. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 131. Hauge Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that involves investing $750,000 in equipment that would have a useful life of 3 years and zero salvage value. The net annual operating cash inflow, which is the difference between the incremental sales revenue and incremental cash operating expenses, would be $390,000 per year. The project would require a one-time renovation expense of $70,000 at the end of year 2. The company uses straight-line depreciation and the depreciation expense on the equipment would be $250,000 per year. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The income tax rate is 30%. The after- tax discount rate is 13%. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 132. Deninno Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that would require investing $240,000 in equipment with a 4 year useful life and zero salvage value. Data concerning that project appear below: The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The company's tax rate is 30% and the after-tax discount rate is 9%. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 133. Revello Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that would require investing $40,000 in equipment with a 4 year useful life and zero salvage value. Data concerning that project appear below: An investment of $30,000 in working capital would be required immediately and would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The company's tax rate is 30% and the after-tax discount rate is 9%. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 134. Crabill Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The expected life of the project and the equipment is 3 years and the equipment has zero salvage value. The working capital would be required immediately and would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment and the depreciation expense on the equipment would be $230,000 per year. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The net annual operating cash inflow is the difference between the incremental sales revenue and incremental cash operating expenses. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 135. El Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The expected life of the project and the equipment is 3 years and the equipment has zero salvage value. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment and the depreciation expense on the equipment would be $200,000 per year. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The net annual operating cash inflow is the difference between the incremental sales revenue and incremental cash operating expenses. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 136. Molima Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 137. Beecroft Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that would require investing $120,000 in equipment with a 4 year useful life and zero salvage value. Annual incremental sales would be $390,000 and annual incremental cash operating expenses would be $300,000. A one- time expense of $40,000 for renovations would be required in year 3. An investment of $20,000 in working capital would be required immediately and would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The company's tax rate is 30% and the after-tax discount rate is 12%. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 138. Flippo Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that would require investing $160,000 in equipment with a 4 year useful life and zero salvage value. Data concerning that project appear below: An investment of $20,000 in working capital would be required immediately and would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The company's tax rate is 30% and the after-tax discount rate is 6%. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 139. Zucker Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 140. Menghini Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that would require investing $120,000 in equipment with a 4 year useful life and zero salvage value. Annual incremental sales would be $300,000 and annual incremental cash operating expenses would be $240,000. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The company's tax rate is 30% and the after-tax discount rate is 6%. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 141. Stortz Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that would require investing $120,000 in equipment with a 4 year useful life and zero salvage value. Annual incremental sales would be $290,000 and annual incremental cash operating expenses would be $210,000. A one- time expense of $30,000 for renovations would be required in year 3. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The company's tax rate is 35% and the after-tax discount rate is 14%. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 142. Forehand Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The working capital would be required immediately and would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The company uses straight-line depreciation. The depreciation expense will be $30,000 per year. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The income tax rate is 30% and the after-tax discount rate is 10%. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 143. Faniel Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The working capital would be required immediately and would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 144. Hohlfeld Corporation is considering a capital budgeting project that would require investing $80,000 in equipment with a 4 year useful life and zero salvage value. Annual incremental sales would be $240,000 and annual incremental cash operating expenses would be $180,000. An investment of $20,000 in working capital would be required immediately and would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The company's tax rate is 30% and the after-tax discount rate is 9%. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 145. Pilarz Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The company uses straight-line depreciation. The depreciation expense will be $20,000 per year. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The income tax rate is 30% and the after-tax discount rate is 8%. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 146. Holzner Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The expected life of the project and the equipment is 3 years and the equipment has zero salvage value. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment and the depreciation expense on the equipment would be $270,000 per year. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The net annual operating cash inflow is the difference between the incremental sales revenue and incremental cash operating expenses. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! 147. Schlagel Corporation has provided the following information concerning a capital budgeting project: The expected life of the project and the equipment is 3 years and the equipment has zero salvage value. The working capital would be required immediately and would be released for use elsewhere at the end of the project. The company uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment and the depreciation expense on the equipment would be $150,000 per year. Assume cash flows occur at the end of the year except for the initial investments. The company takes income taxes into account in its capital budgeting. The net annual operating cash inflow is the difference between the incremental sales revenue and incremental cash operating expenses. Required: Determine the net present value of the project. Show your work! [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 276 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$11.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 07, 2020
Number of pages
276
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 07, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
293






.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)