NR508 Midterm Outline
Midterm Outline
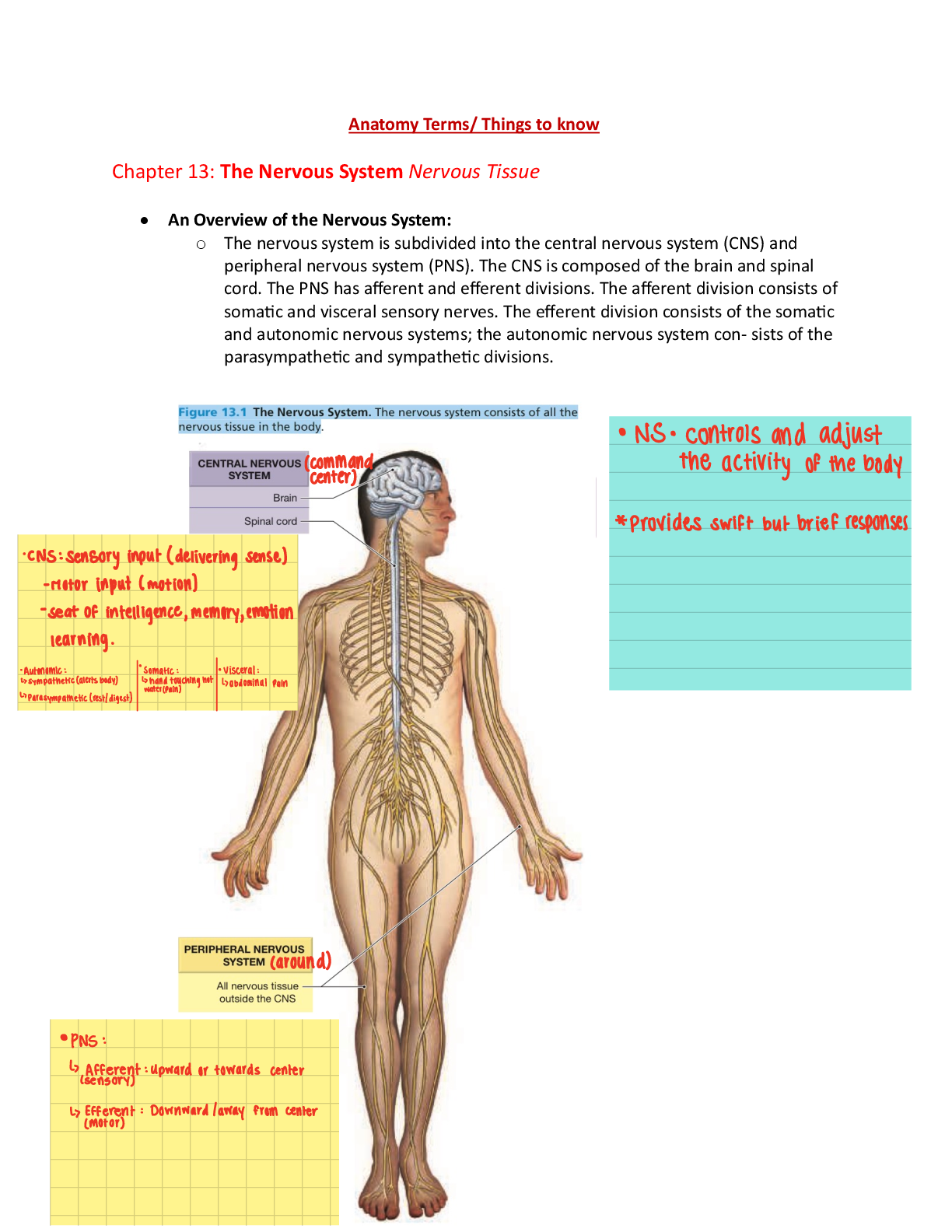
Chapter 1: The Role of the Advanced Practice Nurse as Prescriber
Roles and responsibilities of APRN prescribers
Clinical judgement in Prescribing
Collaboration with other provid
...
NR508 Midterm Outline
Midterm Outline
Chapter 1: The Role of the Advanced Practice Nurse as Prescriber
Roles and responsibilities of APRN prescribers
Clinical judgement in Prescribing
Collaboration with other providers
Autonomy and Prescriptive authority
Chapter 2: Review of Basic Principles of Pharmacology
Metabolism: Metabolism & Half Life
Drug Responses
Receptors: agonists, antagonists
Pharmacokinetics: Absorption, Distribution, Protein Binding, Metabolism (including firstpass and Phase I and II)
Cytochrome P450 metabolism
Excretion: Renal, Biliary, Other (eg for volatile drugs)
Chapter 3: Rational Drug Selection
Process of rational drug prescribing: 6 Steps proposed by WHO:
Define the patient's problem
Specify the therapeutic objective
Collaborate with the patient
Choose the treatment
Educate the patient
Monitor effectiveness
Patient education Poor adherence contributes to worsening disease, hospital admissions and
death
Patient education should be at the 5th or 6th grade level
Include in education:
Purpose of medication
Instructions for administration
Adverse drug reactionsMonitor effectiveness Passive monitoring: patient is educated on expected outcome and
instructed to contact provider
Active monitoring: follow up laboratory tests or monitoring to measure therapeutic effectiveness
Drug, Patient, and Provider factors that influence drug selection
DRUG:Pharmacokinetic factors
Pharmacodynamics factors
Therapeutic factors
Safety
Cost
Patient factors
Provider factors
Alternative therapies
PATIENT: Previous adverse drug reactions
Health beliefs
Current drug therapy
Drug interactions
Consult PharmD regarding complex drug regimens
Patient age
Pregnancy
PROVIDER: Ease of prescribing or monitoring
Formularies
NPs need to be familiar with the formulary they are allowed to prescribe
Personal formulary: each provider develops a small list of drugs they are comfortable
prescribing
Influences on Rational Prescribing: Pharmaceutical Promotion Pharmaceutical promotion
May influence prescribing
When Prescribing Recommendations Change
When guidelines change, providers may need to be coached or reeducated regarding appropriate
prescribing
Chapter 4: Legal and Professional Issues in Prescribing
New Drug Approval process including Clinical Phases
U.S. FDA Regulatory Jurisdiction: official labelling vs off-label use of drugs
Chapter 5: Adverse Drug Reactions
Mechanistic Classification of ADRs including Types of Immune-Mediated ADRs and
Types A-F
Common Causes of ADRs: Risk Factors, including common drugs involved and which
cause skin reactionsTime-Related Classification of ADRs including drugs associated with withdrawal
symptoms
Dose-Related ADRs classification
Chapter 6: Factors that Foster Positive Outcomes
Overview of nonadherence
Keys to effective patient education
Health and Cultural beliefs
Health Literacy
Complexity of Drug Regimen and Polypharmacy
Simplifying the Regimen
Communication Difficulties
Chapter 9: Nutrition and Nutraceuticals
Nutrient-Drug Interactions (eg warfarin and vit K)
Influence of Diet on Pharmacokinetics of Drugs:
Drug absorption
Drug Metabolism
Grapefruit juice and CYP3A4
Cruciferous foods and CYP1A2
Drug Excretion
Drug -Induced Nutrient Depletion (eg folate and B12)
Outcomes of Nutrient-Drug Interactions
Nutritional Management: Table 9-2 Recommended vitamins for the following special
populations: infants and children; women of child bearing age; pregnant women
vegans, older adults; those not exposed to sunlight or with dark skin; alcoholics;
patients taking isoniazid (INH)
Nutraceuticals:
Vitamin that is teratogenic in excessive amounts,
Vitamin that is useful for migraine prophylaxisChapter 12: Pharmacoeconomics
Know what Pharmacoeconomics is
Impact of Cost: Direct and Indirect
Chapter 13: Over-the-counter Medications
OTC Medication characteristics and regulation
OTC Medication Sales
Hazards of OTC Self-Medication
Adverse Effects of OTC Self-Medication
Drug Interactions: antacids, anticholinergics, CNS Depressants, NSAIDS and ASA
Abuse of OTC Medications: Combat Methamphetamine Epidemic Act
Patient Education Regarding OTC Medications
Chapter 14 Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Nervous System
Pharmacodynamics of Alpha2 Agonists
Pharmacodynamics of Beta Blockers, adverse effects, what happens with abrupt
withdrawal of Beta Blockers?
Pharmacokinetics: Beta blockers
Phamacotherapeutics: precautions and Contraindications of beta blockers
Adverse Drug Reactions
Clinical Uses and Dosing of Beta Blockers
Muscarinic Agonists: Pharmacodynamics, MOA, treatment uses,
Chapter 15 Drugs Affecting the Central Nervous System
Anorexiiants: Precautions and Contraindications,
Iminostilbenes: Metabolism and Excretion, MOAs, indications, absolute
contraindications, precautions, monitoring, adverse drug reactions, drug interactions,
Black Box warnings,What does Long Term monitoring consist of with Iminostilbenes?
Succinimides: MOA, Monitoring
Drugs That Affect GABA: Monitoring, ADR’s, Pharmacotherapeutics: Precautions and
Contraindications, Patient Education, Drug interactions(Lamotrigine)
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCA): Precautions and Contradictions,
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors(MAOIs): drug interactions Table15-13, Food and drug
interations.
SSRI: Adverse Drug Reactions, management in children, Drug interactions (including
herbals & supplement), Patient Education
Chapter 28 Chronic Stable Angina and Low Risk Unstable Angina
Additional Patient Variables: Concomitant Diseases
Beta Blocker-diabetes Mellitus
Chapter 36: Heart Failure
Indications for heart failure drugs by stage
First line drugs of choice for heart failure
MOA of ACEIs that benefit heart failure
Indications for use of BBs in patients with heart failure
Drugs that increase life expectancy in patients with heart failure
Digoxin indications and adverse reactions
Drugs contraindicated in heart failure
Drugs for managing heart failure during pregnancy
Patient monitoring of HF
Indications to use anticoagulant therapy
Patient educationChapter 40 Hypertension
Classes of drugs used and their MOAs: Nitrates, BBs, CCBs, ACEIs,
What drugs increase myocardial oxygen supply
Causes of hypertension
Which drugs treat hypertension & BPH, MI, Heart Failure African Americans.
[Show More]
.png)