ORGANISATIONAL BEHAVIOR.
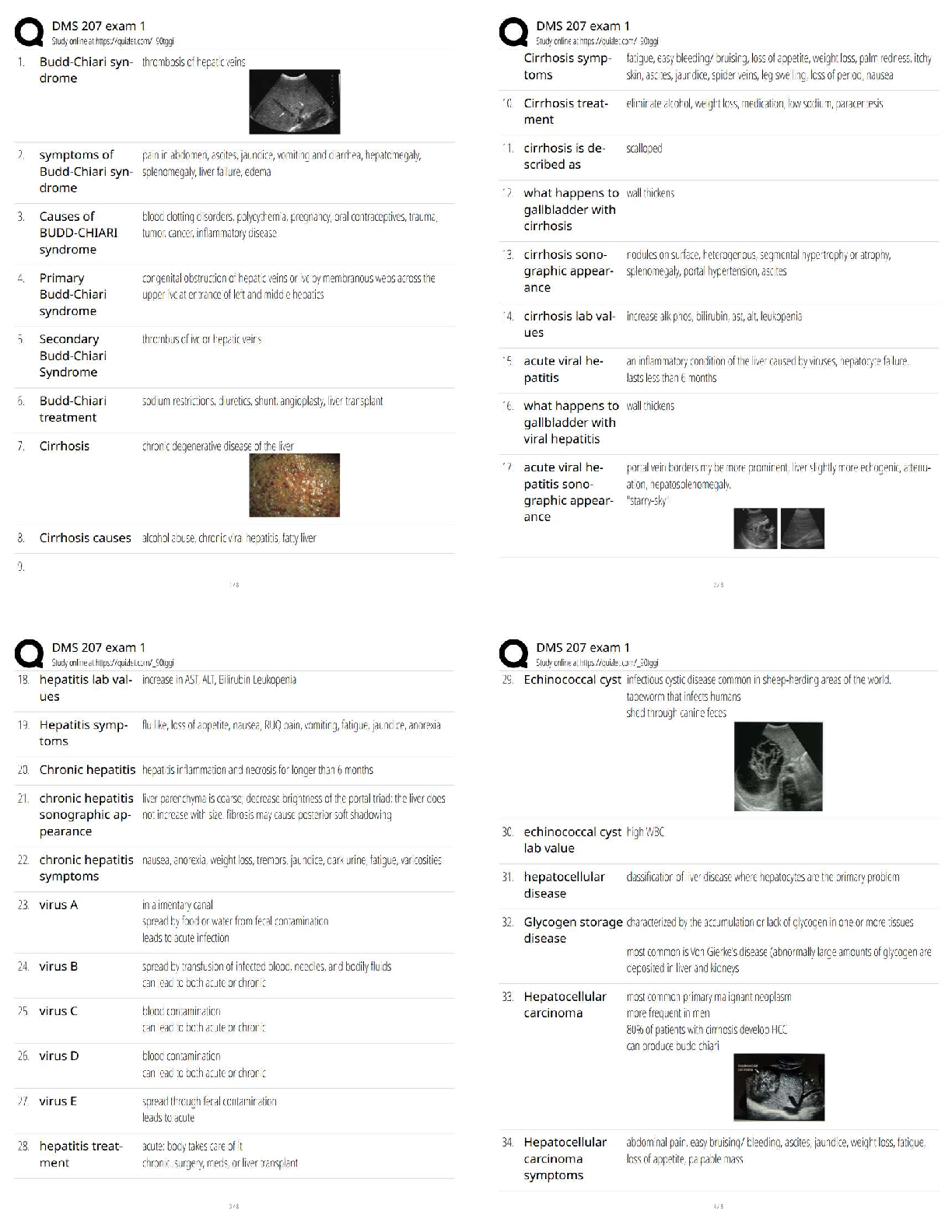
CHAPTER 1 TO 5
Chapter 1 What Is Organizational Behaviour?
1.1 Multiple-Choice Questions
1) Which of the following statements about organizational behaviour (OB) is FALSE?
A) OB is
...
ORGANISATIONAL BEHAVIOR.
CHAPTER 1 TO 5
Chapter 1 What Is Organizational Behaviour?
1.1 Multiple-Choice Questions
1) Which of the following statements about organizational behaviour (OB) is FALSE?
A) OB is relevant only in employment situations.
B) OB can shed light on the interactions among family members.
C) OB can be used in community settings like children's daycare centres.
D) OB can be applied to any organization in order to make it run more effectively.
E) OB focuses on 3 levels of behaviour that can occur in any organization.
Page Ref: 4,5
Skill: Recall
Topic: Defining Organizational Behaviour
Objective: 1
2) Which of the following situations would likely receive the least benefit from studying Organizational Behaviour(OB) techniques?
A) voluntary community groups
B) large family situations and interactions
C) post-secondary education student study groups
D) religious organizations
E) pre-teen paper routes
Page Ref: 4,5
Skill: Recall
Topic: Defining Organizational Behaviour
Objective: 1
3) A field of study that investigates the impact of individuals, groups, and structure on behaviour within organizations is known as
A) psychology.
B) sociology.
C) social psychology.
D) anthropology.
E) organizational behaviour.
Page Ref: 4
Skill: Recall
Topic: Defining Organizational Behaviour
Objective: 1
4) A consciously coordinated social unit composed of a group of people that function on a relatively continuous basis to achieve a common set of goals is known as a(n)
A) work group.
B) team.
C) organization.
D) society.
E) task force.
Page Ref: 4
Skill: Recall
Topic: Defining Organizational Behaviour
Objective: 1
5) Which of the following topics is generally outside the field of OB?
A) therapy
B) absenteeism
C) employment turnover
D) productivity
E) job satisfaction
Page Ref: 4
Skill: Recall
Topic: Defining Organizational Behaviour
Objective: 1
6) Organizational behaviour is generally defined as a field of study that
A) investigates how organizations effectively face competition.
B) investigates the impact that individuals, groups, and structure have on behaviour within organizations.
C) attempts to understand and solve problems regarding individual behaviour on and off the job.
D) seeks ways and means to match human effort with technology.
E) examines how the structure of different organizations contributes to, or inhibits, effective communication.
Page Ref: 4
Skill: Recall
Topic: Defining Organizational Behaviour
Objective: 1
7) What are the three inputs to processes that OB is concerned with?
A) experience, goals and configuration
B) individual, group, and organizational structure
C) structure, social units and teams
D) group, structure and political
E) interpersonal, personal and group
Page Ref: 21
Skill: Recall
Topic: Organizational Behaviour Model
8) Which of the following is NOT considered an organization?
A) church
B) university
C) military unit
D) all 45 year old adults in a community
E) municipal, provincial and federal government agencies
Page Ref: 4
Skill: Recall
Topic: Defining Organizational Behaviour
Objective: 1
9) A(n) ________ is a consciously coordinated social unit composed of two or more people that functions on a relatively continuous basis to achieve a common goal or set of goals.
A) organization
B) unit
C) team
D) ethnic group
E) informal group
Page Ref: 4
Skill: Applied
Topic: Defining Organizational Behaviour
Objective: 1
10) Individuals face various challenges in organizational settings. Which of the following organizational challenges is OB best suited for
A) maintaining stock prices.
B) profit projection.
C) setting common goals.
D) time management.
E) protocol on the job.
Page Ref: 5
Skill: Applied
Topic: Interpersonal Skills
11) As employers attempt to retain high performance employees, what factors in employee-manager relationships become important?
A) supportive dialogue, proactive discussions and high wages
B) high stress workplace, supportive dialogue and proactive discussions
C) lower stress workplace, proactive discussions and supportive dialogue
D) high wages, lower stress workplace and supportive dialogue
E) high wages, high stress workplace and proactive discussions
Page Ref: 6
Skill: Applied
Topic: Interpersonal Relationships
12) When managers have positive social relationships with their employees they are
A) re-engineering the workplace.
B) establishing a new program of TQM.
C) developing new styles of leadership.
D) developing ways of more effectively controlling work.
E) lowering employee stress, which lowers intentions to quit.
Page Ref: 6
Skill: Applied
Topic: Interpersonal Relationships
13) Which of the following is the most accurate description of ethics?
A) Ethics are easy to implement at the organizational level as best illustrated at Enron Corporation.
B) Ethics look at past personal traumas.
C) Ethics is common sense that informs us as to whether our actions are right or wrong.
D) Ethics is the study of moral values that guide our behaviour.
E) Ethics help us do the "right" thing.
Page Ref: 20
Skill: Recall
Topic: Challenges and Opportunities
Objective: 6
14) Toronto-based Dell Canada's technical service lines are handled by technicians located in India. This is an example of
A) repatriation.
B) immigration.
C) emigration.
D) nationalism.
E) outsourcing.
Page Ref: 16
Skill: Recall
Topic: Challenges and Opportunities
15) Which of the following is TRUE about organizational citizenship behaviour, (OCB)?
A) Writing OCB requirements into job descriptions is important.
B) Managers granting control to employees will receive OCB.
C) OCB allows employees to delegate their work to peers.
D) OCB enhances company performance and is highly valued.
E) Employees with high OCB usually ask for more time off.
Page Ref: 23
Skill: Recall
16) Which of the following is TRUE about ethics?
A) is easy to implement at the organizational level
B) is the study of consciously coordinated social units
C) aims to understand motivations for individual behaviours
D) informs us as to whether a job is intrinsically rewarding
E) helps us do the "right" thing
Page Ref: 21
Skill: Applied
Topic: Challenges and Opportunities
Objective: 6
17) A characteristic of Johan's department is that there is a broad mix of people in terms of gender, race and ethnicity. This is known as
A) diversity.
B) empowerment.
C) groupthink.
D) ethics.
E) individual differences.
Page Ref: 16
Skill: Applied
Topic: Challenges and Opportunities
Objective: 6
18) Giselle is using a spreadsheet to measure each employee's efficiency and effectiveness. This is known as the employee's
A) performance.
B) productivity.
C) diversity.
D) culture.
E) ethics.
Page Ref: 23
Skill: Applied
19) Workplace diversity challenges organizations as three main demographic groups make up the workforce; these three groups are
A) Ethicals, Millennial and Generation X.
B) Elders, Baby Boomers and Generation X.
C) Baby Boomers, Generation X and Millennials.
D) Elders, Generation X and Millennials.
E) Ethicals, Elders and Generation X.
Page Ref: 17
Skill: Recall
Topic: Challenges and Opportunities
Objective: 6
20) Everyone loves to work for Peter because he is respectful and a good listener; he is firm with goals and expectations, but gives support with training and flexible timelines. Peter has strong
A) motivational abilities.
B) similarities and demographics.
C) interpersonal skills.
D) quantitative skills.
E) ethics.
Page Ref: 6
Skill: Applied
Topic: Interpersonal Skills
21) Zeke is an employee who achieves his goals. This shows Zeke is
A) performing.
B) efficient.
C) effective.
D) motivated.
E) diverse.
Page Ref: 24
Skill: Applied
22) Workforce diversity is
A) counter-productive to job satisfaction.
B) the variance among workers' pay scales.
C) the distribution of workers by hair colour.
D) the differences among employees based on age.
E) the ratio of assistants to managers.
Page Ref: 16
Skill: Recall
Topic: Challenges and Opportunities
23) Managers improve productivity by developing effective employees and efficient work processes; this supports organizational
A) ethics.
B) diversity.
C) citizenship behaviour.
D) survival.
E) motivation.
Page Ref: 24,25
Skill: Applied
24) Whereas ________ requires organizations to be flexible in working with organizations and people from different countries, ________ requires employees to be flexible when working with others within the organization.
A) workforce diversity; globalization
B) globalization; workforce diversity
C) culture; diversity
D) culturization; workforce diversity
E) globalization; culturization
Page Ref: 16,17
Skill: Recall
Topic: Challenges and Opportunities
25) Sanjay is a very motivated employee who typically does work that is not part of his formal job responsibilities but which furthers the objectives of the organization. This is known as
A) groupthink.
B) organizational citizenship behaviour.
C) diversity.
D) individual differences.
E) efficiency.
Page Ref: 22
Skill: Applied
26) Why should you increase your understanding of workforce diversity?
A) to be politically correct
B) the Canadian workplace is becoming more homogeneous
C) to eliminate differences amongst employees
D) the Canadian workplace is becoming more heterogeneous
E) to communicate more proficiently
Page Ref: 16
Skill: Recall
Topic: Challenges and Opportunities
27) Contributions to Organizational Behaviour on perception come from
A) risk taking.
B) empowerment.
C) sociology.
D) psychology.
E) contingency.
Page Ref: 7
Skill: Recall
Topic: Building Blocks of OB
Objective: 3
28) How organizations develop human strengths, foster vitality and resilience, and unlock potential is called
A) orientation.
B) groupthink.
C) positive organizational scholarship.
D) human dynamics.
E) organizational politics.
Page Ref: 20
Skill: Recall
Topic: Challenges and Opportunities
Objective: 6
29) In all of his undertakings at work, Norm is a leader who looks to do the right thing. This refers to his
A) efficiency.
B) effectiveness.
C) performance.
D) ethics.
E) motivation.
Page Ref: 20
Skill: Applied
Topic: Challenges and Opportunities
Objective: 6
30) Tina is known to produce large amounts of work without having to exert much effort. Tina is
A) diverse.
B) efficient.
C) effective.
D) motivated.
E) ethical.
Page Ref: 24
Skill: Applied
31) A high rate of employee turnover increases
A) bottom up management.
B) recruiting costs.
C) positive organizational scholarship.
D) workplace diversity.
E) individual difference.
Page Ref: 23
Skill: Recall
32) Tom noticed that there is a wide variety of personalities and values among his staff members, which he believes affects how they behave. These are known as
A) empowerment.
B) job satisfaction.
C) groupthink.
D) individual level inputs.
E) motivation.
Page Ref: 21
Skill: Applied
33) ________ is achievement of goals.
A) Efficiency
B) Effectiveness
C) Productivity
D) Motivation
E) Job satisfaction
Page Ref: 24
Skill: Recall
34) Which of the following is an example of being an efficient organization or employee?
A) operating a hospital at the lowest possible cost while achieving higher output
B) being the most pleasant real estate broker in Toronto
C) being a telemarketer who makes the required number of calls each day
D) being a sales person who acquires the most clients of anyone in the company
E) being an instructor who teaches larger classes than other instructors
Page Ref: 24
Skill: Applied
SCENARIO 1-1 Allison and Gail are both university students studying for a final exam in OB. Both students have a goal of making a grade of 90% or better despite the time pressures they face. Gail studied diligently for six hours and made a grade of 92%. Allison studied diligently for nine hours and also made a grade of 92%.
35) Which of the students was effective?
A) only Gail
B) only Allison
C) neither Gail or Allison
D) both Gail and Allison
E) It is impossible to tell from the information given.
Page Ref: 24
Skill: Applied
36) Which of the following statements is most accurate?
A) Gail is more efficient than Allison.
B) Allison is more efficient than Gail.
C) Gail is more effective than Allison.
D) Allison is more effective than Gail.
E) It is impossible to predict efficiency or effectiveness in this case.
Page Ref: 24
Skill: Applied
37) Gail appears to be the more productive student because
A) her efficiency seemed to be better than Allison's.
B) her effectiveness seemed to be better than Allison's.
C) her IQ is higher than Allison's.
D) Allison didn't seem to think that time is an important factor.
E) It is impossible to tell from the information given.
Page Ref: 24
Skill: Applied
38) If today's managers positively address and manage the complex virtual workplace, which of the following increases?
A) employee turnover
B) miscommunications
C) interpersonal conflicts
D) employee well-being
E) employee burnout
Page Ref: 19
Skill: Applied
Topic: Challenges and Opportunities
Objective: 6
SCENARIO 1-2 Sheena Black, manager of operations at New Age Manufacturing and Services Inc., is facing the challenge of keeping the company's manufacturing operations profitable while keeping costs down and employees satisfied with their jobs. Over the years, Sheena has developed a leadership style that she calls a "walk-about" manager—she spends time on the plant floor observing and assisting employees and other managers as necessary. She has also adopted a series of contingency plans to guide problem solving in unusual situations.Sheena Black knows that her organization's success is dependent upon understanding the various disciplines which have contributed to the field of organizational behaviour. She knows that the next several years will require some major changes not only in the technology used by the company, but in the establishment of programs and initiatives to assist other managers and employees in overcoming workplace challenges. Sheena has identified the following priorities she will need to address:- Empowering employees to enable them to assume greater responsibility and share decision making; - Facilitating an improved climate of quality and excellence to challenge competitors in the marketplace; - Developing a new style of leadership and management which will value diversity and respect individuals in a supportive type of environment; and- Carefully examining the whole realm of working conditions and devising strategies to create better job satisfaction and keep employee loyalty.Sheena is also aware that training must become a major focus so that employees can develop new skills and managers can learn new ways of dealing with the problems of combining technology and human effort.
39) William Smith, Sheena's boss, suggested that Sheena examine employee turnover and the effects and costs of turnover to the company. Upon careful examination of the financial records in her department, Sheena noted that the following was a major cost
A) design and development of new evaluation forms.
B) orientation programs for new employees.
C) resistance to new employees by the HR department.
D) recruitment, selection and training of new employees.
E) resentment of new employees by existing employees.
Page Ref: 23
Skill: Applied
40) Sheena decided to improve company effectiveness by increasing employee job satisfaction. Sheena can accomplish this by encouraging her managers to
A) downsize and layoff staff.
B) add new rules and regulations to govern employee behaviour.
C) emphasize to employees that efficiency and profitability are the only goals.
D) increase the use of technology.
E) developing positive social relationships with each employee.
Page Ref: 6
Skill: Applied
Topic: Challenges and Opportunities
Objective: 6
41) As Sheena worked to develop a practical approach to the identified priorities, her frustration began to increase. She discovered that different managers had different views about how technology should be added in to the company processes. Organizational Behaviour would explain these different opinions as challenges
A) of globalization.
B) of behaving ethically.
C) at the individual and group input level.
D) at the individual input level.
E) at the group input level.
Page Ref: 21
Skill: Applied
Topic: Challenges and Opportunities
Objective: 6
42) Why do organizations that have OCB outperform those that do not?
A) OCB promotes the effective functioning of the organization.
B) OCB employees are easier to supervise.
C) OCB increases job satisfaction, increasing productivity.
D) OCB decreases recruitment, selection and training, because turnover is less.
E) OCB is rewarded by increased opportunities for promotions.
Page Ref: 22
Skill: Applied
43) The OB subject of "motivation" has been most influenced by which behavioural science discipline?
A) psychology
B) social psychology
C) sociology
D) political science
E) anthropology
Page Ref: 7
Skill: Recall
Topic: Building Blocks of OB
Objective: 3
44) Which behavioural science discipline contributes to OB's understanding of group decision-making processes?
A) anthropology
B) psychology
C) social psychology
D) sociology
E) political science
Page Ref: 7
Skill: Recall
Topic: Building Blocks of OB
Objective: 3
SCENARIO 1-3 You are an OB specialist at XYZ University and have been charged with the task of bringing together faculty from different behavioural disciplines to author a new textbook in organizational behaviour. You have faculty from the fields of psychology, sociology, social psychology, anthropology, and political science. The key tasks here are to consider the various ideas and structure them in such a manner as to provide a clear and plausible description of organizational behaviour and how it applies to the work environment.
45) You should expect that the faculty member from which field will probably contribute information about inter-group behaviour?
A) sociology
B) psychology
C) social psychology
D) anthropology
E) political science
Page Ref: 7
Skill: Applied
Topic: Building Blocks of OB
Objective: 3
46) Information on which of the following would be a contribution from the faculty member from psychology?
A) conflict
B) power
C) perception and learning
D) intra-organizational politics
E) political environment
Page Ref: 7
Skill: Applied
Topic: Building Blocks of OB
Objective: 3
47) Who would you expect to address issues of communication?
A) the psychologist
B) the anthropologist
C) the political scientist
D) the social psychologist
E) the sociologist
Page Ref: 7
Skill: Applied
Topic: Building Blocks of OB
Objective: 3
48) One of the major considerations which will need to be clearly portrayed is that
A) organizational behaviour is an applied behavioural science.
B) organizational behaviour is largely theoretical and difficult to apply to the real world.
C) leadership cannot be readily studied or understood through organizational behaviour.
D) relationships between leadership and decision making are not clear.
E) organizational behaviour is based largely upon an intuitive approach.
Page Ref: 7
Skill: Applied
Topic: Building Blocks of OB
Objective: 3
49) The most significant contributions to OB with respect to implementing change and reducing barriers to its acceptance has been made by
A) psychology.
B) sociology.
C) social psychology.
D) political science.
E) anthropology.
Page Ref: 7
Skill: Recall
Topic: Building Blocks of OB
Objective: 3
50) The OB subject of "organizational culture" has been most influenced by which behavioural science discipline?
A) anthropology
B) psychology
C) social psychology
D) political science
E) sociology
Page Ref: 7
Skill: Recall
Topic: Building Blocks of OB
Objective: 3
51) The OB subject of "power" has been most influenced by which behavioural science discipline?
A) psychology
B) social psychology
C) anthropology
D) political science
E) sociology
Page Ref: 7
Skill: Recall
Topic: Building Blocks of OB
Objective: 3
52) From which of the following behavioural sciences has the study of "people's influence on one another"?
A) anthropology
B) social psychology
C) psychology
D) political science
E) sociology
Page Ref: 7
Skill: Recall
Topic: Building Blocks of OB
Objective: 3
53) A major theme underlying the process of organizational behaviour is the belief that human behaviour is
A) opaque.
B) instinctual.
C) unpredictable.
D) intuitive.
E) knowable.
Page Ref: 8
Skill: Recall
Topic: Building Blocks of OB
Objective: 3
54) If we understand the written and unwritten rules in a structured situation then human behaviour becomes
A) predictable.
B) predetermined.
C) manageable.
D) controllable.
E) unpredictable.
Page Ref: 9
Skill: Recall
Topic: Building Blocks of OB
Objective: 3
55) Predictability of behaviour is increased if we know
A) that the person is rational.
B) how the person perceives the situation.
C) that behaviour is caused.
D) the person's age.
E) the person's level of education.
Page Ref: 10
Skill: Recall
Topic: Building Blocks of OB
Objective: 3
56) Generally, the best method for obtaining knowledge regarding human behaviour is the
A) common sense approach.
B) observational approach.
C) systematic approach.
D) theoretical approach.
E) intuitive approach.
Page Ref: 10
Skill: Recall
Topic: Systematic Studies
Objective: 4
57) The systematic approach to the study of OB is based on
A) fundamental consistencies.
B) common sense.
C) unstructured observation.
D) gut feelings.
E) predictability.
Page Ref: 10
Skill: Recall
Topic: Systematic Studies
Objective: 4
58) In the study of OB, common sense is generally replaced by
A) systematic study.
B) generalization.
C) listening.
D) prediction.
E) unstructured observation.
Page Ref: 10
Skill: Recall
Topic: Systematic Studies
Objective: 4
59) Amongst the research methods in OB, which would most likely employ the statistics of many different studies?
A) laboratory studies
B) meta-analysis
C) field studies
D) survey studies
E) case studies
Page Ref: 10
Skill: Recall
Topic: Systematic Studies
Objective: 4
60) When we say that OB concepts must reflect situational conditions, we mean
A) behaviour can never be predicted.
B) predicting certain behaviour depends on the context of a structured situation.
C) predicting certain behaviour depends on intuition.
D) regular and unchanging conditions.
E) only certain conditions can be predicted.
Page Ref: 12
Skill: Recall
Topic: OB has Few Absolutes
Objective: 5
61) You are working as an assistant to an OB specialist doing research to determine relationships between certain variables and fundamental consistencies. The specialist is attempting to determine when people are motivated by pay or salary, and when they are motivated by recognition, support and encouragement. By examining the connection between rewards and incentives and motivation under various conditions, the specialist appears to be using which of the following approaches in research?
A) open-systems
B) systematic study
C) human resources approach
D) observational
E) scientific management
Page Ref: 10
Skill: Applied
Topic: Systematic Studies
Objective: 4
62) Among the research methods in OB, which would most likely employ questionnaires and interviews?
A) case studies
B) meta-analysis
C) survey studies
D) field studies
E) laboratory studies
Page Ref: 10
Skill: Recall
Topic: Systematic Studies
Objective: 4
SCENARIO 1-4 An operations manager at a local distribution and supply warehouse wants to learn more about the major determinants of productivity, absenteeism, turnover and job satisfaction within her department. Although many options are available in gathering this information, she has decided to focus on individual-level, group-level and organization systems-level variables.
63) One of the individual level processes the operations manager will probably consider is
A) communication patterns.
B) perception.
C) levels of conflict.
D) human resource policies.
E) conflict resolution.
Page Ref: 7
Skill: Applied
64) Motivation is an important ________ process.
A) group level
B) organizational level
C) individual level
D) industry level
E) departmental level
Page Ref: 21
Skill: Applied
65) Negotiation, conflict, power and politics are ________ processes.
A) group level
B) organizational level
C) individual level
D) industry level
E) departmental level
Page Ref: 21
Skill: Applied
66) Individual level processes that have been shown to affect group and organizational behaviour include
A) technology.
B) organizational culture.
C) perception.
D) human resource policy.
E) group behaviour.
Page Ref: 21
Skill: Recall
67) OB looks at three basic levels of inputs. The group level includes the following
A) group structure, groups roles and values.
B) organizational structure, roles and team responsibilities.
C) organizational culture, team responsibilities and values.
D) team responsibilities, group structure and groups roles.
E) organizational structure and group structure.
Page Ref: 21
Skill: Recall
68) The behavioural science which underlies conflict and power is known as
A) psychology.
B) sociology.
C) social psychology.
D) anthropology.
E) political science.
Page Ref: 7
Skill: Recall
Topic: Building Blocks of OB
Objective: 3
69) Organizational behaviour has implications for all personnel in the workplace. Some of OB's challenges and opportunities include all of the following EXCEPT
A) it acknowledges employees are forces of innovation and change.
B) it offers specific insights to improve interpersonal and people skills.
C) it helps us learn to balance the relationship between efficiency of resources with effectiveness of delivery.
D) it facilitates the improvement of quality and employee productivity.
E) it reinforces the importance of traditional methods of management.
Page Ref: 13-17
Skill: Recall
Topic: Challenges and Opportunities
Objective: 6
70) The behavioural science that underlies work design and performance appraisal is known as
A) sociology.
B) psychology.
C) social psychology.
D) anthropology.
E) political science.
Page Ref: 7
Skill: Recall
Topic: Building Blocks of OB
Objective: 3
71) The behavioural science that underlies communication and inter-group behaviour is known as
A) psychology.
B) sociology.
C) social psychology.
D) anthropology.
E) political science.
Page Ref: 8
Skill: Recall
Topic: Building Blocks of OB
Objective: 3
72) Basing managerial decisions on the best available scientific evidence is called
A) behavioural decision-making.
B) mechanistic decision-making.
C) organic decision-making.
D) evidence-based management.
E) field study management.
Page Ref: 22
Skill: Recall
Topic: Systematic Studies
Objective: 4
73) The behavioural science that underlies organizational culture is known as
A) psychology.
B) sociology.
C) social psychology.
D) anthropology.
E) political science.
Page Ref: 7
Skill: Recall
Topic: Building Blocks of OB
Objective: 3
74) In OB, looking at relationships, attempting to attribute causes and effects, and basing conclusions on scientific evidence is referred to as
A) a contingency approach.
B) an absolute approach.
C) a consistency approach.
D) systematic study.
E) intense scrutiny.
Page Ref: 9,10
Skill: Recall
Topic: Systematic Studies
Objective: 4
75) Considering behaviour within the context in which it occurs is known as the ________ approach.
A) absolute
B) rational
C) fundamental consistency
D) empowerment
E) behavioural
Page Ref: 10
Skill: Recall
Topic: Systematic Studies
Objective: 4
76) Looking in-depth at and individual over time in order to gain insight relates to the examination of
A) case studies.
B) laboratory studies.
C) survey studies.
D) meta-analysis.
E) field studies.
Page Ref: 11
Skill: Recall
Topic: Systematic Studies
Objective: 4
77) Organization behaviour has few
A) theories.
B) contingencies.
C) models.
D) absolutes.
E) field studies.
Page Ref: 12
Skill: Recall
Topic: OB has Few Absolutes
Objective: 5
78) By putting people first, it is thought that employees will become more effective and hence more productive. What are some of the challenges inherent in putting people first?
A) initial loss in production
B) cultural confusion
C) blurring of lines between management and labour
D) balancing cultural sensitivity with the bottom line
E) incompatibility between differing cultural backgrounds
Page Ref: 10
Skill: Recall
Topic: Challenges and Opportunities
Objective: 6
79) A major outcome of workforce diversity is
A) re-engineering the workplace.
B) establishing new programs of TQM.
C) developing new styles of leadership.
D) developing ways of more effectively controlling work.
E) accommodating different life and work styles while maintaining productivity.
Page Ref: 17
Skill: Recall
Topic: Challenges and Opportunities
Objective: 6
80) Which of the following aspects is contingency approach concerned with?
A) common goals
B) similarities between people
C) context
D) co-ordinating differences
E) continuous learning
Page Ref: 12
Skill: Recall
Topic: OB has Few Absolutes
Objective: 5
81) During difficult financial times, company focus moves to helping employees
A) maintain job satisfaction.
B) retain motivation.
C) create reward balance.
D) manage stress.
E) behave ethically on the job.
Page Ref: 15
Skill: Recall
Topic: Challenges and Opportunities
Objective: 6
82) Members of groups must contend with various challenges on the job. A cohesive group is likely to
A) understand management and act to their wishes.
B) accept new people willingly.
C) develop rigid rules to support outsiders.
D) trust and work together by identifying common goals.
E) work with others from different cultures.
Page Ref: 10,11
Skill: Applied
83) When employees use withdrawal behaviours this threatens survival, an outcome at the
A) individual level.
B) group level.
C) competition level.
D) industry level.
E) organizational level.
Page Ref: 22
Skill: Applied
84) Amongst the research methods in OB, which employs simulated and controlled settings?
A) surveys
B) meta-analyses
C) field studies
D) case studies
E) laboratory studies
Page Ref: 10
Skill: Recall
Topic: Systematic Studies
Objective: 4
1.3 Essay Questions
1) Define the concept of an organization and briefly describe the characteristics of an organization.
Answer: Suggested answer:
- organization is consciously coordinated social unit
- two or more people functioning on relatively continuous basis
- achieve common goals; service-oriented or manufacturing-oriented
- large or small private firms; large or small public organization- can be unionized or non-unionized; publicly traded or privately held
- managers may own shares in a private firm; operate in profit or non-profit sectors(Examples can be drawn from text, class discussion, Internet, newspapers such as Globe and Mail, etc.)
Type: ES Page Ref: 4
Skill: Recall
Topic: Defining Organizational Behaviour
Objective: 1
2) List and describe some of the issues the Canadian workplace must address as it moves into the next decade. Provide examples to support your response.
Answer: Suggested answer:
- Economic Pressures
- Global competition
- Workforce diversity
- Improving customer service, people skills
-Enhancing employee well-being
- Job satisfaction and behaving ethically(Examples can be drawn from text, class discussion, Internet, newspapers such as Globe and Mail, etc.)
Type: ES Page Ref: 13-21
Skill: Applied
Topic: Challenges and Opportunities
Objective: 6
3) List the particular issues that challenge organizations today at the individual level.
Answer: - attitudes and stress- task performance- citizenship behaviour- withdrawal behaviour
Type: ES Page Ref: 21,22
Skill: Applied
4) How does employee withdrawal challenge organizational survival? Provide examples to support your response.
Answer: Suggested answer:
- organizations need highly skilled labour and provide specific training to grow employees
- withdrawal can be lateness, absenteeism or turnover, all of which lessen efficiency and effectiveness(Examples can be drawn from text, class discussion, Internet, newspapers such as Globe and Mail, etc.)
Type: ES Page Ref: 23
Skill: Applied
5) Organizational behaviour is an applied behavioural science built upon contributions from a number of different disciplines. What are these disciplines and what are the contributions of each discipline? Be complete in your response and include four different behavioural science disciplines.
Answer: Suggested answer:
- psychology
- social psychology
- sociology
- anthropology(Examples can be drawn from text, class discussion, Internet, newspapers such as Globe and Mail, etc.)
Type: ES Page Ref: 7
Skill: Applied
Topic: Building Blocks of OB
Objective: 3
6) Having a broad range of interpersonal skills upon which to draw makes us more effective organizational participants. What kinds of interpersonal skills do we need in today's workplace? Provide examples to illustrate your points. (You may want to refer to the Competing Values Framework Model as the basis for your answer).
Answer: Suggested answer:
- interpersonal skills or people skills defined- how they impact the workplace in social relationships
- creating pleasant workplaces(Examples can be drawn from text, class discussion, Internet, newspapers such as Globe and Mail, etc.)
Type: ES Page Ref: 6,7
Skill: Applied
Topic: Interpersonal Skills
Chapter 2 Perception, Personality, and Emotions
2.1 Multiple-Choice Questions
1) A process by which individuals organize and interpret their impressions in order to give meaning to their environment is called
A) interpretation.
B) environmental analysis.
C) perception.
D) outlook.
E) environmental impact.
Page Ref: 38
Skill: Recall
Topic: Perception
Objective: 1
2) Stan left Kerry a voicemail message indicating that he wanted to see her right away. He wanted to commend her for her good work on a recent project, but because he said he wanted to see her right away, she thought that she was in trouble. Kerry's interpretation of his message is known as her
A) personality.
B) feelings.
C) perception.
D) viewpoint.
E) concern.
Page Ref: 38
Skill: Applied
Topic: Perception
Objective: 1
3) If two people see the same thing at the same time yet interpret it differently, the factors that shape their dissimilar perceptions reside in
A) the target being perceived.
B) the timing.
C) the context of the situation in which the perception is made.
D) the perceiver.
E) environmental influences.
Page Ref: 38
Skill: Recall
Topic: Perception
Objective: 1
4) Tom was aware that Jonas did not always interpret his messages in the way that they were intended. In this perception situation, Jonas is the
A) target.
B) perceiver.
C) prophesizer.
D) emoter.
E) superior.
Page Ref: 39
Skill: Applied
Topic: Perception
Objective: 1
5) Which of the following is TRUE about our perceptions of a target?
A) Individual perception varies little between different cultures.
B) Expectations do not distort individual perception.
C) Motion, sounds, and size of a target have little affect in how individuals perceive it.
D) Targets are usually perceived in isolation.
E) Timing of events and the situation in which a target is encountered may impact our perception.
Page Ref: 39
Skill: Recall
Topic: Perception
Objective: 1
6) The theory that tries to explain how we judge people differently, depending upon the meaning we assign to a given behaviour, is
A) behavioural theory.
B) judgmental theory.
C) equity theory.
D) attribution theory.
E) situational theory.
Page Ref: 39
Skill: Recall
Topic: Attribution Theory
7) In attribution theory, internally caused behaviours are
A) those believed to be under the personal control of the individual.
B) derived from personality traits.
C) controlled by external factors.
D) usually negative behaviours.
E) outside forces and influences.
Page Ref: 40
Skill: Recall
Topic: Attribution Theory
8) What are the three rules about behaviour that attribution theory relies on?
A) distinctiveness, resemblance, and consistency
B) resemblance, consensus and consistency
C) deviation, distinctiveness, and consistency
D) consistency, consensus and distinctiveness
E) context, consensus and distinctiveness
Page Ref: 39,40
Skill: Recall
Topic: Attribution Theory
9) When individuals observe behaviour, they attempt to determine whether it is internally or externally caused. This is generally referred to as
A) fundamental attribution error.
B) self-serving bias.
C) attribution theory.
D) selective behaviour theory.
E) perception theory.
Page Ref: 40
Skill: Recall
Topic: Attribution Theory
10) When an individual displays different behaviours in different situations, this is termed
A) continuity.
B) integrity.
C) distinctiveness.
D) flexibility.
E) consensus.
Page Ref: 39
Skill: Recall
Topic: Attribution Theory
11) Behaviour that is observed as being different from the behaviour previously demonstrated, refers to
A) differentiation.
B) consistency.
C) consensus.
D) distinctiveness.
E) unanimity.
Page Ref: 40
Skill: Recall
Topic: Attribution Theory
12) If a person appears to respond the same way over time, attribution theory states that the behaviour shows
A) distinctiveness.
B) consensus.
C) consistency.
D) continuity.
E) reliability.
Page Ref: 40
Skill: Recall
Topic: Attribution Theory
SCENARIO 2-1 You have hired a 55-year-old employee who has successfully worked in large firms. Your company is a small, closely-knit organization with many young employees; most do not have as much work experience as this newcomer. You have prided yourself on being flexible with your employees and being open to their needs. They requested an informal dress code for Fridays and you adopted this policy four months ago.
13) You should expect that your new employee
A) will be excited by the new dress code.
B) will perceive the dress code in the same way as the other employees.
C) may have a different perception of the dress code because of differences in the target.
D) may have a different perception of the dress code because of differing past experiences.
E) will ignore the new dress code.
Page Ref: 38
Skill: Applied
Topic: Perception
Objective: 1
14) You may discover your younger employees believe the older employee to be rigid and intolerant of various behaviours and values. This is due to their
A) expectations.
B) motives.
C) targets.
D) situations.
E) interests.
Page Ref: 38
Skill: Applied
Topic: Perception
Objective: 1
15) The factor in the situation that may cause your younger employees perceptions to be different is
A) novelty.
B) attitudes.
C) social setting.
D) genetics.
E) heredity.
Page Ref: 38
Skill: Applied
Topic: Perception
Objective: 1
16) According to attribution theory, the more consistent the behaviour of another person is, the more the observer is inclined to
A) depend on the behaviour.
B) attribute it to internal causes.
C) attribute it to consensus.
D) attribute it to external causes.
E) attribute it to the environment.
Page Ref: 40
Skill: Recall
Topic: Attribution Theory
17) Suppose a sales manager is unhappy with the performance of her sales people and attributes this to laziness on their part. Closer scrutiny of the real situation, however, shows that the sales manager has made a "fundamental attribution error." This means that she has
A) only attended to superficial indicators.
B) inadequately explored the job satisfaction of the sales people.
C) merely stereotyped employees.
D) underestimated the effects of external factors relative to internal factors.
E) ignored her responsibility in the entire process of not holding workers accountable.
Page Ref: 40
Skill: Applied
Topic: Attribution Theory
18) How does selective perception work as a shortcut in judging other people?
A) Bits and pieces of what we observe are chosen randomly.
B) Bits and pieces of what we observe are selectively chosen according to our interests and background.
C) Such observations allow us to arrive at warranted judgments quickly.
D) It allows us to "speed-read" without the risk of inaccurate conclusions.
E) Bits and pieces of what we observe allow us to judge people with complete accuracy.
Page Ref: 41
Skill: Recall
Topic: Attribution Theory
19) Which of the following is considered to be outside the shortcuts we utilize in judging others?
A) stereotyping
B) halo effect
C) projection
D) self-serving bias
E) contrast effects
Page Ref: 41
Skill: Recall
Topic: Attribution Theory
20) There are many examples of shortcuts we make in judging others. Which shortcut below is least likely to be an error in perception about a new employee named Jo?
A) using "high intelligence" of Jo to make a general impression about Jo's effectiveness on the job
B) using my ability to respond to individual differences between Jo and myself
C) letting my own attitudes and interests influence my impression of Jo
D) deciding that Jo wants challenge and change since that's what I want
E) knowing how good Jo will be because Jo has the same degree I have
Page Ref: 38-43
Skill: Applied
Topic: Attribution Theory
SCENARIO 2-2 Work on your team is difficult because of the other two individuals. The work has been divided among the three of you, but each time your team meets Janet and Jim disagree about the progress that the team has made on the project. Janet is convinced that Jim's lack of progress is because he is inherently lazy and not because some information is still not available to him because Janet has not completed some of her work according to the schedule she agreed to. The truth seems to be that Janet is not doing her part of the work.
21) You might attempt to understand Janet and Jim by using ________ theory.
A) social relevance
B) attribution
C) optimizing
D) satisficing
E) perception
Page Ref: 39
Skill: Applied
Topic: Attribution Theory
22) Janet seems to be guilty of
A) proximity bias.
B) ethnocentrism.
C) fundamental attribution error.
D) self-serving bias.
E) selective perception.
Page Ref: 40
Skill: Applied
Topic: Attribution Theory
23) Janet may be attributing to Jim some of her own characteristics. She might exhibiting
A) projection.
B) the halo effect.
C) contrast effect.
D) stereotyping.
E) selective perception.
Page Ref: 43
Skill: Applied
Topic: Attribution Theory
24) You have decided after consultation with your manager that the problem between Janet and Jim must be solved; somehow Janet must be made aware of the impact of her work not being completed within the required timeline. In order to resolve the situation and maintain as much objectivity as possible, you want to create a response that avoids
A) selective perception and stereotyping.
B) a problem solving approach.
C) communication with both Janet and Jim.
D) assigning responsibility for future behaviour.
E) acting in a leadership capacity.
Page Ref: 41-45
Skill: Applied
Topic: Attribution Theory
25) The perception shortcut that involves evaluation of a person based on how they compare to other individuals recently encountered.
A) selective perception
B) contrast effects
C) halo effect
D) prejudice
E) projection
Page Ref: 43
Skill: Recall
Topic: Attribution Theory
26) The unfounded belief that younger workers are more appealing than older workers is an example of
A) the halo effect.
B) contrast effects.
C) projection.
D) prejudice.
E) stereotyping.
Page Ref: 45
Skill: Recall
Topic: Attribution Theory
27) When a person stereotypes another person, the individual is making generalizations based upon
A) a predefined group to which the other person belongs.
B) a key strength of the other person.
C) a key weakness of the other person.
D) the values of the other person.
E) the speaking style of the other person.
Page Ref: 44
Skill: Recall
Topic: Attribution Theory
28) ________ generally starts with stereotypes and then has negative emotional content added.
A) Contrast effects
B) The halo effect
C) Prejudice
D) Projection
E) Attribution error
Page Ref: 45
Skill: Recall
Topic: Attribution Theory
29) Because Northern Beverages wants to expand and grow, the HR Manager knows she needs to hire an individual who is skilled in business strategy. She believes that university graduates who participated extensively in athletics are ambitious and hard working, compared to university students who did not. When she interviews university grads that were athletes, she is likely to engage in
A) projection.
B) stereotyping.
C) contrast effect.
D) risk management.
E) halo effect.
Page Ref: 44
Skill: Applied
Topic: Attribution Theory
SCENARIO 2-3 Students in your class are making oral presentations as the final part of a project they have been working on for the past few months. You know from courses you have taken and from discussions with peers that there are perception shortcuts used when judging others. You are now wondering if your instructor will use any of these.
30) Jennifer has previously made two excellent presentations. The one she completed today is not as good as her first two, yet she still receives the same high grade. Which statement best explains the perception error the instructor may have made when evaluating Jennifer?
A) The contrast effect is distorting the instructor's perception.
B) The halo effect is operating.
C) The instructor has stereotyped Jennifer.
D) The instructor is projecting that Jennifer is an "A" student.
E) The instructor is engaged in selective perception.
Page Ref: 43
Skill: Applied
Topic: Attribution Theory
31) Allison has just completed a very good presentation. You are afraid that the ________ will operate and you will be perceived less favorably than if you had presented before her.
A) stereotyping effect
B) halo effect
C) contrast effect
D) projection effect
E) selective perception
Page Ref: 43
Skill: Applied
Topic: Attribution Theory
32) You have heard that the instructor believes men perform better in oral presentations than women. If this is TRUE, the instructor's perception shortcut is
A) halo effect.
B) contrast effect.
C) projection.
D) stereotyping.
E) selective perception.
Page Ref: 44
Skill: Applied
Topic: Attribution Theory
33) Sally is normally a very calm and composed manager, but the other day she raised her voice on the telephone. When staff heard her angry tone they tried to figure out why she was upset. This is an example of
A) the halo effect.
B) contrast effects.
C) projection.
D) stereotyping.
E) attribution theory.
Page Ref: 39
Skill: Applied
Topic: Attribution Theory
34) When a fire truck's siren was heard, everyone ran to the window to see what was happening. That everyone responded in the same way is an example of which aspect of Attribution Theory?
A) consistency
B) consensus
C) distinctiveness
D) selective perception
E) contrast effects
Page Ref: 40
Skill: Applied
Topic: Attribution Theory
35) John usually responds positively when asked to do something, but recently his boss has noticed that he was does not seem as enthusiastic and positive when requests are made of him. Which aspect of Attribution Theory does this observation relate to?
A) consensus
B) distinctiveness
C) consistency
D) selective perception
E) contrast effects
Page Ref: 40
Skill: Applied
Topic: Attribution Theory
36) The tendency to underestimate the influence of external factors and overestimate the influence of internal factors when making judgments about the behaviour of others is known as
A) distinctiveness.
B) fundamental attribution error.
C) selective perception.
D) self-serving bias.
E) halo effect.
Page Ref: 41
Skill: Recall
Topic: Attribution Theory
37) Terry is a good communicator, and those who know this assume she is very competent at her job. This is an example of
A) selective perception.
B) the halo effect.
C) contrast effects.
D) projection.
E) consensus.
Page Ref: 43
Skill: Applied
Topic: Attribution Theory
38) When Carrie drove up in her new car, Ken told her that she had made a mistake. Even though the car was very sporty, easy on gas, and had lots of trunk space, he ignored these attributes and told her it would need to be repaired frequently. He said this because he had previously owned the same car, and that was his experience. This is an example of
A) the halo effect.
B) contrast effects.
C) projection.
D) selective perception.
E) stereotyping.
Page Ref: 41
Skill: Applied
Topic: Attribution Theory
39) Sidney generally had a negative view of company competitors, and felt that everyone he worked with had a similar view. This is an example of
A) the halo effect.
B) contrast effects.
C) projection.
D) selective perception.
E) stereotyping.
Page Ref: 41
Skill: Applied
Topic: Attribution Theory
40) The tendency for individuals to attribute their own successes to internal factors while putting the blame for failures on external factors is called
A) the halo effect.
B) projection.
C) stereotyping.
D) self-serving bias.
E) contrast effects.
Page Ref: 41
Skill: Recall
Topic: Attribution Theory
41) When Jose passed the new employee's office, he was reminded of Tina, the manager of the sales department; Jose noticed that both seemed to have messy desks with lots of papers piled on them. This is an example of
A) the halo effect.
B) contrast effects.
C) projection.
D) selective perception.
E) stereotyping.
Page Ref: 43
Skill: Applied
Topic: Attribution Theory
42) Judging someone on the basis of one's perception of the group to which that person belongs is known as
A) projection.
B) the halo effect.
C) stereotyping.
D) selective perception.
E) contrast effects.
Page Ref: 44
Skill: Recall
Topic: Attribution Theory
43) Self-fulfilling prophecy is a concept that proposes a person will behave
A) in ways inconsistent with how he or she is perceived by others.
B) in ways that are similar to self-interest.
C) in ways consistent with how he or she is perceived by others.
D) in ways that are dissimilar to self-interest.
E) in ways consistent with how he or she perceives him-/herself.
Page Ref: 46
Skill: Recall
Topic: Attribution Theory
44) Gillian was very upset that others perceived her as lazy. This bothered her so much that she began to neglect her work responsibilities and began to spend most of her time surfing the Internet. This is an example of
A) the halo effect.
B) contrast effects.
C) stereotyping.
D) selective perception.
E) self-fulfilling prophecy.
Page Ref: 46
Skill: Applied
Topic: Attribution Theory
45) A trait, which is NOT inherited, is
A) muscle composition and reflexes.
B) energy level.
C) cultural norms.
D) psychological makeup.
E) gender.
Page Ref: 47
Skill: Recall
Topic: Personality
Objective: 3
46) An environmental factor that might influence personality is
A) parents' height.
B) school experience.
C) gender.
D) muscle coordination.
E) sense of smell.
Page Ref: 47
Skill: Recall
Topic: Personality
Objective: 3
47) If co-workers know that you are relaxed at home but become tense and anxious at work, they are attributing your behaviour to which of the following?
A) heredity
B) environmental factors
C) situational conditions
D) locus of control
E) projection
Page Ref: 47
Skill: Applied
Topic: Personality
Objective: 3
48) What are personality traits?
A) enduring characteristics that describe an individual's behaviour.
B) fleeting characteristics that describe an individual's behaviour.
C) individual characteristics that are based solely on heredity.
D) individual characteristics that are based solely on situational conditions.
E) individual characteristics that are based solely on environmental factors.
Page Ref: 48
Skill: Recall
Topic: Personality
Objective: 3
49) A term that best describes an extraverted, sensing, thinking, judging person is
A) quiet.
B) domineering.
C) reserved.
D) organized.
E) visionary.
Page Ref: 49
Skill: Recall
Topic: MBTI
Objective: 4
SCENARIO 2-4 Sally is assembling a team to work on a long-term project requiring creativity, stamina, and farsightedness. This project is important for the future growth of Sally's organization and she recognizes that she must succeed. Sally is in the process of selecting individuals who will significantly contribute to the project. The only information available to Sally is the Myers-Briggs type of each individual. Sally must use her knowledge of the four basic characteristics of each person to choose individuals appropriate for various roles.
50) Sally needs to choose a lead person for the team. This person must have vision, be creative and energetic as it will take great drive to complete the project on time. Sally will probably pick
A) ENTP.
B) INTJ.
C) ENFP.
D) ISFP.
E) STPE.
Page Ref: 49
Skill: Applied
Topic: MBTI
Objective: 4
51) Sally is also looking for an organized person who will be practical and realistic about timelines and budgets. She will probably pick
A) ESTJ.
B) ENTP.
C) ISFP.
D) STPE.
E) INTJ.
Page Ref: 49
Skill: Applied
Topic: MBTI
Objective: 4
52) Sally needs an individual who is innovative and individualistic to help push the project beyond the normal practices of the company. With strong leadership from others, she wants to find a person who will bring innovative ideas to the team. She will probably choose
A) STJE.
B) INTJ.
C) ENTP.
D) ESFJ.
E) ISFP.
Page Ref: 49
Skill: Applied
Topic: MBTI
Objective: 4
SCENARIO 2-5 You are the manager of a small retail store and have decided to apply the Big Five Model in order to understand your employees and their work habits.
53) Mike Jackson, one of your newest employees, is an extravert. Which of the following statements best describes Mike at work?
A) Mike will find music and noise distracting in the workplace.
B) Mike will be gregarious and can stay engaged with customers for long periods of time.
C) Mike is will engage with customers when they approach him, but otherwise will focus quietly on his work.
D) Mike will be comfortable working alone for long periods of time.
E) Mike be reserved and not easily express himself to others.
Page Ref: 49
Skill: Applied
Topic: Big Five Personality
Objective: 5
54) Jane Simpson rates low on conscientiousness. You should expect she would
A) be easily distracted.
B) find comfort in the familiar.
C) be nervous, depressed, and insecure.
D) be comfortable with solitude.
E) be achievement oriented.
Page Ref: 50
Skill: Applied
Topic: Big Five Personality
Objective: 5
55) Which of the five personality dimensions are probably most important in predicting the job performance of your employees?
A) extroversion
B) agreeableness
C) conscientiousness
D) emotional stability
E) openness to experience
Page Ref: 49
Skill: Applied
Topic: Big Five Personality
Objective: 5
56) People who show initiative and persevere are
A) high extroversion.
B) proactive personality.
C) type A personality.
D) high propensity for risk-taking.
E) type B personality.
Page Ref: 57
Skill: Recall
Topic: Big Five Personality
Objective: 6
57) Individuals who rate high in self-monitoring
A) adjust behaviour to external, situational factors.
B) have lower absenteeism rates.
C) need higher levels of supervision.
D) are more involved on their jobs.
E) thrive in routine jobs.
Page Ref: 55
Skill: Recall
Topic: Big Five Personality
Objective: 6
58) Within the framework of the Big Five Personality Factors, openness to experience is a personality factor that describes the degree to which a person is
A) sociable, talkative, and assertive.
B) good natured, cooperative, and trusting.
C) creative, artistically sensitive, and flexible.
D) calm, self confident, and secure.
E) responsible, dependable, persistent, and achievement oriented.
Page Ref: 50
Skill: Recall
Topic: Big Five Personality
Objective: 5
59) Characteristics of individuals high in Machiavellianism include which of the following?
A) maintains emotional distance; highly authoritative; believes in swift discipline
B) impulsive; emotionally involved; has strong ethical beliefs
C) pragmatic; maintains emotional distance; believes ends can justify means
D) focuses most available time on people issues
E) develops a realistic and empathetic approach to dealing with employees
Page Ref: 53
Skill: Recall
Topic: Big Five Personality
Objective: 6
60) People with high narcissism
A) are less likely to adapt to new situations.
B) tend to be more self-centered and may enjoy their work more.
C) tend to be less satisfied with their work.
D) tend to be more committed to their organizations.
E) generally have lower expectations of success.
Page Ref: 54
Skill: Recall
Topic: Big Five Personality
Objective: 6
61) Within the framework of the Big Five Personality Factors, conscientiousness is a personality factor that describes the degree to which a person is
A) sociable, talkative, and assertive.
B) imaginative, artistically sensitive, and intellectual.
C) calm, self confident, and secure.
D) responsible, dependable, persistent, and achievement oriented.
E) good natured, cooperative, and trusting.
Page Ref: 50
Skill: Recall
Topic: Big Five Personality
Objective: 5
62) How would you describe an individual who believes the ends justify the means and maintains emotional distance in situations?
A) narcissist
B) psychopath
C) machiavellian
D) self-monitor
E) risk-taker
Page Ref: 55
Skill: Recall
Topic: Big Five Personality
Objective: 6
63) People who score high in psychopathy tend to
A) display their true dispositions and attitudes in every situation.
B) believe they control what happens to them.
C) lack remorse of guilt when they have caused others harm.
D) be persuaded less by others.
E) measure success in terms of their acquisitions.
Page Ref: 55
Skill: Recall
Topic: Big Five Personality
Objective: 6
64) In which of the following occupations is a high risk-taking personality more suited?
A) accountant performing auditing activities
B) stock trader in a brokerage firm
C) computer systems expert working in security
D) marketing representative selling pharmaceuticals
E) retail sales, men's clothing
Page Ref: 55
Skill: Applied
Topic: Personality
65) Which of the following is TRUE of positive core self-evaluation?
A) They tend to be work slower and more thoughtfully.
B) They can play for fun and relaxation, rather than to exhibit superiority.
C) They tend to like themselves and feel in control of their environment.
D) They are less liked by others, because of their successes.
E) They don't suffer from a sense of time urgency and impatience.
Page Ref: 55,56
Skill: Recall
Topic: Big Five Personality
Objective: 6
66) Which of the following is a TRUE statement?
A) High self-monitors rarely vary their responses to specific challenges.
B) It is estimated that about 25% of the North American population are psychopaths.
C) There are common personality types for a given country.
D) We should expect that most successful salespersons age have high core self-evaluation.
E) Psychopaths are never successful in the workplace.
Page Ref: 56
Skill: Recall
Topic: Personality
67) Which of the following statements is TRUE of narcissists?
A) They feel less guilt and remorse when they harm others.
B) They alter their behaviour to reflect the external situation they are in.
C) They have poor long-term health outcomes.
D) They are low key and tend to keep emotional distance.
E) They are more likely to engage in self-promotion in social media.
Page Ref: 54
Skill: Recall
Topic: Big Five Personality
Objective: 6
68) A proactive personality
A) can identify opportunities, shows initiative, takes action, and perseveres until meaningful change occurs.
B) cannot identify opportunities, show initiative, take action, or persevere until meaningful change occurs.
C) has many behaviours that organizations find undesirable.
D) is most likely seen as a follower and likely to obstruct change within an organization.
E) is most likely to guard the status quo to achieve career success.
Page Ref: 57
Skill: Recall
Topic: Big Five Personality
Objective: 6
SCENARIO 2-6 Michael is angry that he was disciplined by his boss and demoted from produce clerk to the job of stocking shelves. He has not been greeting customers with a smile and friendly hello, although this is required in his job. He takes extra time collecting his supplies from the back of the warehouse, and then works quickly when working in the public areas of the store. He sometimes hides in the washroom during his shift to avoid talking to his boss.
69) Michael is
A) high in self-monitoring.
B) deep acting.
C) surface acting.
D) displaying emotional labour.
E) expressing felt emotions.
Page Ref: 60
Skill: Applied
Topic: Emotions and Moods
70) Michael shows employee deviance by
A) being angry.
B) taking extra time in the warehouse.
C) working quickly in the public areas of the store.
D) hiding from the boss in the washroom.
E) smiling at customers.
Page Ref: 64
Skill: Applied
Topic: Emotional Intelligence
Objective: 9
71) Michael's emotional intelligence is most likely
A) high.
B) low.
C) displayed.
D) felt.
E) appropriate.
Page Ref: 61
Skill: Applied
Topic: Emotional Intelligence
Objective: 9
72) The anger Michael feels toward his boss is
A) emotional labour.
B) emotional dissonance.
C) a mood.
D) an emotion.
E) a perception.
Page Ref: 58
Skill: Applied
Topic: Emotions and Moods
73) If a manager has high emotional intelligence he will likely engage in
A) projection.
B) stereotyping.
C) narcissism.
D) self-monitoring.
E) extroversion.
Page Ref: 61
Skill: Applied
Topic: Emotional Intelligence
Objective: 9
74) Diana is often referred to as a "people person" who is very outgoing and friendly. These characteristics are known as her
A) projections.
B) halo effects.
C) contrast effects.
D) selective perception.
E) personality traits.
Page Ref: 50
Skill: Applied
Topic: Big Five Personality
Objective: 5
75) Ken is a decisive person who prefers structured situations and likes to control his work environment. According to the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator, he is a
A) judging type.
B) organizing type.
C) feeling type.
D) extrovert type.
E) introvert type.
Page Ref: 49
Skill: Applied
Topic: MBTI
Objective: 3
76) Tonya is extremely talkative, sociable, and assertive. According to the Big Five Personality Model, this relates to her
A) agreeableness.
B) emotional stability.
C) conscientiousness.
D) extraversion.
E) openness to experience.
Page Ref: 49
Skill: Applied
Topic: Big Five Personality
Objective: 4
77) Eli is a very competent worker and he knows it. People find him to be extremely arrogant and he is considered to be someone that feels entitled to special treatment. If these perceptions are TRUE, they are examples of Eli's
A) emotions.
B) narcissism.
C) perceptions.
D) self-monitoring.
E) self-esteem.
Page Ref: 54
Skill: Applied
Topic: Big Five Personality
Objective: 6
78) Timothy thinks nothing of berating his staff in order to get them to meet deadline; when his staff meet the deadlines, it confirms to Timothy that he is right to behave this way. Timothy's personality likely includes
A) Machiavellianism.
B) perception.
C) agreeableness.
D) extraversion.
E) emotional intelligence.
Page Ref: 53
Skill: Applied
Topic: Big Five Personality
Objective: 5
79) A person uses emotional labour in the workplace when they express
A) their felt emotions.
B) agreeableness.
C) organizationally desired emotions.
D) narcissism.
E) emotional fluidity.
Page Ref: 59,60
Skill: Recall
Topic: Emotional Labour
Objective: 8
80) Samir is a self-proclaimed "hot head"; when he is angry with others, he communicates this by screaming at them. This is an example of Samir's
A) perception.
B) moods.
C) emotions.
D) self-esteem.
E) proactivity.
Page Ref: 58
Skill: Applied
Topic: Emotions and Moods
81) Ava never gives up; she persists in what she is trying to accomplish even when setbacks occur. This shows her
A) personality.
B) moods.
C) core self-evaluation.
D) emotional dissonance.
E) self-esteem.
Page Ref: 57
Skill: Applied
Topic: Big Five Personality
Objective: 6
82) Seymour is unhappy and often ill; he often looks sullen and withdrawn. When his boss asked him if he was unwell, Seymour indicated he feels fine. This is an example of
A) emotional intelligence.
B) emotional dissonance.
C) self-esteem.
D) Machiavellianism.
E) distress.
Page Ref: 59
Skill: Applied
Topic: Emotions and Moods
83) When an employee expresses organizationally desired emotions during interpersonal interactions, it is called
A) emotional intelligence.
B) moods.
C) emotional labour.
D) self-esteem.
E) emotional dissonance.
Page Ref: 59
Skill: Recall
Topic: Emotions
Objective: 3
84) Trying to modify one's TRUE inner feelings based on display rules is known as
A) emotional labour.
B) emotional dissonance.
C) deep acting.
D) surface acting.
E) self-awareness.
Page Ref: 60
Skill: Recall
Topic: Emotional Labour
Objective: 8
85) Hiding one's inner feelings and foregoing emotional expressions in response to display rules is known as
A) emotional labour.
B) emotional dissonance.
C) deep acting.
D) surface acting.
E) self-awareness.
Page Ref: 60
Skill: Recall
Topic: Emotional Labour
Objective: 8
2.3 Essay Questions
1) What factors reside in the perceiver, the target being perceived, or the context of the situation that operate to shape and sometimes distort perception?
Answer: Suggested answer:
- Attempts to interpret what is seen are influenced by personal characteristics of perceiver.
- Attitudes, motives, interests, past experiences shape the way we perceive.
- We often interpret others' behaviour based on our own behaviour.
- Personal expectations can distort perception.- Characteristics of target (e.g. volume, appearance, motion, sound, size), physical or time proximity of targets, and similarity of targets will influence what we perceive.
- Situational factors such as location, light, heat, events, work setting, social setting can influence perception.
Type: ES Page Ref: 38,39
Skill: Applied
Topic: Perception
Objective: 1
2) Imagine you are mentoring a new manager who is going to supervise a staff of twelve employees. In a short period of time you conclude this manager demonstrates many introvert characteristics: she listens carefully and takes her time composing her responses; she shuts the door to her office several times a day, asking staff not to interrupt her; she leaves the office at lunch time and walks in a nearby park by herself, saying she needs to "recharge." Discuss the introvert as a manager; what will challenge this personality in this job? what can you conclude this personality will be good at as a manager?
Answer: Suggested answer: Introvert strengths:
-good listeners; often can absorb large amounts of information for synthesis; more likely to know the opinions and thoughts of those around them
-able to work alone for periods of time, which many managers need to do.
introvert challenges:
-lose energy when interacting with others and in high pace environments, so need to pace themselves
-quiet nature may make individual find conflict challenging and draining
-introvert/extrovert are not absolutes but a range on the scale, so all introverts will show degrees of the characteristics
Type: ES Page Ref: 49
Skill: Applied
Topic: MBTI
Objective: 3
3) Explain how perception and perceptual errors, such as stereotype and halo effect, create issues for managers in employment interviews, and performance evaluations.
Answer: Suggested answer:
- Perception—is about judgments and all people make shortcuts in judgments; managers must be self-aware in order to avoid negatively impacting their hiring decisions or performance evaluations
- Stereotype—may be a shortcut a manager makes in an interview or performance evaluation; being aware of personal preferences may help managers to limit the use of stereotypes and/or cause managers to seek further information to support or disconfirm their perceptions;
- Halo Effect—may be a shortcut a manager makes in an interview or performance evaluation; being aware of personal preferences may help managers to limit the use of stereotypes and/or cause managers to seek further information to support or disconfirm their perceptions;(Examples can be drawn from text, class discussion, Internet, newspapers such as Globe and Mail, etc.)
Type: ES Page Ref: 45,46
Skill: Applied
Topic: Perception
Objective: 1
4) Discuss the "Big Five" model of personality and provide examples to show how this affects managers in an organizational setting.
Answer: Suggested Answer:
- Extroversion—comfort level with relationships (e.g., outgoing or reserved)
- Agreeableness—propensity to defer to others (e.g., valuing harmony or focusing more on own needs)
- Conscientiousness—number of goals on which a person focuses (e.g. focusing on fewer goals in a more purposeful way as opposed to pursuit of many goals and easily distracted)
- Emotional stability—ability to withstand stress (e.g., calm, secure, enthusiastic as opposed to nervous, depressed, insecure)
- Openness to experience—range of interests (e.g., innovative and imaginative versus conventional and finding comfort in the familiar)(Examples can be drawn from text, class discussion, Internet, newspapers such as Globe and Mail, etc.)
Type: ES Page Ref: 49-52
Skill: Applied
Topic: Personality
5) As a manager, you hire a person you know to be high in proactive personality. What might be positive outcomes and contributions this person could make, based on this personality trait? What might be the less desirable outcomes?
Answer: positives:
- identify opportunities for the company or department
- take initiative to help out/make decisions without waiting to be asked
- persevere with ideas or actions despite resistance or obstacles
- entrepreneurial in attitude to work; willing to try new ideas and work through problems
- willing to develop career and plan how to progress
negatives:
- may challenge present policy or practise if they think it is not valid
- more likely to leave the organization to start their own business
- may jump over the managers who supervise them, as they tend to seek out others and information in the organization, including those at high levels
- if career planning has been undertaken, they may still leave the company, creating a gap.
Type: ES Page Ref: 57
Skill: Applied
Topic: Big Five Personality
Objective: 6
Chapter 3 Values, Attitudes, and Diversity in the Workplace
3.1 Multiple-Choice Questions
1) What are values?
A) goals that individuals would like to achieve during their lifetime
B) convictions or beliefs that guide our decisions and evaluations of how to behave
C) principles that guide behaviour and inform us whether actions are right or wrong
D) preferable ways of behaving
E) fixed or predetermined policy or mode of action
Page Ref: 80
Skill: Recall
Topic: Values
Objective: 1
2) Within the framework of the Rokeach value survey, what are terminal values?
A) goals that individuals would like to achieve during their lifetime
B) principles that guide behaviour and inform us whether actions are right or wrong
C) preferable ways of behaving
D) convictions or beliefs that guide our decisions and evaluations of how to behave
E) fixed or predetermined policies or modes of action
Page Ref: 80
Skill: Recall
Topic: Terminal vs Instrumental Values
Objective: 1
3) Within the framework of the Rokeach value survey, what are instrumental values?
A) goals that individuals would like to achieve during their lifetime
B) concepts or beliefs that guide how we make decisions about, and evaluations of, behaviours and events
C) principles that guide behaviour and inform us whether actions are right or wrong
D) fixed or predetermined policies or modes of action
E) preferable ways of behaving
Page Ref: 80
Skill: Recall
Topic: Terminal vs Instrumental Values
Objective: 1
4) Which of the following best describes ethics?
A) concepts or beliefs that guide how we make decisions about, and evaluations of, behaviours and events
B) principles that guide behaviour and inform us whether actions are right or wrong
C) preferable ways of behaving
D) fixed or predetermined policies or modes of action
E) goals that individuals would like to achieve during their lifetime
Page Ref: 81
Skill: Applied
Topic: Terminal vs Instrumental Values
Objective: 1
5) Which of the following statements about values is incorrect?
A) Values facilitate the understanding of attitudes and motivation.
B) Values influence our perceptions.
C) Values can cloud objectivity and rationality.
D) Values generally have no effect on job satisfaction.
E) Values generally influence attitudes and behaviour.
Page Ref: 80, 81
Skill: Recall
Topic: Values
Objective: 1
6) According to the Global Leadership and Organizational Behaviour Effectiveness (GLOBE) research program, what are the nine dimensions along which national cultures differ?
A) assertiveness, future orientation, gender differentiation, uncertainty avoidance, power distance, individualism/collectivism, collectivism, performance orientation and humane orientation
B) ethics, future orientation, gender differentiation, certainty avoidance, power distance, individualism/collectivism, in-group collectivism, performance orientation and humane orientation
C) assertiveness, future orientation, gender differentiation, certainty avoidance, power distance, individualism/collectivism, in-group collectivism, performance orientation and humane orientation
D) ethics, future orientation, gender differentiation, uncertainty avoidance, power avoidance, individualism/collectivism, in-group collectivism, performance orientation and humane orientation
E) assertiveness, future orientation, gender differentiation, uncertainty avoidance, power distance, individualism/collectivism, in-group collectivism, performance orientation and humane orientation
Page Ref: 84
Skill: Recall
Topic: Hofstede's Cultural Values
7) The GLOBE value describing the acceptance of unequal levels of power in institutions and organizations is called
A) institutional distribution theory.
B) collectivism.
C) power distance.
D) organizational power theory.
E) bureaucracy.
Page Ref: 84
Skill: Recall
Topic: Hofstede's Cultural Values
8) Individualism is the degree to which people prefer to act as ________, whereas collectivism is the equivalent of ________.
A) individuals; group behaviour
B) individuals; uncertainty avoidance
C) individuals; low individualism
D) power brokers; low individualism
E) power brokers; low self-esteem
Page Ref: 81
Skill: Recall
Topic: Hofstede's Cultural Values
9) A society that prefers structured situations to alleviate unpredictability experiences
A) certainty avoidance.
B) power distance.
C) gender differentiation.
D) uncertainty avoidance.
E) assertiveness.
Page Ref: 82
Skill: Recall
Topic: Hofstede's Cultural Values
10) Within Hofstede's research, a culture emphasizing ________ would value thrift, persistence and tradition.
A) long-term orientation
B) short-term orientation
C) power distance
D) collectivism
E) individualism
Page Ref: 82
Skill: Recall
Topic: Hofstede's Cultural Values
11) A society that encourages and rewards group members for performance improvement and excellence would fall into which of the following GLOBE dimensions?
A) collectivism
B) future orientation
C) performance orientation
D) humane orientation
E) gender differentiation
Page Ref: 84
Skill: Recall
Topic: Hofstede's Cultural Values
12) According to Hofstede, which of the following countries scored high on power distance?
A) Norway
B) Denmark
C) Finland
D) Malaysia
E) Netherlands
Page Ref: 83
Skill: Recall
Topic: Hofstede's Cultural Values
13) Values are
A) flexible and adaptable.
B) synonymous with attitudes.
C) consistent among occupational groups.
D) fairly stable over time.
E) based solely on perception.
Page Ref: 80
Skill: Recall
Topic: Values
Objective: 1
14) According to Hofstede's dimensions, which of the following countries scored low on masculinity?
A) Canada
B) France
C) Denmark
D) China
E) Japan
Page Ref: 83
Skill: Recall
Topic: Hofstede's Cultural Values
15) Generation X is characterized by which of the following common values?
A) belief in order and authority
B) belief in, and practice of, the Christian moral code
C) strong concern for the environment
D) flexibility and achievement of job satisfaction
E) intimidated by change
Page Ref: 86
Skill: Recall
Topic: Values in the Canadian Workplace
Objective: 3
16) Which of the following statements is most accurate when looking at anglophone and francophone values?
A) Francophones have generally been found to be more collectivist or group-oriented with a greater need for achievement.
B) Anglophone managers tend to value autonomy and intrinsic job values, and thus are more achievement oriented.
C) Francophone managers tend to value affiliation and extrinsic job values such as technical supervision.
D) There are no significant differences between anglophone and francophone managers in individualism and collectivism.
E) There appear to be few differences between anglophones and francophones.
Page Ref: 89
Skill: Recall
Topic: Values in the Canadian Workplace
Objective: 3
17) Why have non-Aboriginals traditionally viewed Aboriginal values as "an impediment to economic development" and organizational effectiveness?
A) incompatible gender differentiation
B) incompatible power distance
C) low rating on assertiveness
D) time orientation and consensus decision making
E) low rating on uncertainty avoidance
Page Ref: 90
Skill: Recall
Topic: Values in the Canadian Workplace
Objective: 3
18) Canada is a multicultural society and is becoming more diverse than it was 20 years ago. This means there are many new differences between people that challenge managers. What kinds of accommodations of value differences should managers provide in today's Canada?
A) Some cultures value social activities over work activities and this requires accommodation at all times.
B) Some cultures have sacred days and practices that may require work accommodations from time to time.
C) Some cultures assert their own specialness and expect to be accommodated all the time.
D) Some cultures believe that racism is OK and this should be accommodated from time to time.
E) Some cultures are anti-materialistic and should not be made to be part of the modern utilitarian/capitalistic system.
Page Ref: 88
Skill: Applied
Topic: Values in the Canadian Workplace
Objective: 3
19) In contrasting values and attitudes, which of the following is TRUE?
A) They come from different sources.
B) There is no significant correlation between the two.
C) Attitudes are more stable than values.
D) Values are more stable than attitudes.
E) Values are based on diversity issues.
Page Ref: 92
Skill: Applied
Topic: Attitudes
Objective: 4
20) Jon is a middle level manager at Apex Corporation, a manufacturer of electronic switches for the telecommunications industry. Jon has been in his position for about three years and has been heard on several occasions telling others he likes his job. Jon is expressing his
A) attitude about work.
B) values about work.
C) perceptions about work.
D) frustration by making a positive comment.
E) Jon is really not expressing anything significant.
Page Ref: 93
Skill: Applied
Topic: Attitudes
Objective: 4
21) An employee who actively helps colleagues, takes minimal breaks, and alerts others to work-related problems is
A) high in job satisfaction.
B) high in organizational citizenship behaviour.
C) high in job stability.
D) high in organizational commitment.
E) low in organizational loyalty.
Page Ref: 96
Skill: Applied
Topic: Job Satisfaction
22) ________ is dissatisfaction expressed by an individual actively and constructively attempting to improve conditions.
A) Exit
B) Loyalty
C) Voice
D) Trust
E) Neglect
Page Ref: 98
Skill: Recall
Topic: Job Dissatisfaction
Objective: 8
23) The extent to which an employee identifies and is involved with a particular organization and wishes to maintain membership in that organization is known as
A) organizational performance.
B) job performance.
C) job involvement.
D) organizational commitment.
E) job satisfaction.
Page Ref: 99
Skill: Recall
Topic: Job Dissatisfaction
Objective: 8
24) According to John Meyer's research on organizational commitment, which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Continuance commitment is based on the obligation and employee feels to stay.
B) Normative commitment is based on the economic harm of quitting.
C) Affective commitment is based on shared values.
D) Cognitive commitment is directly correlated to the mental ability of the employee to stay committed to organizational goals.
E) Normative commitment is loyalty to coworkers.
Page Ref: 102,103
Skill: Recall
Topic: Job Dissatisfaction
Objective: 8
25) Which of the following statements describes organizational commitment?
A) Employees comply due to compensation and wages.
B) Employees identify with the organization's goals.
C) Strong leadership makes employees fear leaving.
D) Low work hours with high pay create loyalty.
E) employees' willingness to learn other skills on the job
Page Ref: 99
Skill: Recall
Topic: Job Dissatisfaction
Objective: 8
26) If employees have a negative attitude toward their jobs, they do NOT have
A) organizational commitment.
B) values.
C) job satisfaction.
D) job involvement.
E) job stability.
Page Ref: 98
Skill: Applied
Topic: Job Dissatisfaction
Objective: 4
27) Which is TRUE of job satisfaction and pay?
A) the higher the pay, the higher the job satisfaction
B) Moderate pay is associated with job satisfaction, but high pay is not associated with job satisfaction.
C) High paying jobs have moderate job satisfaction.
D) Low paying jobs always have high job satisfaction.
E) Low paying jobs always have low job satisfaction.
Page Ref: 94
Skill: Recall
Topic: Job Satisfaction
Objective: 6
28) If job satisfaction is high, then performance and productivity are likely to be moderate to high as well, especially if the job is
A) simple, with little discretion.
B) complex, with little discretion.
C) simple, with discretion.
D) complex with discretion.
E) without discretion.
Page Ref: 95
Skill: Applied
Topic: Job Satisfaction
Objective: 6
29) Which one of the following is most likely to lead to high job satisfaction?
A) being married
B) mentally challenging work
C) an outgoing personality
D) working alone
E) working in a team
Page Ref: 93
Skill: Recall
Topic: Job Satisfaction
Objective: 6
30) Job satisfaction is ________ to turnover.
A) positively related
B) unrelated
C) negatively related
D) equal in number
E) No relationship can be reasonably expressed.
Page Ref: 97
Skill: Recall
Topic: Job Satisfaction
Objective: 6
31) Employee dissatisfaction can be expressed in a variety of ways. These do NOT include which of the following?
A) complaining
B) stealing company property
C) insubordination
D) conforming to company values
E) shirking part of their responsibilities
Page Ref: 98
Skill: Recall
Topic: Job Dissatisfaction
Objective: 4
32) What are the major workforce diversity groups?
A) gender, height, age, disability, domestic partners, non-Christian
B) gender, weight, age, disability, domestic partners, non-Christian
C) gender, national origin, age, disability, height, non-Christian
D) gender, national origin, age, disability, domestic partners, non-Christian
E) gender, national origin, age, disability, political ideology, non-Christian
Page Ref: 103
Skill: Recall
Topic: Managing Diversity
Objective: 9
33) Why do some organizations value diversity in the workplace?
A) to be politically correct
B) to comply with equity legislation
C) to reduce job satisfaction and reward
D) to better serve a diverse market of customers and clients
E) to intensify job commitment
Page Ref: 103
Skill: Recall
Topic: Managing Diversity
Objective: 9
34) The cultural intelligence profile that works best with people of a similar background is
A) chameleon.
B) provincial.
C) analyst.
D) natural.
E) mimic.
Page Ref: 107
Skill: Recall
Topic: Managing Diversity
Objective: 10
35) The cultural intelligence profile that is able to match the cultural styles of others, but doesn't understand the significance of the behaviours is
A) chameleon.
B) provincial.
C) analyst.
D) natural.
E) mimic.
Page Ref: 108
Skill: Recall
Topic: Managing Diversity
Objective: 10
36) Managing diversity issues in the workplace requires managers to
A) determine how to accommodate the diverse needs of employees.
B) develop adequate rules and regulations to govern work.
C) determine how to best simplify the various affiliations of individuals.
D) attempt to develop programs which will assimilate diversity.
E) determine how to accommodate the needs of the organization.
Page Ref: 104
Skill: Recall
Topic: Managing Diversity
Objective: 10
37) Generational values challenge today's managers. The group that most values achievement and material success is
A) Elders.
B) Boomers.
C) Gen X.
D) Gen Y.
E) Anglophones.
Page Ref: 86
Skill: Recall
Topic: Values in the Canadian Workplace
Objective: 3
38) Components of organizational commitment include
A) affective, normative and continuance commitment.
B) effective, normative and continuance commitment.
C) affective, normative and citizenship commitment.
D) effective, productive and continuance commitment.
E) effective, productive and citizenship commitment.
Page Ref: 99
Skill: Recall
Topic: Job Dissatisfaction
Objective: 8
39) Single day diversity training programs almost always results in
A) more women and minorities in upper management.
B) no difference in the number of women and minorities in upper management.
C) fewer women and minorities in upper management.
D) more women, but fewer minorities in upper management.
E) no difference in the number of women, but more minorities in upper management.
Page Ref: 104
Skill: Recall
Topic: Managing Diversity
Objective: 9
40) Employers who want to make certain that each of their employees is accepting of those from different cultures will probably offer
A) group therapy.
B) mentoring.
C) legal seminars on discrimination.
D) diversity training.
E) individual rights seminars.
Page Ref: 104
Skill: Recall
Topic: Managing Diversity
Objective: 9
41) Organizations with higher morale tend to be more effective than organizations with less morale; most managers
A) measure morale but make no effort to improve morale.
B) measure morale and make an effort to improve it.
C) don't measure morale or overestimate the level of morale in their organizations.
D) don't measure morale or underestimate the level of morale in their organizations.
E) don't measure morale but instead measure absenteeism and turnover rates.
Page Ref: 99
Skill: Recall
Topic: Job Dissatisfaction
Objective: 8
42) Employees high in organizational citizenship behaviour are valued because they
A) go beyond their job duties by helping colleagues with their workloads and take more breaks.
B) accomplish their job duties by working collaboratively with colleagues.
C) go beyond their job duties by helping colleagues with their workloads and alerting others to work-related problems.
D) accomplish their job duties by alerting others to work-related problems.
E) accomplishing their job duties independently without need for supervision.
Page Ref: 96
Skill: Recall
Topic: Job Satisfaction
Objective: 6
43) When it comes to workplace stress, research confirms
A) most workplace stress is caused by individual factors such as values and personality.
B) companies can do very little to limit or manage the stress their employees feel.
C) frontline workers experience more stress than any other level within the organization.
D) executives have a higher predisposition to serious illnesses because of stress.
E) a single stressor may be unimportant in itself, but it can be the "additive" factor that pushes people beyond their ability to cope with high stress.
Page Ref: 121
Skill: Recall
Topic: OB on the Edge—Stress at Work
Objective: OB on the Edge: Stress at Work
44) According to a recent survey conducted by Statistics Canada, which region had the highest proportion of respondents with quite a lot of stress?
A) the Prairies
B) Atlantic Canada
C) British Columbia
D) Ontario
E) Quebec
Page Ref: 119
Skill: Recall
Topic: OB on the Edge—Stress at Work
Objective: OB on the Edge: Stress at Work
45) The three categories of workplace stressors are
A) environmental, personal and organizational factors.
B) environmental, group and organizational factors.
C) personal, group and organizational factors.
D) personal, group and environmental factors.
E) personal, group, organizational and environmental factors.
Page Ref: 120,121
Skill: Recall
Topic: OB on the Edge—Stress at Work
Objective: OB on the Edge: Stress at Work
46) Which of the following jobs would rank as being the most stressful of all those listed?
A) air traffic controller
B) stockbroker
C) airline pilot
D) real estate agent
E) accountant
Page Ref: 120
Skill: Recall
Topic: OB on the Edge—Stress at Work
Objective: OB on the Edge: Stress at Work
47) Of all the jobs listed below, which ranks the lowest in terms of "on the job" stress?
A) air traffic controller
B) lawyer
C) college professor
D) school principal
E) tenured university professor
Page Ref: 120
Skill: Recall
Topic: OB on the Edge—Stress at Work
Objective: OB on the Edge: Stress at Work
48) Which of the following doesn't contribute to workplace stress?
A) work overload
B) role conflict
C) incompetent colleagues
D) lack of personal fit with a job
E) clear job description
Page Ref: 120
Skill: Recall
Topic: OB on the Edge—Stress at Work
Objective: OB on the Edge: Stress at Work
49) Which of the following causes workplace stress?
A) turning down extra work
B) identifiable chain of command
C) ethnic employees
D) hostile bosses
E) experienced employees
Page Ref: 121
Skill: Recall
Topic: OB on the Edge—Stress at Work
Objective: OB on the Edge: Stress at Work
50) Which activity has long been recommended by physicians as a way to deal with excessive stress levels?
A) football
B) walking
C) soccer
D) boxing
E) rugby
Page Ref: 123
Skill: Recall
Topic: OB on the Edge—Stress at Work
Objective: OB on the Edge: Stress at Work
51) Time management helps with stress management because
A) making daily lists of activities gives a person purpose.
B) prioritizing activities from a list gives a person a sense of control.
C) scheduling activities gives a person a fixed plan of the time spent at work.
D) making daily lists provides a feedback mechanism.
E) new appointments and/or tasks can be refused if they weren't already in the time managements plan, giving the person a sense of control.
Page Ref: 123
Skill: Recall
Topic: OB on the Edge—Stress at Work
Objective: OB on the Edge: Stress at Work
52) Which of the following is NOT considered to be a way to deal with excessive stress?
A) aerobics
B) jogging
C) swimming
D) riding a bike
E) tennis match
Page Ref: 123
Skill: Recall
Topic: OB on the Edge—Stress at Work
Objective: OB on the Edge: Stress at Work
SCENARIO 3-1 Making sense of behaviour in organizations is challenging at the best of times. Many changes occur on almost a daily basis, which affects a company's ability to compete and maintain profitability while at the same time paying attention to employee needs, globalization and increasing multiculturalism.Jack Fraser, director of human resources at Central Telecom, wished to take some further training and join managers from other organizations to learn about the forces that shape workplace diversity. During his training sessions, Jack became keenly aware of the many factors that cause and contribute to diversity and what some of the impacts are upon employees individually and collectively.Jack determined that if Central Telecom is to keep pace with the competition and provide a good place for employees to work and also retain their services over the longer term, he would have to develop a program and standards to facilitate the process. Good dialogue with company personnel, accurate information from others with similar experiences, and a dedication toward a quality work life would all assist.Sensitive issues centered on employee values and attitudes would have to be addressed and the impact from the larger society considered and incorporated. In short, Jack needs to grasp not only a full understanding of organizational dynamics, but must use his experience and expertise to apply the process to his company.
53) On a recent trip to the United States, Jack found himself discussing diversity issues. Jack found that American managers appeared to rely more on hierarchy in their organization structures. This leads Jack to conclude that
A) Canadian values appear to be somewhat inferior to American values.
B) Americans appear to be more suited to working in teams.
C) Canadian and American managers will likely behave somewhat differently.
D) Americans will always follow the directives of their managers more.
E) Canadians value individuality and individual performance more than Americans.
Page Ref: 80,90
Skill: Applied
Topic: Managing Diversity
Objective: 3
54) In discussions with the CEO of a Canadian electronic manufacturing firm, Jack learned that many Canadian companies have a lack of diversity on their board of directors. This may hinder Canadian companies because research shows diverse boards
A) spend more time and attention on board agendas.
B) make more conservative and fiscally responsible decisions.
C) are more committed to organizational goals.
D) have better discussions with more perspectives, leading to greater innovation.
E) are more responsive to CEO and executive team concerns.
Page Ref: 106
Skill: Applied
Topic: Managing Diversity
Objective: 9
55) In researching further, Jack found that some corporations choose to highlight the value of diversity because
A) traditional business practices can best be served by diverse talents.
B) financial planning becomes easier and more logical.
C) planning is likely to be less complex since everyone accepts diversity values.
D) organizational structures can be re-engineered more logically.
E) globalization makes diversity an important strategic issue and goal.
Page Ref: 105
Skill: Applied
Topic: Managing Diversity
Objective: 9
56) Jack has completed a review of recent research on organizational commitment; his research tells him that organizational commitment is
A) less universally understood as a value than job satisfaction.
B) not an attitude which can be used to predict organizational citizenship behaviour.
C) a valid predictor for employee attitudes and values.
D) the same as job involvement and can be used to predict success.
E) probably a better predictor of employee turnover than job satisfaction.
Page Ref: 101
Skill: Applied
Topic: Job Dissatisfaction
Objective: 8
57) To design a successful diversity training program Jack will need to design an approach that will focus on
A) changing employee attitudes to reflect shifting perspectives on racial, gender, and other diversity issues.
B) complying with provincial and federal government policy and regulations.
C) assimilating individuals of different cultures and backgrounds.
D) eliminating the focus on individuality.
E) emphasizing individual productivity measures as opposed to team based performance.
Page Ref: 103
Skill: Applied
Topic: Managing Diversity in the Workplace
Objective: 9
58) Despite the fact that Jack is focusing on diversity issues, he realizes that employees at Central Telecom also must have job satisfaction if productivity is to increase and if employees are to be retained over the long term. Which of the following factors will Jack ignore as he designs his plan to increase job satisfaction?
A) fair and equitable rewards
B) opportunity to use skills and abilities
C) supportive working environment
D) federal and provincial policy on minimum pay standards
E) immediate supervisor who is supportive and understanding
Page Ref: 95
Skill: Applied
Topic: Job Satisfaction
Objective: 6
59) Sam was a very hard-working, ambitious and sincere employee who was also polite and cheerful in dealing with his co-workers. What type of values is Sam exhibiting according to Rokeach?
A) terminal
B) instrumental
C) traditional
D) insightful
E) ethical
Page Ref: 80
Skill: Applied
Topic: Values
Objective: 1
60) Diane had always tried to pursue a comfortable life that would bring her pleasure, excitement and inner harmony. What type of values is Diane exhibiting according to Rokeach?
A) terminal
B) instrumental
C) traditional
D) insightful
E) ethical
Page Ref: 80
Skill: Applied
Topic: Values
Objective: 1
61) Tim always tried to do the right thing for everyone involved whenever he was faced with a dilemma that affected other people at work. Which of the "Magnificent Seven Principles" is he exhibiting?
A) dignity of human life
B) autonomy
C) honesty
D) loyalty
E) the common good
Page Ref: 81
Skill: Applied
Topic: Values
Objective: 1
62) Even though Tim's department had a reputation for being populated by "slackers," he still felt that all of his staff members were intrinsically valuable and had the right to self-determination. Which of the "Magnificent Seven Principles" is he exhibiting?
A) dignity of human life
B) autonomy
C) fairness
D) humaneness
E) honesty
Page Ref: 81
Skill: Applied
Topic: Values
Objective: 1
63) Li had recently arrived in Spain from Indonesia, and was very surprised to discover how little emphasis was placed on encouraging and rewarding individuals for being fair, altruistic, generous, and kind to others. Thus, in her view, Spain lacked
A) power distance.
B) a future orientation.
C) assertiveness.
D) a humane orientation.
E) uncertainty avoidance.
Page Ref: 84
Skill: Applied
Topic: Hofstede's Cultural Values
64) Ada, who recently relocated from Greece to the United States, and was surprised to see how much emphasis was placed on rewarding group members for performance improvements and excellence. Thus, in her view, the US emphasized
A) power distance.
B) performance orientation.
C) autonomy.
D) assertiveness.
E) a future orientation.
Page Ref: 84
Skill: Applied
Topic: Hofstede's Cultural Values
65) Farrah is eager to participate in teamwork, and enjoys her manager because he treats her as an equal, rather than exerting his authority over her. Farrah is likely a member of which of the follow demographic groups?
A) Elders
B) Baby Boomers
C) Generation X
D) Generation Y
E) Echo Boomers
Page Ref: 85
Skill: Applied
Topic: Values in the Canadian Workplace
Objective: 3
66) Tyrone likes to stay connected with his friends through technology, even when he is at work; he has high expectations and is seeking a job that will be meaningful to his values. He is likely a member of which of the follow demographic groups?
A) Elders
B) Baby Boomers
C) Generation X
D) Millennials
E) Echo Boomers
Page Ref: 85
Skill: Applied
Topic: Values in the Canadian Workplace
Objective: 3
67) When in a group setting, Chase is the most likely member of the group to take the contrarian point of view on any given issue, but at the same time he is very collaborative. He is likely a member of which of the follow demographic groups?
A) Elders
B) Baby Boomers
C) Millennials
D) Echo Boomers
E) Generation X
Page Ref: 86
Skill: Applied
Topic: Values in the Canadian Workplace
Objective: 3
68) Leanne is a model employee. She is always willing to go beyond her regular job duties if needed, and she consistently performs beyond expectations. Leanne is exhibiting
A) loyalty.
B) job satisfaction.
C) organizational citizenship behaviour.
D) polarity.
E) positivity.
Page Ref: 96
Skill: Applied
Topic: Job Satisfaction
Objective: 6
69) Norma has been working for the same organization for 25 years. She has worked there so long she is an invaluable resource to people across the organization; she feels an obligation to stay with this organization for the rest of her career. Norma is exhibiting
A) continuance commitment.
B) normative commitment.
C) affective commitment.
D) personal commitment.
E) citizenship commitment.
Page Ref: 99
Skill: Applied
Topic: Job Dissatisfaction
Objective: 8
70) As manager who is labelled as an "natural" in cultural intelligence is most likely to use ________ to understand a cross-cultural situation.
A) cues from others
B) research
C) charm
D) intuition
E) rules
Page Ref: 107
Skill: Recall
Topic: Cultural Intelligence
Objective: 1
71) As manager who is labelled as an "analyst" in cultural intelligence is most likely to use ________ to understand a cross-cultural situation.
A) cues from others
B) research
C) charm
D) intuition
E) rules
Page Ref: 85
Skill: Recall
Topic: Values
Objective: 1
72) Carol just started her first job, and even though she was inexperienced, she had a strong belief in her inner worth and basic competence, so she expected to perform well. Carol is exhibiting positive
A) core self-evaluation.
B) self-respect.
C) self-esteem.
D) self-righteousness.
E) self-awareness.
Page Ref: 95
Skill: Applied
Topic: Job Satisfaction
Objective: 6
73) Of all of the employees in her department, Donna seemed to be the most enthusiastic, involved and satisfied with the work she was assigned to do. Donna was thus exhibiting
A) core self-evaluation.
B) positivity.
C) employee engagement.
D) prognostication.
E) self-awareness.
Page Ref: 101
Skill: Applied
Topic: Job Dissatisfaction
Objective: 8
74) John was being trained by his employers for an important posting to China. One of the concepts discussed was guanxi; understanding guanxi will help John make decisions about
A) appropriate interpersonal relations in his work role in China.
B) legal interpersonal relations in his work role in China.
C) internal pressures on his work performance in China.
D) appropriate attitudes to job satisfaction in China.
E) appropriate attitudes to power distance in China.
Page Ref: 92
Skill: Applied
Topic: Values in the Canadian Workplace
Objective: 3
75) Tina was somewhat shy and insecure, so she relied on the other people in her department to protect her and look after her. Tina is exhibiting a high degree of
A) individualism.
B) power distance.
C) collectivism.
D) uncertainty orientation.
E) terminality.
Page Ref: 82
Skill: Applied
Topic: Hofstede's Values
76) Tony has always "stuck to his own" so to speak. He therefore seemed to have difficulty working in a new department that was culturally diverse. Tony is exhibiting
A) high cultural intelligence.
B) high culture shock.
C) low cultural intelligence.
D) multiculturalism.
E) culture curiosity.
Page Ref: 107
Skill: Applied
Topic: Cultural Intelligence
Objective: 10
77) Stacy was trying to figure out how best to interact with Abdul, who recently joined her department and is from the Middle East; Stacy is focusing on understanding Abdul's cultural rules and expectations as she decides how to approach him. Stacy is exhibiting which cultural intelligence profile?
A) mimic
B) analyst
C) ambassador
D) chameleon
E) provincial
Page Ref: 107
Skill: Applied
Topic: Cultural Intelligence
Objective: 10
78) Zena gets along so well with people of other cultures that you would almost think that she is part of their cultures. She is exhibiting which cultural intelligence profile?
A) analyst
B) mimic
C) chameleon
D) provincial
E) ambassador
Page Ref: 108
Skill: Applied
Topic: Cultural Intelligence
Objective: 5
79) Peter is very unhappy in his current job, so he has been "going through the motions" for a long time now. He is frequently absent and often late. His response to his dissatisfaction can thus be referred to as
A) neglect.
B) voice.
C) loyalty.
D) exit.
E) withdrawal.
Page Ref: 98
Skill: Applied
Topic: Job Dissatisfaction
Objective: 4
80) Dana is pragmatic; as a manager of supply chain, she accepted a transfer to do the same job in a smaller community because house prices were lower and she felt she could acquire a larger house for her family at a lesser cost. She is likely a member of which of the follow demographic groups?
A) Elders
B) Baby Boomers
C) Generation X
D) Generation Y
E) Nexters
Page Ref: 86
Skill: Applied
Topic: Values in the Canadian Workplace
Objective: 3
81) Sean isn't altogether happy with his job, but has decided to stay because based on his calculation of his pension benefits, he cannot get a comparable pension with another company. Sean is exhibiting
A) affective commitment.
B) normative commitment.
C) continuance commitment.
D) implicit commitment.
E) resigned commitment.
Page Ref: 98
Skill: Applied
Topic: Job Dissatisfaction
Objective: 8
82) Ted has expressed that among his life goals are to write a book, volunteer extensively, and travel abroad. These are examples of Ted's
A) instrumental values.
B) fundamental values.
C) core values.
D) terminal values.
E) global values.
Page Ref: 80
Skill: Applied
Topic: Values
Objective: 1
83) Sara is a self-proclaimed activist whose ultimate terminal value is likely
A) honesty.
B) equality.
C) courage.
D) capability.
E) happiness.
Page Ref: 80
Skill: Applied
Topic: Values
Objective: 1
3.3 Essay Questions
1) As a Canadian manager relocating to Norway, you discover Hofstede's cultural values and research those for Norway and Canada. Define and describe each dimension listed and explain how you might have to alter your behaviour in the Norwegian setting.
Hofstede Dimension Norway's Rating Canada's Rating
a. Power Distance 31 39
b. Masculinity vs Femininity 8 52
c. Long-term vs Short-term Orientation 44 23
Answer: Suggested answer:
- Power distance—degree to which a society accepts that power in organizations is distributed unequally; a low to medium score describes low distance, meaning that employees want to make decisions with their managers
- Canada and Norway appear roughly similar, although Norwegians are lower and would not expect the boss to make decisions for them all the time.
- Masculinity vs Femininity—the extent which society maximizes traditional gender role differences; masculinity is high tradition, a low score means low tradition or femininity; Norway is less traditional than Canada so we would expect to see women managing companies and men actin as nurses and executive assistants; also more fathers might stay home with young children
-Long-term vs Short-term Orientation—Long-term orientation emphasizes thrift, the future and persistence and would show with a high score; short-term orientation emphasizes past and present, respects tradition and social obligations based on traditions; the higher the score the greater the willingness to change and alter for the benefit of the future rather than the present. Norway is modest in long-term orientation and Canada is more short-term in orientation, so Norwegians would likely be more adaptable and accept change
Type: ES Page Ref: 83
Skill: Applied
Topic: Hofstede's Cultural Values
2) List and describe the dominant values of each of the three age groups who make up the workforce. Provide examples to support your response.
Answer: Suggested answer:
- Boomers–rejection of authority; skepticism regarding motives of big business and government; strong environmental concerns; strong desire for equality in the workplace and society; one of the groups characterized by anger, intimidated by change, and anxious about their professional and financial future
- Generation X–experience-seeking; adaptable; concerned with personal image among peers.
- Millennials — high expectations and seek meaning in their work; more have a life goal of being rich(Examples can be drawn from text, class discussion, Internet, newspapers such as Globe and Mail, etc.)
Type: ES Page Ref: 85
Skill: Applied
Topic: Values in the Canadian Workplace
Objective: 3
3) Discuss how job satisfaction can impact employee productivity, absenteeism and turnover.
Answer: Suggested answer:
- Productivity—affected by external conditions and job satisfaction; improves when behaviour not controlled by outside factors; satisfaction-performance correlation stronger for higher-level employees; working environment influences productivity factors; productivity can lead to satisfaction; rewards increase productivity; job satisfaction-productivity link much stronger when looking at organization as a whole rather than at individual employees.
- Absenteeism—dissatisfaction leads to absenteeism, influenced by organizational rules and regulations such as sick leave benefits
- Turnover—influenced by labour market conditions, alternative job opportunities, length of tenure; important moderators are employee's level of performance and general disposition toward life
Type: ES Page Ref: 95-98
Skill: Applied
Topic: Job Satisfaction
4) List and explain at least four causes of stress as well as two consequences of stress.
Answer: Suggested answer for causes can include:
Environmental Factors
Technological change—Learning new technology without having the proper training.
Economic change— economy contracting makes people anxious about their job security Organizational Factors
Task demands—job design, working conditions and physical layout of work
Role demands—pressures because of role in organization
Interpersonal demands—pressures created by other employees, such as lack of support or harassment
Personal Factors
Family-work balance
Money management
Suggested answer for consequences can include:
Physiological symptoms—high blood pressure, headaches, heart attacks, increased breathing rates and dizziness.
Psychological symptoms—tension, anxiety, boredom, irritability.
Behavioural symptoms—alcohol, rapid speech, fidgeting and sleep disorders; increased workplace violence.
Type: ES Page Ref: 120-123
Skill: Applied
Topic: OB on the Edge—Stress at Work
Objective: OB on the Edge: Stress at Work
Chapter 4 Theories of Motivation
4.1 Multiple-Choice Questions
1) Motivation is
A) a component of ability, personal traits and desire.
B) an individual's intensity, direction and persistence.
C) an effort toward creating goals.
D) a constant intensity.
E) an attitudinal trait.
Page Ref: 128
Skill: Recall
Topic: Elements of Motivation
Objective: 1
2) Kane was a manager who believed most employees were lazy, working only to earn money. He assumed that they disliked work, and as a result
A) he lets employees choose their own goals.
B) he allows employees to use discretion.
C) he imposes strict controls.
D) he makes extensive use of delegating authority.
E) he allows employees to make decisions.
Page Ref: 128
Skill: Applied
Topic: Elements of Motivation
Objective: 1
3) Lilly was a strong employee who was committed to the objectives of her department and the goals of her company. Which of the following would likely also be applicable to her?
A) dislikes work
B) needs to be controlled
C) avoids responsibility
D) exercises self-direction
E) displays little ambition
Page Ref: 128
Skill: Applied
Topic: Elements of Motivation
Objective: 1
4) Which of the following statements would most likely be made by a manager who has a Theory X approach to human beings?
A) "Focus on the organization and people will take care of themselves."
B) "I treat people differently in different ways based on the situation we are facing."
C) "The only way to get people to work hard is to push them hard."
D) "People work best if left alone."
E) "People will generally seek greater responsibility and accountability when given the opportunity."
Page Ref: 128
Skill: Applied
Topic: Elements of Motivation
Objective: 1
SCENARIO 4-1 You are a new employee with Pace Analytics. Your supervisor has explained your job to you and has indicated that you will have a great deal of control over your job once you develop your skills and prove yourself. He compliments your history of accepting responsibility and suggests that you are free to offer constructive criticism about the way your job is structured.
5) Your supervisor seems to assume that your basic nature is
A) Theory X.
B) Theory Y.
C) Theory Z.
D) based on Herzberg's motivation-hygiene theory.
E) Theory Y and Z combined.
Page Ref: 128
Skill: Applied
Topic: Elements of Motivation
Objective: 1
6) As a Theory Y manager, your supervisor can be expected to do all of the following EXCEPT
A) assume that you will be internally motivated.
B) assume that you want to do your job.
C) allow you freedom to do your job as you believe it should be done.
D) monitor your work closely for signs that you are "slacking off."
E) support your efforts to self-direct.
Page Ref: 128
Skill: Applied
Topic: Elements of Motivation
Objective: 1
7) Unlike her co-workers, Jane was motivated by challenge, personal satisfaction, and by doing interesting work; most of her coworkers were just in it for the money. Jane was motivated by
A) intrinsic motivators.
B) safety motivators.
C) social motivators.
D) extrinsic motivators.
E) esteem motivators.
Page Ref: 128
Skill: Applied
Topic: Elements of Motivation
Objective: 1
8) Chao has a lot of internal drive. His overall goal in life is to "be all that he can be" in all aspects of his life. Which level of Maslow's hierarchy of needs is reflected in Chao's attitude?
A) social
B) self-actualization
C) physiological
D) esteem
E) safety
Page Ref: 129
Skill: Applied
Topic: Early Theories of Motivation
SCENARIO 4-2 Your department is diverse-it is made up of people who are different in their lifestyles and their stages of life. Mary is a 23-year-old single parent who is working for minimum wage. Jonathan is 60 years old, extremely wealthy and works because he enjoys it. Jane is single, 45 years old and has few friends or activities outside the office. You have decided to attempt to apply Maslow's hierarchy of needs to motivate each of these individuals.
9) You would expect that Mary is trying to satisfy which need?
A) social
B) esteem
C) physiological
D) self-actualization
E) safety
Page Ref: 130
Skill: Applied
Topic: Early Theories of Motivation
10) You would expect that Jane is attempting to satisfy which need?
A) social
B) esteem
C) physiological
D) self-actualization
E) safety
Page Ref: 130
Skill: Applied
Topic: Early Theories of Motivation
11) Which of the following do you think would motivate Mary the most?
A) more vacation time
B) more responsibility
C) greater discretion over her job
D) more money
E) more satisfying work
Page Ref: 130
Skill: Applied
Topic: Early Theories of Motivation
12) James had dreamed of making lots of money since he was a child, and that has driven him to great success. James is motivated by
A) intrinsic motivators.
B) esteem motivators.
C) extrinsic motivators.
D) safety motivators.
E) social motivators.
Page Ref: 129
Skill: Applied
Topic: Elements of Motivation
Objective: 1
13) Maslow's hierarchy of needs is arranged in which order?
A) physiological, esteem, safety, social, and self-actualization
B) physiological, safety, social, esteem, and self-actualization
C) safety, physiological, esteem, social, and self-actualization
D) physiological, social, safety, esteem, and self-actualization
E) physiological, social, safety, self-actualization, and esteem
Page Ref: 130
Skill: Recall
Topic: Early Theories of Motivation
SCENARIO 4-3 Sara is a new manager hired by Glass Industries Inc. She has discovered that working conditions are not good for her employees—they work in an old building with a poor heating, air-conditioning and ventilation system. The work itself is tedious and a supervisor who reports directly to Sara is rarely available to assist and help them make decisions on unique work orders. Sara has decided to analyze this work situation using Herzberg's motivation-hygiene.
14) Sara decided first to analyze the dissatisfiers in the work situation. Sara will be reviewing
A) working conditions.
B) intrinsic rewards.
C) recognition.
D) advancement.
E) responsibility.
Page Ref: 131
Skill: Applied
Topic: Early Theories of Motivation
15) Which of the following would motivate the employees according to Herzberg?
A) improvement in working conditions
B) fixing the heating system
C) receiving recognition for a job well done
D) having the supervisor "hang around" more
E) eliminating the supervisor's position
Page Ref: 131
Skill: Applied
Topic: Early Theories of Motivation
16) Which of the following would Herzberg classify as a hygiene factor?
A) responsibility
B) growth
C) company policy
D) achievement
E) self-satisfaction
Page Ref: 131
Skill: Recall
Topic: Early Theories of Motivation
17) Which one of the following would be considered a motivator in the motivation-hygiene theory?
A) salary
B) supervision
C) working conditions
D) recognition
E) company policy
Page Ref: 131
Skill: Recall
Topic: Early Theories of Motivation
18) Herzberg investigated which of the following questions?
A) What do people need from their jobs?
B) What do people dislike about their jobs?
C) What do people want from their jobs?
D) What do people take from their jobs?
E) What do people do at their jobs?
Page Ref: 131
Skill: Recall
Topic: Early Theories of Motivation
19) According to Maslow, when does a need stop motivating?
A) when it is substantially satisfied
B) It never stops motivating.
C) when one returns to a lower level need
D) when a higher level need comes into focus
E) when too many other needs come into focus
Page Ref: 130
Skill: Recall
Topic: Early Theories of Motivation
20) The theory which asserts that motivation depends upon the strength of a tendency to act in a certain way, which in turn depends on the strength of an expectation that the act will be followed by a given outcome and on the attractiveness of that outcome to the individual, is called
A) Herzberg's dual-factor theory.
B) McClelland's three needs theory.
C) Vroom's expectancy theory.
D) Maslow's hierarchy of needs.
E) Alderfer's ERG theory.
Page Ref: 135
Skill: Recall
Topic: Expectancy Theory
Objective: 3
21) The needs for achievement, power, and affiliation are part of whose theory?
A) Frederick Herzberg's
B) David McClelland's
C) Victor Vroom's
D) Abraham Maslow's
E) Douglas McGregor's
Page Ref: 132
Skill: Recall
Topic: Early Theories of Motivation
22) What are three dissatisfiers?
A) work conditions, pay and challenge
B) work conditions, challenge and growth opportunities
C) challenge, growth opportunities and company policy
D) company policy, challenge and work conditions
E) company policy, work conditions and pay
Page Ref: 131
Skill: Recall
Topic: Early Theories of Motivation
23) In contrast to the hierarchy of needs theory, McClelland suggests that
A) no more than one need may be working at one time.
B) all needs are lower level.
C) more than one need may be working at the same time.
D) McClelland identifies motivators, not needs.
E) interpersonal relationships are always the highest need to be satisfied.
Page Ref: 130-134
Skill: Recall
Topic: Early Theories of Motivation
24) Which of the following is least important in goal-setting theory?
A) goal difficulty
B) goal specificity
C) equity among co-workers
D) feedback
E) participation in goal setting
Page Ref: 143
Skill: Applied
Topic: Other Theories of Motivation
Objective: 4
25) Management by objectives (MBO) emphasizes setting goals with the employee; according to MBO, goals should be
A) easy to attain.
B) approved by management.
C) tangible, verifiable, measurable.
D) easy to create and develop.
E) general in nature.
Page Ref: 139
Skill: Recall
Topic: Other Theories of Motivation
Objective: 3
26) For the individual employee, MBO provides
A) specific, personal performance objectives.
B) increased monetary compensation.
C) communication between co-workers.
D) a means to an end.
E) a way to keep the company accountable.
Page Ref: 139
Skill: Applied
Topic: Other Theories of Motivation
Objective: 4
27) An example of a SMART goal is
A) Do your best, but be sure to finish before our next meeting.
B) Have it done by Friday and use the correct font this time.
C) Complete your draft proposal for reorganizing the warehouse by Friday; we will review it then and make plans to finalize.
D) Complete the report as soon as possible.
E) By Friday, I want to see progress on the warehouse proposal.
Page Ref: 140
Skill: Applied
Topic: Other Theories of Motivation
Objective: 4
28) SMART stands for
A) specific, measurable, attainable, reliable, and time-bound.
B) specific, unfixed, attainable, results-oriented, and time-bound.
C) specific, measurable, attainable, results-oriented, and time-bound.
D) equivocal, measurable, attainable, results-oriented, and time-bound.
E) specific, measurable, inaccessible, results-oriented, and time-bound.
Page Ref: 140
Skill: Recall
Topic: Other Theories of Motivation
Objective: 4
29) ________ is the theory that individuals act depending upon their evaluation of whether their effort will lead to good performance, followed by an outcome that is attractive to them.
A) Goal-setting theory
B) Rewards theory
C) Instrumental theory
D) Valence theory
E) Expectancy theory
Page Ref: 135
Skill: Recall
Topic: Expectancy Theory
Objective: 3
SCENARIO 4-4 Your organization has decided to institute a management by objectives program. The people in your department have asked you to explain the program and help them understand how it will affect them.
30) You want to make certain they understand the ingredients common to MBO programs. Which of the following is one of those ingredients?
A) Goals should be general enough to allow creativity.
B) Decision making will be autocratic.
C) Time periods will be implicit.
D) Feedback will not be given on each employee's performance.
E) Goals will be specific and measurable.
Page Ref: 139
Skill: Applied
Topic: Other Theories of Motivation
Objective: 4
31) Which of the following is an example of an MBO objective?
A) Telephone orders should be processed promptly.
B) Quality of all products should increase substantially.
C) Sales should be increased by two percent.
D) Company costs should be decreased as much as possible.
E) New customers should be brought in on a regular basis.
Page Ref: 139
Skill: Applied
Topic: Other Theories of Motivation
Objective: 4
32) The objectives for each individual will be set
A) unilaterally by you, the supervisor.
B) by each employee.
C) by a committee of peers.
D) by the employee and you, the supervisor.
E) by a committee of both employees and management.
Page Ref: 139
Skill: Applied
Topic: Other Theories of Motivation
Objective: 4
33) Allowing employees to participate in goal setting, rather than have their boss arbitrarily assign a goal, has an additional effect: each person is more likely to ________ even a difficult goal.
A) reject
B) misunderstand
C) begin resenting
D) resist achieving
E) accept
Page Ref: 140
Skill: Recall
Topic: Other Theories of Motivation
Objective: 4
SCENARIO 4-5 When you first went off to college, your father wanted you to study computer science and mathematics. Your grades during your freshman year were not very good. During your sophomore year, you decided to pursue a major in human resource management and your grades have gone up considerably. Your current goal is to graduate within four years and find human resources management job in a medium-sized corporation.
34) Your freshman grades may be explained because the goal of a major in computer science and mathematics was
A) too specific.
B) not hard enough.
C) not one you had committed to.
D) made public.
E) too difficult to achieve.
Page Ref: 140
Skill: Applied
Topic: Other Theories of Motivation
Objective: 4
35) ________ is the belief that performance is related to rewards.
A) Valence
B) Expectancy
C) Self-esteem
D) Instrumentality
E) Perception
Page Ref: 136
Skill: Applied
Topic: Expectancy Theory
Objective: 3
36) Bikram, a recent B.Eng. (engineer), has started his first job with an engineering firm; Bikram uses a self-outside comparison to determine if the company is treating him fairly. Bikram will compare his treatment to
A) his experience as a work study student.
B) a fellow male B.Eng recently hired by the firm.
C) a fellow female B.Eng hired by the firm two years ago.
D) a fellow female B.Eng recently hired by another firm.
E) a woman with an M.Sc. hired with Bikram for the same department.
Page Ref: 147
Skill: Applied
Topic: Equity Theory
Objective: 5
37) When people perceive an imbalance in their outcome-input ratio relative to others
A) an illegal situation is assumed.
B) they expect to be promoted.
C) tension is created.
D) turnover is inevitable.
E) goal setting needs to be renewed.
Page Ref: 149
Skill: Applied
Topic: Equity Theory
Objective: 5
SCENARIO 4-6 You graduated from college two years ago and began working at Hampstead Electronics. You have received good performance evaluations and a raise. You just found out that a recent college graduate with no experience has been hired at a higher salary than you are now making.
38) Which theory will you probably use in evaluating how you regard this situation?
A) equity
B) expectancy
C) goal setting
D) reinforcement
E) performance-reward
Page Ref: 147
Skill: Applied
Topic: Equity Theory
Objective: 5
39) Your referent comparison for equity theory is termed
A) self-inside.
B) self-outside.
C) other-inside.
D) other-outside.
E) self-other.
Page Ref: 148
Skill: Applied
Topic: Equity Theory
Objective: 5
40) Jessica feels she received an appropriate salary increase this year, but does not believe that the company's methods for determining salary increases are fair. She believes there is a problem with the firm's
A) interpersonal justice.
B) distributive justice.
C) equity practices.
D) procedural justice.
E) goal setting methods.
Page Ref: 149
Skill: Applied
Topic: Organizational Justice
Objective: 6
41) Within the framework of the equity theory, if an employee perceives iniquitous treatment and decides to work harder, what choice have they made?
A) adjust perceptions of others
B) choose a different referent
C) adjust perceptions of self
D) change their outcomes
E) change their inputs
Page Ref: 147
Skill: Applied
Topic: Equity Theory
Objective: 5
42) Within the framework of the equity theory, if an employee perceives iniquitous treatment and decides to exert less effort, what choice have they made?
A) change their inputs
B) change their outcomes
C) adjust perceptions of self
D) choose a different referent
E) adjust perceptions of others
Page Ref: 147
Skill: Recall
Topic: Equity Theory
Objective: 5
43) Extrinsic reward for a task may shift employees from
A) high performance to higher performance.
B) linking performance to appropriate rewards.
C) perceiving the work task to be of less importance than others.
D) linking employee recognition to organizational goals.
E) intrinsic motivation to extrinsic motivation.
Page Ref: 152
Skill: Applied
Topic: Intrinsic and Extrinsic
44) Equity theory demonstrates that, for most employees, motivation is influenced by
A) relative rewards.
B) input-output ratio.
C) absolute rewards.
D) relative and absolute rewards.
E) job satisfaction.
Page Ref: 147
Skill: Applied
Topic: Equity Theory
Objective: 5
45) Historically, equity theory focused on ________ justice.
A) distributive
B) procedural
C) organizational
D) interactional
E) relative
Page Ref: 148
Skill: Recall
Topic: Organizational Justice
Objective: 6
46) ________ justice is the perceived fairness of process used to determine the distribution of rewards.
A) Distributive
B) Interactional
C) Organizational
D) Procedural
E) Relative
Page Ref: 149
Skill: Recall
Topic: Organizational Justice
Objective: 6
47) Kenneth Thomas identifies four key rewards that increase an individual's intrinsic motivation; they are
A) sense of choice, sense of competence, sense of meaningfulness, sense of progress.
B) sense of justice, sense of competence, sense of meaningfulness, sense of progress.
C) sense of choice, sense of competence, sense of meaningfulness, sense of task.
D) sense of choice, sense of competence, sense of meaningfulness, sense of justice.
E) sense of choice, sense of judgment, sense of meaningfulness, sense of progress.
Page Ref: 153
Skill: Recall
Topic: Intrinsic and Extrinsic
48) When a salesperson is paid a commission based on some aggregate of sales, this is evidence of
A) gain sharing.
B) an individual performance award.
C) objective goal setting.
D) management discretion.
E) participative decision making.
Page Ref: 145
Skill: Applied
Topic: Other Theories of Motivation
Objective: 4
49) Sense of competence is
A) the opportunity to delegate authority.
B) the opportunity to pursue worthwhile tasks.
C) the opportunity to compete with others.
D) the opportunity to select what one will do and perform the way one thinks best.
E) the feeling of accomplishment from doing a good job.
Page Ref: 153
Skill: Recall
Topic: Intrinsic and Extrinsic
50) Which of the following set of four behaviours has Kenneth Thomas identified as ones that managers can use to build intrinsic rewards for employees?
A) leading for choice, leading for justice, leading for meaningfulness, and leading for progress
B) leading for choice, leading for competence, leading for meaningfulness, and leading for progress
C) leading for passion, leading for competence, leading for meaningfulness, and leading for progress
D) leading for choice, leading for competence, leading for meaningfulness, and leading for satisfaction
Page Ref: 153
Skill: Recall
Topic: Intrinsic and Extrinsic
51) An employee motivated by intrinsic rewards, would most likely choose
A) ongoing opportunities for education and training.
B) a company car.
C) incentive bonuses.
D) increased salary.
E) generous employee benefits.
Page Ref: 152
Skill: Applied
Topic: Intrinsic and Extrinsic
52) According to Cognitive Evaluation Theory, providing incentive pay
A) causes co-workers to compete with each other for rewards.
B) encourages employees to perform at a higher level to balance the i/o ratio.
C) changes the employee's perceptions of self.
D) decreases employees' overall levels of intrinsic motivation.
E) helps employees meet their need for achievement.
Page Ref: 151
Skill: Recall
Topic: Intrinsic and Extrinsic
53) Which theory considers the issue of whether intrinsic and extrinsic motivators are independent?
A) expectancy
B) reinforcement
C) equity
D) cognitive evaluation
E) goal-setting
Page Ref: 151
Skill: Recall
Topic: Intrinsic and Extrinsic
54) Which of the following is suggested by cognitive evaluation theory?
A) It would make sense to make an individual's pay non-contingent on performance.
B) Employees are motivated by a hierarchy of needs.
C) Extrinsic rewards increase intrinsic rewards.
D) Needs are divided into higher-order and lower-order categories.
E) It would make sense to make an individual's pay contingent on performance.
Page Ref: 151
Skill: Recall
Topic: Intrinsic and Extrinsic
55) Of the following statements, the weakest set of criteria to evaluate employee performance would be
A) good attitude or self-confidence.
B) promptness in submitting monthly reports.
C) average number of contact calls per day.
D) number of new accounts established.
E) dollar increase in sales.
Page Ref: 154
Skill: Applied
Topic: Motivating Employees
Objective: 9
56) Assigning goals appears to generate greater goal commitment in
A) all cultures around the globe.
B) in low individualism cultures.
C) in low power distance cultures.
D) in high power distance cultures.
E) in high individualism cultures.
Page Ref: 156
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivating Employees
Objective: 9
SCENARIO 4-8 Alice Ann Jones is the new director of human resources for a small consulting firm and has been charged with developing a performance evaluation and reward system. Alice Ann recognizes the importance of performance evaluation and rewards on employee behaviour and asks for your opinion and advice.
57) Alice Ann tells you that the firm pays on the basis of the productivity of each employee. Research on motivation would say this creates
A) higher intrinsic motivation towards tasks.
B) lower intrinsic motivation toward tasks.
C) self determination.
D) higher job satisfaction.
E) lower productivity.
Page Ref: 152
Skill: Applied
Topic: Intrinsic and Extrinsic
58) Alice Ann's firm would like employees to be creative in their thinking and empowered to act and solve problems that arise. You suggest that goal setting with employees may be a positive process to help accomplish this. Which of the following is TRUE of goal setting?
A) If the employee chooses the goal because of intrinsic interest, the employee is likely to be happier when the goal is achieved.
B) If the employee chooses the goal because of intrinsic interest, the employee is more likely to achieve the goal.
C) If the employee chooses the goal because of intrinsic interest, the employee is less likely to achieve the goal.
D) If the employee chooses the goal because of intrinsic interest, the employee is likely to be unhappy if the goal is not achieved.
E) If the employee chooses the goal because of intrinsic interest, there must still be an extrinsic reward for the goal to be motivating.
Page Ref: 152
Skill: Applied
Topic: Intrinsic and Extrinsic
59) If Alice provides rewards that increase intrinsic motivation of the employees, she would be offering employees a sense of
A) choice, competence and conditioning.
B) choice, meaningfulness and conditioning.
C) competence, determination and progress.
D) choice, competence and meaningfulness.
E) determination, competence and meaningfulness.
Page Ref: 153
Skill: Applied
Topic: Intrinsic and Extrinsic
60) Don was in the habit of reprimanding employees when they arrived late for work. The second time an employee was late, he or she would be docked pay. Don is using which type of reinforcement?
A) positive
B) negative
C) punishment
D) extinction
E) critical incident
Page Ref: 145
Skill: Applied
Topic: Other Theories of Motivation
Objective: 4
61) If a manager uses positive or negative reinforcement when an employee completes a task, the manager is trying to
A) strengthen the behaviour of completing the task.
B) weaken the behaviour of completing the task.
C) strengthen the behaviour of completing the task with positive reinforcement and weaken the behaviour of completing the task with negative reinforcement.
D) weaken the behaviour of completing the task with positive reinforcement and strengthen the behaviour of completing the task with negative reinforcement..
E) intermittently strengthen the behaviour by using positive reinforcement and then negative reinforcement.
Page Ref: 145
Skill: Recall
Topic: Other Theories of Motivation
Objective: 4
62) Reinforcement theory allows managers to vary rewards and punishments based on
A) time intervals and fixed schedules.
B) time intervals and behaviour ratios.
C) intermittent schedules and fixed intervals.
D) continuous reinforcement behaviour intervals.
E) intermittent schedules.
Page Ref: 156
Skill: Recall
Topic: Other Theories of Motivation
Objective: 4
63) Tina is a weak manager because when she trains people the reinforcement type she uses is
A) positive reinforcement.
B) fixed interval.
C) fixed ratio.
D) punishment.
E) intermittent extinction.
Page Ref: 145
Skill: Applied
Topic: Other Theories of Motivation
Objective: 5
64) Weekly paychecks are an example of what type of schedule of reinforcement?
A) continuous
B) fixed-interval
C) fixed-ratio
D) variable-interval
E) variable-ratio
Page Ref: 145
Skill: Applied
Topic: Other Theories of Motivation
Objective: 4
SCENARIO 4-9 Central Manufacturing Inc. fabricates medium- and large-scale watercraft, primarily for commercial use. They also manufacture accessories for a variety of boats and marine service vessels. Central Manufacturing struggles to keep costs down while maintaining profitability in a highly competitive market. Military and commercial contracts are its main source of business. Employees at Central Manufacturing appear to be dedicated individuals who, through their combined efforts, were able to save the company $1.5 million in energy costs by means of simple efficiency. For this initiative, they did not receive much recognition other than some encouragement and T-shirts recognizing their contribution to the company. Robert West, operations supervisor, believed that if other savings could be realized the company would welcome them. Although supportive of employee efforts, Robert didn't acknowledge the impact on the company's bottom line. Dan White, vice president of operations, recognized that Central Manufacturing needed to change its operations in order to shake its bureaucratic and authoritarian image. Although Robert praised employees and talked about performance, the reward process was limited. Dan undertook the initiative to change things, which meant creating a new process for both managers like Robert West and his employees. The employees had assumed that they were fairly secure in their jobs, since the company had a monopoly on specialized watercraft manufacturing. As with most manufacturing concerns in Canada, however, when a recession occurred, 200 employees, representing about one third of the workforce, were suddenly laid off. Although this was a major blow to Central Manufacturing, Dan White and George North, director of human resources, launched a new program to track, monitor, measure, recognize and reward employees for their efforts. Accountability and performance were to be a major focus in these programs. As the program commenced, some employees and their supervisors started to display progress charts. More ideas for operations improvement began to flow once it became evident what was actually going on. Positive feedback was forthcoming from customers and Dan realized that his initiative was starting to pay off.
65) Robert West appeared to be a manager oriented towards traditional ways of doing things. He was convinced that individuals needed to be monitored carefully with respect to their jobs and the tasks they accomplished. It is likely that Robert
A) was a Theory Y manager.
B) emphasized ERG theory.
C) was a Theory X manager.
D) emphasized goal-setting theory.
E) was a Theory Z manager.
Page Ref: 128
Skill: Applied
Topic: What is Motivation?
Objective: 1
66) White recognizes that equity theory will play a large role in how he organizes and develops his new program. Individual employees have a tendency to compare themselves with others and have a series of options available to them if they perceive that some sort of inequity exists. Which of the following is a typical employee response to a perceived inequity?
A) Employees will exert more effort.
B) Employees will tend to keep their outcomes unchanged.
C) Employees will maintain their perceptions of others.
D) Employees will have a tendency to quit their jobs.
E) Employees will embrace the process of goal setting.
Page Ref: 147
Skill: Applied
Topic: Equity Theory
Objective: 5
67) In the long term, White decides that equity theory will provide the best guidance for motivating and providing recognition to the employees. He is also aware that the unions may battle his new initiatives. Equity theory demonstrates that, for most employees, motivation is influenced
A) significantly by goal setting as well as by ability to be productive.
B) by union influence over their welfare.
C) solely by monetary rewards.
D) significantly by relative rewards as well as by absolute rewards.
E) significantly by goal setting as well as by absolute rewards.
Page Ref: 148
Skill: Applied
Topic: Equity Theory
Objective: 5
68) Roy really disliked his job. He forced himself to go to work each day out of fear of losing his only source of income. Roy was working mainly because of
A) negative reinforcement.
B) operant conditioning.
C) positive reinforcement.
D) intermittent reinforcement.
E) continuous reinforcement.
Page Ref: 145
Skill: Applied
Topic: Other Theories of Motivation
Objective: 4
69) Kelly, a single mother, recently re-entered the workforce in order to be able to pay for her most basic needs, namely food shelter and clothing for her and her son. According to Maslow, which need level was she trying to fulfill?
A) self-actualization
B) esteem
C) safety
D) social
E) physiological
Page Ref: 130
Skill: Applied
Topic: Early Theories of Motivation
70) When Brock was recently deciding between two job offers, his decision came down to which offer reflected the better health insurance, pension plan, and safe working conditions. According to Maslow, which need level is he focusing on in his decision?
A) esteem
B) physiological
C) safety
D) social
E) self-actualization
Page Ref: 130
Skill: Applied
Topic: Early Theories of Motivation
71) Don was a real "people person" so he was glad when his employer began to emphasize working in teams. Don enjoyed working with others as opposed to by himself. According to Maslow, which need level is motivating Don?
A) esteem
B) safety
C) self-actualization
D) physiological
E) social
Page Ref: 130
Skill: Applied
Topic: Early Theories of Motivation
72) ABC Inc. is well known as a company that uses a human relations approach; the company nurtures creativity and self-control in its employees. This company was following
A) Theory X.
B) Theory Z.
C) Theory Y.
D) Theory T.
E) Theory Q.
Page Ref: 128
Skill: Applied
Topic: What is Motivation?
Objective: 1
73) Zeke was a manager who believed that, in general, people disliked work; he believed people had to be forced or threatened with punishment to motivate them to work. Zeke believes in which of the following management theories?
A) Theory Z
B) Theory X
C) Theory Y
D) Theory Q
E) Theory T
Page Ref: 128
Skill: Applied
Topic: What is Motivation?
Objective: 1
74) When dealing with his employees, Ted sets aside time to find out what kind of rewards each of his employees prefers and strives to offer these in the work environment He is likely following
A) equity theory.
B) goal-setting theory.
C) expectancy theory.
D) EKG theory.
E) hygiene theory.
Page Ref: 135
Skill: Applied
Topic: Expectancy Theory
Objective: 3
75) Based on her long experience as a manager, Stella was convinced that people exert higher levels of effort when the goals set out for them are challenging and specific. Stella appears to be an advocate of
A) expectancy theory.
B) equity theory.
C) goal-setting theory.
D) Theory Y.
E) motivation-hygiene theory.
Page Ref: 141
Skill: Applied
Topic: Other Theories of Motivation
Objective: 4
76) Harry was concerned about Karen, of his best employees. She was great at what she did, but she was chronically late for work. To correct this, every time Karen wasn't late for work, he made a point of acknowledging it. Harry was utilizing
A) intermittent reinforcement.
B) negative reinforcement.
C) operant reinforcement.
D) continuous reinforcement.
E) variable reinforcement.
Page Ref: 145
Skill: Applied
Topic: Other Theories of Motivation
Objective: 4
77) The premise that people learn how to behave to get something that they want or to avoid something that they don't want is called
A) positive reinforcement.
B) extinction.
C) operant conditioning.
D) continuous reinforcement.
E) intermittent reinforcement.
Page Ref: 144
Skill: Recall
Topic: Other Theories of Motivation
Objective: 4
78) Which of the following is a process theory of motivation?
A) equity theory
B) expectancy theory
C) needs theory
D) hygiene theory
E) ERG theory
Page Ref: 135
Skill: Recall
Topic: Expectancy Theory
Objective: 3
79) Tonya was confused. In order to motivate Sam, one of her employees, she began to pay him for work that she knew he liked to do and for which he was previously not paid. However, she noticed that his overall level of motivation appeared to decrease. The motivation theory that best explains this change is
A) operant conditioning.
B) distributive justice.
C) cognitive evaluation theory.
D) Maslow theory.
E) Theory X.
Page Ref: 151
Skill: Applied
Topic: Organizational Justice
Objective: 6
80) Jason faced an uproar recently after his employees received their annual pay increases. The employees complained that the company didn't follow a fair process in awarding the increases. This is an example of
A) distributive justice.
B) procedural justice.
C) interactional justice.
D) operant justice.
E) equitable justice.
Page Ref: 150
Skill: Applied
Topic: Organizational Justice
Objective: 6
81) Carrie was unhappy with the pay increase that she recently received. She didn't think that the dollar value was fair relative to her performance, and she was even more upset that some of her coworkers received a greater increase than she did. This is an example of
A) distributive justice.
B) procedural justice.
C) interactional justice.
D) operant justice.
E) equitable justice.
Page Ref: 148
Skill: Applied
Topic: Organizational Justice
Objective: 6
82) The premise that higher level needs can't emerge until lower level needs are met is part of
A) Maslow's theory.
B) ERG theory.
C) process theory.
D) expectancy theory.
E) valence theory.
Page Ref: 130
Skill: Applied
Topic: Early Theories of Motivation
83) The concept that individuals with a high need for achievement prefer to work on tasks of moderate difficulty is consistent with
A) ERG Theory.
B) Maslow's theory.
C) McClelland's theory.
D) expectancy theory.
E) valence theory.
Page Ref: 133
Skill: Recall
Topic: Early Theories of Motivation
84) Tony was so concerned that his department's project be completed on time that he offered all of his employees a $100 bonus for each day that the project was completed ahead of schedule. This is an example of
A) extinction.
B) valence.
C) variable reinforcement.
D) positive reinforcement.
E) extrinsic reward.
Page Ref: 128
Skill: Applied
Topic: What is Motivation?
Objective: 1
85) An individual's belief that he or she is capable of performing a task is known as
A) self-fulfillment.
B) self-respect.
C) self-esteem.
D) self-efficacy.
E) self-starting.
Page Ref: 143
Skill: Recall
Topic: Other Theories of Motivation
Objective: 4
4.3 Essay Questions
1) Discuss the assumptions held by managers who subscribe to Theory X and those held by managers who subscribe to Theory Y. Provide examples to support your response.
Answer: Suggested answer:
- Theory X—employees inherently dislike work and attempt to avoid it; employees must be coerced, controlled or threatened; employees will avoid responsibility and seek formal direction; employees display little ambition as security factors are prime.
- Theory Y—employees view work as natural; people exercise self-direction and self-control if committed; people will accept and even seek responsibility; individuals are creative and can make innovative decisions. (Examples can be drawn from text, class discussion, Internet, newspapers such as Globe and Mail, etc.)
Type: ES Page Ref: 132
Skill: Applied
Topic: What is Motivation?
Objective: 1
2) Using examples, compare and contrast Maslow's hierarchy of needs with McClelland's theory of needs.
Answer: Suggested answer:
-Maslow's theory is more general, applying motivation to general life, whereas McClelland's focuses on motivational needs and applies them to the workplace and managerial roles
- Maslow's physiological and safety needs meet basic life needs on an extended time basis; McClelland's has no equivalent for these, but the individual's with high N-ach may be attracted to money to attain needs
- Maslow's social need is a need for acceptance by others into the group; this matches to McClelland's need for affiliation; McClelland explained this was not a good need to be high in if a person was a high level manager, as it creates a need for harmony and possibly an avoidance of conflict
-Maslow's esteem needs create a desire for recognition and status; McClelland's need for achievement is much more of an intrinsic need for self-accomplishment, although status rewards could be valued by high n-ach individuals.
-Maslow's need for self-actualization meets some of the criteria of McClelland's need for achievement as it is internal, personal achievements that are valued -Maslow has a strict hierarchy with only one need activated at a time; McClelland's needs could all be active, some high some low, at all times; McClelland also believed the environment impacted needs and could make them more dominant or less so, this a better tool for training managers through increasing or decreasing their needs.
Type: ES Page Ref: 129-33
Skill: Applied
Topic: Early Theories of Motivation
3) Describe goal-setting and list the four ways that it motivates employees.
Answer: Suggested answer:
- Goals direct attention — concise statements of specific accomplishments; tangible objectives that can be measured and evaluated and have time lines.
- Goals regulate effort — suggests how much effort an individual will need to give to the task; employee awareness is clear.
- Goals increase persistence — even in the face of obstacles, if goals are clear employees will strive to complete them.
- Goals encourage the development of strategies and action plans — once agreed to, employees can develop plans and strategies for accomplishing.
Type: ES Page Ref: 139-140
Skill: Applied
Topic: Other Theories of Motivation
Objective: 4
4) Using examples, discuss equity theory and explain how a manager might apply it in the workplace.
Answer: Suggested answer:
- equity theory—employees compare their job inputs and outcomes to those of others; self-inside, self-outside, other-inside, other-outside
- four moderating variables—gender, length of tenure, level in organization, amount of education
- perceived inequities can be handled by employees changing inputs and/or outcomes, adjusting perceptions of self and/or others, choosing a different referent, or leaving the field.
- employees influenced by relative as well as absolute rewards.
- elements of inputs, outputs and ways of improving job situation are unclear.(Examples can be drawn from text, class discussion, Internet, newspapers such as Globe and Mail, etc.)
Type: ES Page Ref: 148-150
Skill: Applied
Topic: Responses to the Reward System
Objective: 4
5) What is meant by the term "organizational justice"?
Answer: organizational justice is the overall perception of what is fair in the workplace. Fairness or equity can be subjective, and it resides in the perception of the person.
Type: ES Page Ref: 147-150
Skill: Applied
Topic: Equity Theory
Objective: 5
Chapter 5 Motivation in Action
5.1 Multiple-Choice Questions
1) Thinking of money as a motivator, expectancy theory mainly suggests that
A) money plays no part in motivating employee behaviour.
B) money is the only extrinsic motivator.
C) individuals need to value the reward, whether it is money or something else, or it won't be motivational.
D) individuals care little about the value of the reward but appreciate the gesture.
E) the mere suggestion of more money will motivate employees.
Page Ref: 166
Skill: Recall
Topic: From Theory to Practice—The Role of Money
Objective: 1
2) Money is probably the most emotionally meaningful object in contemporary life. Only
A) sex and ambition are its close competitors.
B) ego and ambition are its close competitors.
C) shelter and ambition are its close competitors.
D) food and sex are its close competitors.
E) food and shelter are its close competitors.
Page Ref: 166
Skill: Recall
Topic: From Theory to Practice—The Role of Money
Objective: 1
3) When using bonuses, managers should be mindful of
A) the amount, so that the bonus does not negatively effect the profits of the company.
B) not recognizing friends within the company.
C) the size of the bonus in relation to the event recognized.
D) potential unexpected behaviours arising when employees try to ensure they will receive bonuses.
E) very little, the bonus is just so effective.
Page Ref: 170
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
4) One strength of a variable-pay program is that it
A) encourages individuals to work together effectively.
B) increases the skill levels of employees.
C) motivates task performance.
D) can reduce the number of employees needed.
E) can cause unhealthy competition among employees.
Page Ref: 168
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
5) Profit sharing plans
A) focus on past financial results.
B) are company-established benefit plans in which employees acquires stock as part of their benefits.
C) give employees the right to buy stock in the company at a later date for a guaranteed price.
D) focus on future financial results.
E) give employees the right to buy stock in the company at a later date for the market price at that time.
Page Ref: 172
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
6) Skill-based pay is attractive to organizations because it tends to create a
A) flexible workforce with interchangeable skills.
B) responsive workforce to management requests.
C) lower cost base or starting point for all employees.
D) single-pay system that is easy for everyone to understand.
E) focus on past performance.
Page Ref: 172
Skill: Applied
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
7) Taylor Inc. has different benefits plans for employees who are single parents as compared to those for single employees with no dependents. Specifically, single parents get additional disability insurance as well as life insurance. This type of benefit plan is known as
A) core-plus.
B) modular.
C) flexible spending.
D) cafeteria.
E) secondary.
Page Ref: 173
Skill: Applied
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
8) Gainsharing is a variable-pay program that is an incentive plan for
A) individuals, where improvements in an individual's productivity, from one period to another, determine the amount awarded.
B) all employees of the company, where employees gain when the company gains market share.
C) workplace groups or departments, where improvements in group productivity, from one period to another, determine the amount shared.
D) all employees of the company, where every employee gains when the company increases productivity.
E) individuals, where an individual who accomplishes specific goals, receives a percentage of company profit.
Page Ref: 172
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
9) Variable-pay or pay-for-performance programs operate reward programs at three levels
A) individual, group and organizational.
B) individual, departmental and organizational.
C) individual, departmental and community.
D) individual, group and community.
E) individual, group and managerial.
Page Ref: 168
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
10) Research on pay found organizations paying more attracted better-qualified, more motivated employees who stayed with the organization longer; these organizations have
A) higher employee morale.
B) higher customer satisfaction.
C) higher employee productivity.
D) higher employee productivity and higher customer satisfaction.
E) higher employee morale, higher employee productivity and higher customer satisfaction.
Page Ref: 180
Skill: Applied
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
11) Pay for performance means employees must
A) share only in the rewards of a company.
B) share in the risks as well as the rewards of their employer's business.
C) share in the risks at the expense of the rewards of their employer's business.
D) share all aspects of a company's business.
E) share very little yet gain from any success the company might achieve.
Page Ref: 168
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
12) Studies have shown that the most powerful workplace motivator is
A) a company dinner.
B) promotion.
C) time in lieu.
D) money.
E) recognition.
Page Ref: 175
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
Objective: 3
13) Paying a data entry clerk an hourly rate plus bonus per page is an example of a
A) variable-pay plan.
B) modified piece-rate plan.
C) teamwork incentive plan.
D) gainsharing plan.
E) piece-rate plan.
Page Ref: 169
Skill: Applied
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
14) If an organization wants a group of individuals to function as a team, emphasis needs to be on
A) individual rewards, rather than team-based awards.
B) team-based performance, rather than team-based rewards.
C) individual rewards, rather than team-based rewards.
D) a sense of company loyalty.
E) team-based rewards, rather than individual rewards.
Page Ref: 172
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
15) One weakness of skill-based pay programs is that
A) employees may "top out", or learn all the skills available.
B) team performance can be difficult to evaluate.
C) earnings vary from year to year.
D) individuals do not always have control over factors that affect productivity.
E) equity problems could arise if all members are paid equally.
Page Ref: 171
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
16) Terry likes to see a direct connection between her performance and the compensation she receives each year. Terry prefers a
A) merit-based pay program.
B) seniority-based pay program.
C) inflation-based pay program.
D) variable pay program.
E) profit sharing pay program.
Page Ref: 169
Skill: Applied
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
17) A $5 employee bonus, awarded by employees to a colleague who has been helpful and supportive, would
A) motivate individual performance goals.
B) be too difficult to track.
C) cause colleagues to compete against one another.
D) motivate organizational citizenship behaviour.
E) be a form of variable pay.
Page Ref: 176
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
Objective: 3
18) Profit-sharing plans share company profit based on
A) past financial results.
B) monthly expectations.
C) individual performance results.
D) future financial results.
E) projected financial results.
Page Ref: 173
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
Objective: 3
19) According to expectancy theory, for employees to be motivated
A) performance must be directly linked to rewards.
B) their compensation must be incremental.
C) they can expect to work less but still find financial benefits.
D) rewards are irrelevant and performance is the key driver for motivation.
E) performance must be indirectly linked to rewards.
Page Ref: 172
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
Objective: 1
20) The financial meltdown of September 2008 may have been related to
A) a failing global stock market.
B) lack of proper accounting procedures within mortgage lending.
C) bonus compensation strategies in mortgage lending.
D) too few regulatory managers.
E) an unrealistic need for profit.
Page Ref: 171
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
21) Two specific forms of individual-based pay-for-performance programs
A) stock options and gainsharing.
B) piece-rate wages and gainsharing.
C) profit-sharing and gainsharing.
D) variable-pay programs and piece-rate wages.
E) piece-rate wages and bonuses.
Page Ref: 168
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
22) In a piece-rate pay plan, employees are paid
A) a piece of company profits equal to their production quota.
B) a piece of their salary and increases when specific targets are met or surpassed.
C) a fixed hourly rate and a bonus for achieving targets.
D) a fixed sum for each unit of production completed.
E) a fixed sum based on their performance appraisal.
Page Ref: 169
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
23) Expectancy theory tells us that a key component of motivation is
A) the link between satisfaction and compensation.
B) the link between seniority and compensation.
C) the link between productivity and compensation.
D) the link between performance and reward.
E) the link between profit and compensation.
Page Ref: 166
Skill: Recall
Topic: From Theory to Practice—The Role of Money
Objective: 1
24) Variable-pay programs are consistent with expectancy theory predictions; expectancy theory perceives a strong relationship between performance and
A) rewards.
B) productivity.
C) stock options.
D) salary.
E) seniority.
Page Ref: 166
Skill: Recall
Topic: From Theory to Practice—The Role of Money
Objective: 1
25) Some studies suggest that money is a better motivator in the short-term, but in the long-term,
A) recognition in the workplace mattered more.
B) promotion in the workplace mattered more.
C) accomplishments in the workplace mattered more.
D) non-financial incentives in the workplace mattered more.
E) benefits in the workplace mattered more.
Page Ref: 174
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
Objective: 3
26) Bonuses reward ________ behaviour, rather than historical performance and are ________ rewards rather than ongoing entitlements.
A) intrinsic, current
B) recent, one-time
C) extrinsic, one-time
D) innovative, current
E) innovative, intrinsic
Page Ref: 170
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
27) The research on ESOPs indicates
A) CEOs with ESOP plans are more likely to lie to affect stock price.
B) ESOPs positively affect employee satisfaction but the effect on performance is unclear.
C) ESOPs positively affect profit growth for a company, including net profit.
D) ESOPs negatively affect employee satisfaction but positively effect performance.
E) ESOPs positively affect revenues per employee but have a negative affect on job satisfaction on employees.
Page Ref: 172
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
28) Personally congratulating an employee in private for a good job is an example of
A) managerial effectiveness.
B) Maslow's hierarchy theory.
C) employee recognition.
D) Herzberg's motivation-hygiene theory.
E) expectant behaviour.
Page Ref: 175
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
Objective: 3
29) A spontaneous and private "thank you," or a "bragging board," are examples of
A) employee recognition programs.
B) intrinsic employee reward systems.
C) union-sponsored recognition programs.
D) gainsharing and profit-sharing programs.
E) motivation theories.
Page Ref: 174
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
Objective: 3
30) Last month a company produced 1000 items/10,000 person hours and this month they produced 1000 items/9,000 person hours. Dividing the productivity savings between company and employees is an example of
A) gainsharing.
B) profit sharing.
C) a piece-rate plan.
D) a variable-pay plan.
E) recognition program savings.
Page Ref: 171
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
31) Motivation theories are culturally sensitive and managers should be sensitive to national differences. Intrinsic job characteristics and job involvement were valued in the
A) US and Japan, but not in Hungary.
B) US and Hungary, but not in Japan.
C) US and Japan, but not in Canada.
D) US, Japan, and Hungary.
E) US, but not in Japan or Hungary.
Page Ref: 192
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivation—Putting It All Together
Objective: 8
32) In a country with high uncertainty avoidance, employees would prefer the reward of
A) pay for performance.
B) individual incentives.
C) flexible benefits.
D) seniority-based pay.
E) workplace child-care programs.
Page Ref: 192
Skill: Applied
Topic: Motivation—Putting It All Together
Objective: 8
33) Organizations hoping for improved teamwork and collaboration should reward
A) individual team members for individual productivity.
B) individual team members who mentor good group relationships.
C) team leaders who direct the team.
D) team members equally for team productivity.
E) only after training in teamwork in provided.
Page Ref: 175
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
34) Strategies for authentic motivation, according to Alfie Kohn, include
A) communicating to employees the company viewpoint.
B) setting goals and explaining to employees the outcomes if goals are not achieved.
C) focusing on what the employee is doing wrong and how that affects the company.
D) providing choice to employees over how they do the task.
E) helping employees rather than putting them under surveillance.
Page Ref: 177
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
Objective: 3
35) Jace is foreman of a team of welders; the team meets at the beginning of each shift to discuss what work tasks must be completed, decides how the work will be processed and assigns roles to each worker. Of Alfie Cohen's recommendations, this style represents
A) incentive pay.
B) authentic motivation.
C) cooperative process.
D) providing choice.
E) technical achievement.
Page Ref: 178
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
Objective: 3
36) Which is TRUE of jobs high in job characteristics - variety, significance, autonomy and feedback?
A) Organizational goals and individual rewards are easily achieved when the model is used.
B) Only cultures high in uncertainty avoidance are most successful using this model.
C) All cultures value variety, significance, autonomy and feedback.
D) Not all individuals value variety, significance, autonomy and feedback on the job.
E) The model lonely applies to the modern workplace.
Page Ref: 187
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 4
37) When skill variety, task identity and task significance are all present in a job they create
A) autonomy.
B) self-efficacy.
C) distributive justice.
D) continuance commitment.
E) meaningful work.
Page Ref: 179
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 4
38) Employees in a country that values individualism would likely prefer the reward of
A) stock options.
B) maternity leave programs.
C) career-break schemes.
D) flexible benefit.
E) skill-based pay.
Page Ref: 192
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivation—Putting It All Together
Objective: 8
39) An example of a country that generally prefers certainty in compensation system rewards is
A) Greece.
B) Sweden.
C) United States.
D) United Kingdom.
E) Australia.
Page Ref: 192
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivation—Putting It All Together
Objective: 8
40) An example of a country where employees would prefer social benefits as rewards is
A) Greece.
B) the Netherlands.
C) United Kingdom.
D) Australia.
E) Portugal.
Page Ref: 192
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivation—Putting It All Together
Objective: 8
41) If a country put a high value on humane orientation, its reward preference would be
A) stock options.
B) individual incentives.
C) pay for performance.
D) skill-based pay.
E) workplace child-care programs.
Page Ref: 192
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivation—Putting It All Together
Objective: 8
42) Alfie Kohn, in his book Punished by Rewards, proposes that we re-evaluate evaluation and, as a result, the performance evaluation system might be structured
A) around the employee listening better.
B) more on what you are doing poorly.
C) more on who is performing poorly.
D) more like a two-way conversation.
E) more on who gets raises or promoted.
Page Ref: 177
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
Objective: 3
43) When Carol walked out of her annual performance review, she felt good. She felt that the meeting was fair and constructive, and that the manager who did the review was sincere. There is no financial component to Carol's performance review, it is just an open discussion. This form of review can be described as
A) peer-based.
B) 360.
C) modular.
D) effective.
E) a waste of time.
Page Ref: 177
Skill: Applied
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
Objective: 3
44) If a hard-working athlete or student with modest abilities consistently outperforms a more gifted, but lazy student, this indicates that
A) if both ability and motivation are inadequate, performance will be negatively affected.
B) if either ability or motivation is inadequate, performance will be negatively affected.
C) if either ability or compensation is inadequate, performance will be negatively affected.
D) if either ability or motivation is inadequate, performance will be positively affected.
E) if both ability and motivation are inadequate, performance will be positively affected.
Page Ref: 167
Skill: Applied
Topic: From Theory to Practice—The Role of Money
Objective: 1
45) "We are most likely to become enthusiastic about what we are doing—and all else being equal, to do it well—when we are free to make decisions about the way we carry out a task." This speaks to which of the following approaches to creating a motivating work environment?
A) establish incentive pay
B) encourage collaboration
C) enhance content
D) provide choice
E) provide the conditions for authentic motivation
Page Ref: 178
Skill: Applied
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
Objective: 3
46) Carefully matching people to their jobs and giving them the opportunity to try new jobs is an example of creating a more motivating work environment by
A) encouraging collaboration.
B) enhancing content.
C) providing the opportunity to perform.
D) providing choice.
E) enhancing autonomy.
Page Ref: 177
Skill: Applied
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
Objective: 3
47) Job rotation is defined as
A) changing jobs every month so as to keep the newness level high.
B) changing jobs every week so as to keep the newness level high.
C) an opportunity for employees to change jobs when they feel the need.
D) the systematic removal of employees and their replacement by new, energetic employees.
E) the periodic shifting of an employee from one task to another.
Page Ref: 182
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 5
48) Kerry was happy with recent changes to her job. She now has more freedom, independence, and responsibility, as she now is able to complete all seven steps of assembly by herself. She also inspects her product to ensure it is functioning. This is an example of
A) job rotation.
B) job enrichment.
C) job security.
D) job sharing.
E) job evaluation.
Page Ref: 183
Skill: Applied
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 5
49) Sam periodically shifts his employees from one task to another in order to give them a change of routine and the opportunity to learn new skills. This practice is known as
A) job design.
B) job enrichment.
C) job rotation.
D) job satisfaction.
E) job enlargement.
Page Ref: 183
Skill: Applied
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 5
50) The JCM is well researched and evidence supports that there is a multiple set of
A) task variety.
B) job characteristics.
C) task identity.
D) task significance.
E) skill variety.
Page Ref: 180
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 4
51) Nursing the sick in a hospital intensive care unit is an example of
A) high feedback.
B) high task significance.
C) high task identity.
D) high autonomy.
E) high skill variety.
Page Ref: 179
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 4
52) As Gail has gained more experience as a customer service representative in a bank, she has been given more freedom to complete transactions for clients by herself and she has been given more responsibilities for planning her training courses and skill development. Gail is experiencing
A) job design.
B) job enrichment.
C) job rotation.
D) job satisfaction.
E) job enlargement.
Page Ref: 183
Skill: Applied
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 5
53) A call center operator who must answer calls as they come according to routine, highly scripted procedures is an example of low
A) task identity.
B) skill variety.
C) autonomy.
D) feedback.
E) task significance.
Page Ref: 179
Skill: Applied
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 4
54) A designer who designs a belt, selects the leather, shaves and tools the leather and finishes it to perfection is an example of high
A) autonomy.
B) task identity.
C) task significance.
D) skill variety.
E) feedback.
Page Ref: 179
Skill: Applied
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 4
55) Jobs that are high on motivating potential must be high on both
A) creativity and responsibility.
B) autonomy and feedback.
C) compensation and responsibility.
D) variety and potential.
E) idealism and responsibility.
Page Ref: 180
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 4
56) Sweeping hospital floors is an example of
A) low task significance.
B) low skill variety.
C) low task identity
D) low autonomy.
E) low feedback.
Page Ref: 180
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 4
57) A home security system installer who schedules work for the day, makes visits without supervision, and decides the most effective system and techniques for each installation has a job that has
A) high autonomy.
B) high significance.
C) high identity.
D) high variety.
E) high feedback.
Page Ref: 180
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 4
58) Flex time and telework grant employees
A) low task identity.
B) high task significance.
C) higher autonomy.
D) low skill variety.
E) low feedback.
Page Ref: 179, 186
Skill: Applied
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 6
59) A factory worker who assembles microchips but passes quality control inspections to another department has a job with
A) low skill variety.
B) high task identity.
C) low task significance.
D) high feedback.
E) low autonomy.
Page Ref: 180
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 4
60) The JCM allows us to make this statement with relative confidence
A) People who work on jobs with high core job dimensions are generally more motivated, satisfied and productive than are those who do not.
B) People who work on jobs with low core job dimensions are generally more motivated, satisfied and productive than are those who do.
C) People who work on jobs with high core job dimensions are generally less motivated, satisfied and productive than are those who do not.
D) People who work on jobs with high core job dimensions cannot be motivated, satisfied and productive.
E) People who work on jobs with high core job dimensions are generally motivated through salary and recognition.
Page Ref: 180
Skill: Applied
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 4
61) Jason was a unique employee. He has a wide range of appropriate skills and gets frustrated when he doesn't get a chance to utilize them on the job. To motivate Jason, it is important that his job reflect
A) autonomy.
B) skill variety.
C) security.
D) teamwork.
E) gainsharing.
Page Ref: 180
Skill: Applied
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 4
62) Job enrichment is
A) giving an employee more tasks while paying at the same level.
B) expanding a job horizontally.
C) a result of downsizing, as employees must cover the duties of the departed employee.
D) giving an employee a title which suggest he or she has more responsibility, but in fact does not.
E) expanding a job vertically.
Page Ref: 183
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 5
63) Job enrichment refers to
A) the vertical expansion of jobs.
B) the horizontal expansion of jobs.
C) both vertical and horizontal expansion of jobs.
D) the complexity of motivational incentives being offered in the workplace.
E) the relationship between motivation and bonuses.
Page Ref: 183
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 5
64) Job enrichment increases the degree to which workers control the
A) number of motivational incentives in the workplace.
B) hours and pay of their job.
C) ability to communicate with managers within the workplace.
D) planning, motivation and incentives of their work.
E) planning, execution and evaluation of their work.
Page Ref: 183
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 5
65) The JCM describes jobs in terms of five core dimensions
A) motivational factors, performance outcomes, satisfaction, activities, and growth.
B) skill variety, task identity, task significance, autonomy and feedback.
C) meaningfulness, experience, outcomes, tasks, skill acquisition.
D) collaboration, choice, evaluation, motivation and opportunity.
E) skill variety, collaboration, outcomes, satisfaction and feedback.
Page Ref: 179
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 4
66) Within the JCM, core job dimensions can be combined into a single predictive index called the
A) motivating polarized score.
B) motivating positive self-esteem.
C) motivating positive score.
D) motivating potential score.
E) motivating predictive score.
Page Ref: 181
Skill: Recall
Topic: Job Redesign
Objective: 4
67) If jobs score high on motivating potential, the MPS model predicts improved
A) teamwork, collaboration and achievement.
B) responsibility, growth and commitment.
C) empowerment, involvement and development.
D) teamwork, performance and satisfaction.
E) motivation, performance and satisfaction.
Page Ref: 181
Skill: Applied
Topic: Job Redesign
Objective: 4
68) When two or more people split a 40 hour a week job it is called
A) job compression.
B) job sharing.
C) job rotation.
D) telework.
E) job expansion.
Page Ref: 187
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 6
69) Flextime is short for
A) flexible time off.
B) flexible employee schedules.
C) flexible work hours.
D) flexible variations at work.
E) flexible break times.
Page Ref: 184
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 6
70) The three categories of jobs identified as most appropriate to telecommuting are
A) routine information-handling tasks, public relations tasks, and repetitive tasks.
B) routine information-handling tasks, intricate tasks, and repetitive tasks.
C) routine information-handling tasks, mobile activities and professional/knowledge-related tasks.
D) routine information-handling tasks, managerial tasks, and service-related tasks.
E) routine information-handling tasks, routine tracking tasks, and routine organizational tasks.
Page Ref: 187
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 6
71) Jessica works from her home via her computer, which is linked to her office network. This is an example of
A) telecommuting.
B) job sharing.
C) job enlargement.
D) flextime.
E) job rotation.
Page Ref: 186
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 6
72) The major difficulty of job sharing is
A) finding a compatible pair of employees who can successfully coordinate the demands of the job.
B) finding a clear and concise job description to share.
C) finding enough employees to fill the position.
D) finding a job where the manager can deal with this recent phenomenon.
E) finding a job with a clear division of labour.
Page Ref: 186
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 6
73) Job sharing is defined as the practice of
A) having an employee share his or her experience with other employees.
B) having two or more people split a 40-hour-a-week job.
C) having an employee work at home for a portion of the week.
D) having an employee report on the effectiveness of his or her performance.
E) having two or more people working at the same time.
Page Ref: 186
Skill: Applied
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 6
74) When a manager located in Vancouver reports to an executive in Toronto regarding work being done in Calgary, this is an example of
A) job sharing.
B) telecommuting.
C) job enriching.
D) job friendly.
E) satellite communication.
Page Ref: 187
Skill: Applied
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 6
75) Telecommuting is defined as
A) conducting business via technology.
B) conducting job through smartphone outreach in your community.
C) an arrangement where employees are encouraged to meet with clients via technology, rather than make face-to-face visits.
D) an arrangement where employees work away from an office, connecting to work and office via technology.
E) an arrangement where employees fax documents from home to office.
Page Ref: 187
Skill: Applied
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 6
76) When an organization has employees who sit on the company's board of directors the company is increasing employee involvement through
A) participative management.
B) collaborative labour relations.
C) representative participation.
D) hierarchical participation.
E) high power distance.
Page Ref: 189
Skill: Recall
Topic: Employee Involvement
77) Participative management includes
A) workers setting targets with co-workers.
B) subordinates reporting to supervisors.
C) workers participating as team leaders.
D) subordinates sharing decision-making with immediate superiors.
E) workers sitting on the board of directors.
Page Ref: 189
Skill: Recall
Topic: Employee Involvement
78) Participative management is linked to
A) Herzberg's hygiene.
B) Herzberg's dissatisfaction scale.
C) Theory X.
D) Theory Y.
E) McClelland's need for power.
Page Ref: 190
Skill: Recall
Topic: Employee Involvement
79) Nunavut has had great difficulty finding doctors willing to commit to serving the territory for more than short periods of time. This problem could be solved by
A) job enrichment.
B) job redesign.
C) job enlargement.
D) job sharing.
E) gainsharing.
Page Ref: 187
Skill: Applied
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 6
80) Bill Leung is the HR Director for Copper Inc., a mining firm. The business has been losing money over the past three years due to a worldwide slump in copper prices. There is pressure to reduce labour costs and increase productivity. Bill must recommend a plan for the research department staff. It's difficult to assess researchers' performance because of the kind of work they do. Recently, a number of researchers have been laid off because of the company's losses; remaining staff members must get involved in new projects. Flexibility and communication between project team members is very important. What kind of incentive plan would meet Bill's needs best?
A) skill-based pay
B) piece rate
C) profit sharing
D) ESOP
E) gainsharing
Page Ref: 172
Skill: Applied
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
Objective: 1
81) Ama Foods uses thank you cards to express gratitude to individuals and teams that have benefited the organization. This is an example of management providing
A) extrinsic rewards.
B) intrinsic rewards.
C) gainsharing.
D) skill-based compensation.
E) flexible benefits.
Page Ref: 174
Skill: Applied
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
82) Carol works for a tailor and she is being paid a fixed sum for each garment that she alters to customer specifications. Carol is receiving pay that is
A) merit-based.
B) skill-based.
C) piece-rate.
D) gainsharing.
E) ESOP.
Page Ref: 169
Skill: Applied
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
Objective: 1
83) The production workers at ABC Inc. were getting better at their jobs as they gained more experience with the new technology that had recently been installed. The company knew that significant savings would result if they continued to be able to produce the same number of units of product in less time. To motivate the workers to do so, ABC Inc. should consider using
A) stock options.
B) bonuses.
C) gainsharing.
D) piece-rate wages.
E) intrinsic rewards.
Page Ref: 172
Skill: Applied
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
84) People who work at baseball parks selling peanuts and soft drinks are typically paid according to
A) salary.
B) bonuses.
C) piece rate.
D) gainsharing.
E) profit sharing.
Page Ref: 169
Skill: Recall
Topic: Creating Effective Reward Systems
85) Employee involvement strategies try to increase an employee's
A) distributive justice.
B) organizational commitment.
C) organizational rivalry.
D) participative management.
E) gainsharing.
Page Ref: 189
S。kill: Recall
Topic: Employee Involvement
5.3 Essay Questions
1) Using examples, contrast job rotation, job enlargement and job enrichment.
Answer: Suggested answer:
- Job rotation—cross-training; rotation to another job at same level with similar skill requirements; allows for more flexibility in scheduling, adapting to change, and filling vacancies. - Job enlargement—expanding jobs horizontally; increasing number and variety of tasks; more job diversity; does little to add challenge or meaningfulness to work activities.
- Job enrichment—vertical expansion of jobs; increases degree to which worker controls planning, execution and evaluation of work; allows worker to do complete activity; increases freedom, independence and responsibility; provides feedback. (Examples can be drawn from text, class discussion, Internet, newspapers such as Globe and Mail, etc.)
Type: ES Page Ref: 182-183
Skill: Applied
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 5
2) Discuss, using examples, the three alternative work arrangements: telecommuting, job sharing, and flextime.
Answer: Suggested answer:
Telecommuting allows employees to work anywhere away from the office; generally increases employee satisfaction, reduces turnover, absenteeism; easier to recruit employees; positive impact on environment; additional support for managing work and family conflicts. Allows management to reduce office costs and draw from a large supply of available talent
- Job sharing—allows two or more individuals to split traditional 40-hour workweek; draws on talents of more than one individual; opportunity to acquire skilled workers who may not be available on full-time basis; increases flexibility and motivation.
- Flextime—flexible work hours; some employee discretion over arriving and leaving work; established core hours; accumulate extra hours for free day; reduced absenteeism and increased productivity; lessened hostility toward management; reduced overtime expenses; reduced traffic congestion; elimination of tardiness; increased autonomy, responsibility, satisfaction. (Examples can be drawn from text, class discussion, Internet, newspapers such as Globe and Mail, etc.)
Type: ES Page Ref: 184-188
Skill: Applied
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 6
3) Identify and describe five actions a manager can take to enrich jobs.
Answer: Suggested answer:
- Combine tasks—combine fractionalized tasks to form new and larger modules of work; increase skill variety and task identity.
- Create natural work units—tasks form an identifiable and meaningful whole; increases employee ownership; work viewed as meaningful and important rather than irrelevant and boring.
- Establish client relationships—direct relationships between workers and customers; increases skill variety, autonomy and feedback.
- Expand jobs vertically—employees given responsibility and control formerly reserved for management; closes gap between the doing and controlling aspects.
- Open feedback channels—information on performance; how well employees are doing and whether performance is improving, deteriorating or remaining constant; feedback should be immediate rather than occasional. (Examples can be drawn from text, class discussion, Internet, newspapers such as Globe and Mail, etc.)
Type: ES Page Ref: 178-183
Skill: Applied
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 4
4) Money alone does not motivate. Explain the latest research findings of how pay affects employees.
Answer:
- high pay has a moderate relationship to job satisfaction.
- high pay leads to autonomy, but does not increase well-being or happiness.
- Boomer and Millennials find having great teams to work with, challenging work assignments, new experiences, and recognition to be as important as money.
-personality and demographics may influence a person's attitude to money.
-men value money more than women, women tend to value recognition more highly than money.
Type: ES Page Ref: 166
Skill: Recall
Topic: Motivating by Job Redesign
Objective: 3
5) Identify and explain a variable-pay program for each of the following: individual level, group level and organizational level.
Answer:
-individual level: piece-rate pay plans, merit-based pay plans, bonuses or skill-based pay
- group level: gainsharing
-organizational level: profit-sharing plan, ESOP
Type: ES Page Ref: 168-173
Skill: Recall
Topic: The Role of Money
Objective: 3
[Show More]











.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)