Economics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Pennsylvania State University - ECON 102Exam_2_More_Practice_Key. (All)
Pennsylvania State University - ECON 102Exam_2_More_Practice_Key.
Document Content and Description Below
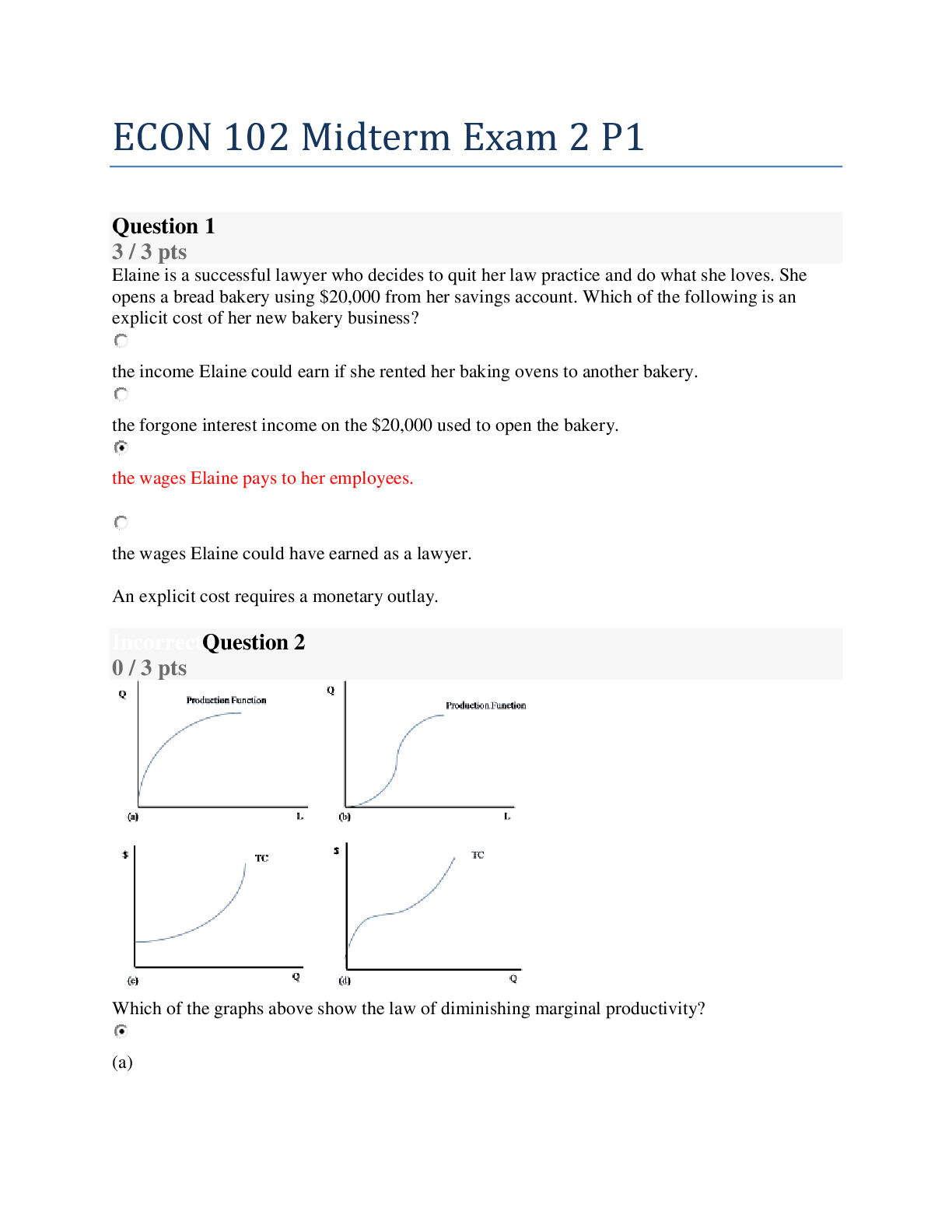
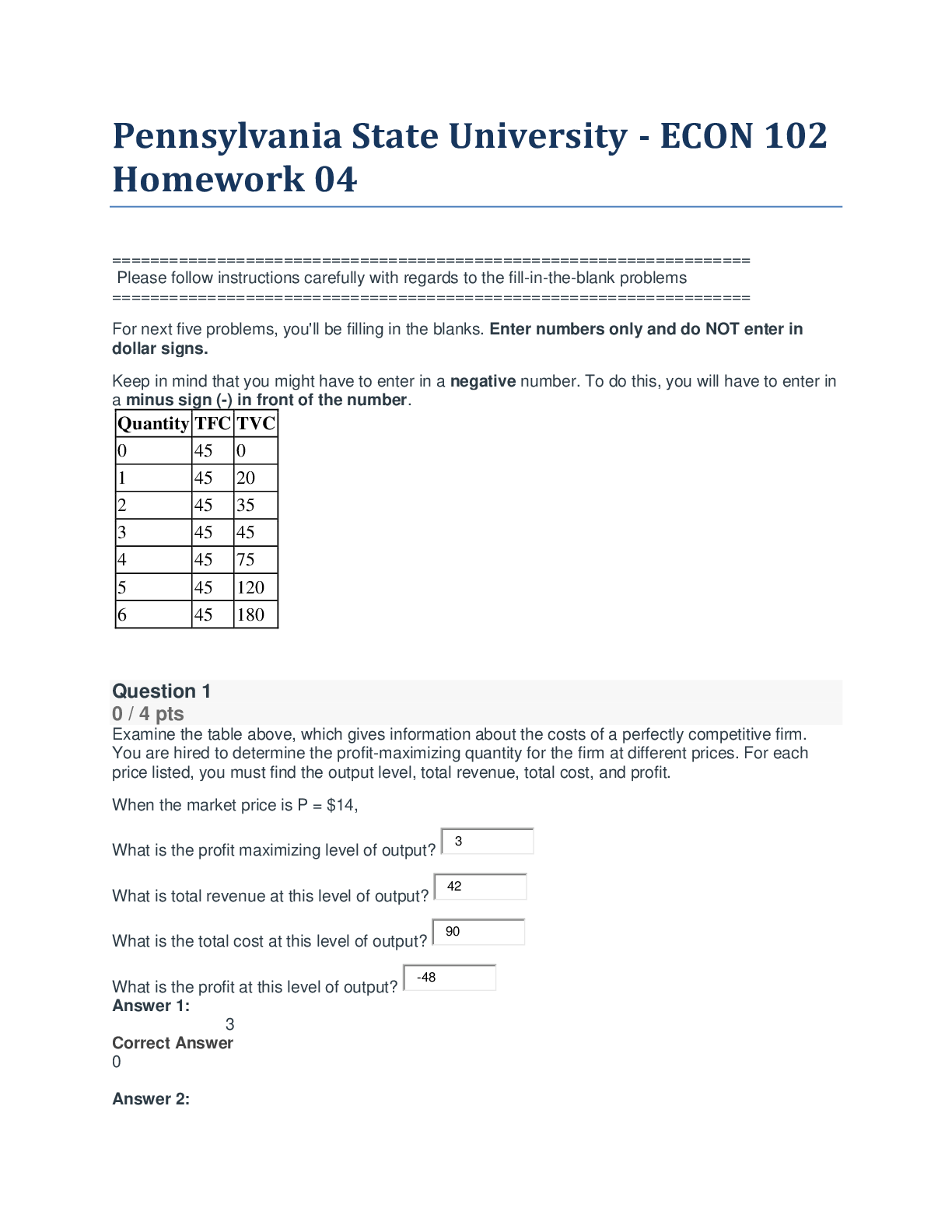
A. Explain the shape of the short run marginal product of labor (MPL) curve B. Explain the shape of the short run marginal cost (MC) curve and average cost (ATC, AVC) curves C. Explain the shape ... of the long run average cost curve (LRAC). How is the long-run average cost (LRAC) curve found? What is its importance to the firm? ECON102 – Dr. Dave Brown – Exam 2 More Practice Key 1. For a hotdog vender, the hotdog stand represents his A. fixed input. B. variable input. C. diseconomies of scale. D. none of the above. 2. For a hotdog vender, the hotdog buns represents his A. fixed input. B. variable input. C. sunk cost. D. none of the above. 3. The concept of the production function implies that a firm using resources inefficiently will A. obtain less output than the theoretical production function shows. B. obtain more output than the theoretical production function shows. C. obtain exactly the amount that the theoretical production function shows. D. not be subject to diminishing marginal product. 4. A negative value for the marginal physical product would indicate that A. the company has not yet reached the point of saturation. B. total output increased by a significant amount. C. total output decreased when the extra unit of the variable input was added. D. total output increased, but the increase was very small. 5. If the marginal product curve is increasing from workers 1-89 and then decreases steadily, crossing the horizontal axis at 190 workers, we know that A. the total output curve increases from workers 1-89, decreases from workers 90-189, and becomes 0 at the 190th worker. B. the total output curve is increasing at an increasing rate from workers 1-89, then increases at a decreasing rate until the 190th worker, after which it decreases. C. the total output curve is increasing throughout, although at an increasing rate for the first 190 workers and at a decreasing rate after the 190th worker. D. diminishing marginal product sets in with the 190th worker. 6. Marginal physical product of the first worker is 100, 120 for the second, 80 for the third, 30 for the fourth, 5 for the fifth, 3 for the sixth, 2 for the seventh, 1 for the eighth, and 0 for the ninth. What is total product after the fifth worker and the ninth worker are added, respectively? A. 335; 341 B. 335; 0 C. 5; 0 D. 0; 5ECON102 – Dr. Dave Brown – Exam 2 More Practice Key 7. In the above table, average physical product is 30 snowboards when A. 4 workers are employed. B. 3 workers are employed. C. 2 workers are employed. D. 1 worker is employed. 8. In the above table, when the firm employs 4 workers, the marginal product will be A. 140 snowboards. B. 30 snowboards. C. 35 snowboards. D. 208 snowboards. 9. In the table, when the firm employs 3 workers, the marginal product will be A. 42 snowboards. B. 30 snowboards. C. 36.67 snowboards. D. 208 snowboards. 10. In the above table, how many workers are employed when marginal product reaches its maximum? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 11. In the above table, diminishing marginal product occurs after employing the A. first worker. B. second worker. C. third worker. D. fourth worker. 12. In the above table, marginal product becomes negative after employing the A. second worker. B. third worker. C. fourth worker. D. fifth worker. 13. In the above table, the marginal product of the second worker is A. 68. B. 98. C. 38. D. It cannot be determined. 14. In the above table, the average product of the fifth worker is A. 35. B. 135. C. -5. D. 27. 15. In the above table, which two workers have the same marginal physical product? A. 1 and 2 B. 2 and 4 C. 1 and 3 D. 1 and 4ECON102 – Dr. Dave Brown – Exam 2 More Practice Key 16. Refer to the above table. When the quantity of labor equals 2, what does the average product equal? A. 46 B. 23 C. 26 D. 92 17. Refer to the above table. When the quantity of labor equals 3, what does the average product equal? A. 21 B. 17 C. 63 D. 189 18. Refer to the above table. When the quantity of labor equals 4, what does the average product equal? A. 9 B. 18 C. 72 D. 216 19. Refer to the above table. What does the marginal product equal when the quantity of labor goes from 1 to 2? A. 46 B. 23 C. 26 D. 92 20. Refer to the above table. What does the marginal product equal when the quantity of labor goes from 2 to 3? A. 21 B. 17 C. 63 D. 189 21. Refer to the above table. What does the marginal product equal when the quantity of labor goes from 3 to 4? A. 9 B. 18 C. 72 D. 216ECON102 – Dr. Dave Brown – Exam 2 More Practice Key 22. Refer to the above table. At an output of 4 units, average variable costs are A. $16. B. $22. C. $38.50. D. $44. 23. At an output of 3 units, average variable costs are A. $42. B. $30. C. $44. D. $14. 24. At an output of 2 units, average total costs are A. $61. B. $122. C. $16. D. $45. 25. At an output of 5 units, average total costs are A. $18. B. $19. C. $37. D. $185. 26. When output rises from 2 units to 3 units, marginal costs are A. $7. B. $10. C. $22. D. $41. 27. When output rises from 3 units to 4 units, marginal costs are A. $16. B. $10. C. $22. D. $31. 28. When output rises from 4 units to 5 units, marginal costs are A. $19. B. $10. C. $22. D. $31. 29. When output rises from 2 units to 5 units, marginal costs are A. $26.50. B. $31. C. $21. D. $63. 30. What is AVC at an output of 2 units? A. $7 B. $16 C. $45 D. $61 31. What is MC when output rises from 0 unit to 1 unit? A. $0 B. $25 C. $90 D. $115 32. MC is the lowest A. between 0 and 1 units of output. B. between 1 and 2 units of output. C. between 3 and 4 units of output. D. at 0 units of output.ECON102 – Dr. Dave Brown – Exam 2 More Practice Key 33. In the above figure, if this firm produces output level Q2, it has average variable costs of A. OF B. OE C. OC D. OD 34. In the above figure, if this firm produces output level Q2, it has average total costs of A. OF B. OE C. OC D. OD 35. In the above figure, at an output level of Q1, total variable cost is A. OF * Q1 B. OD * Q2 C. OF D. OF -- DF Where does this answer come from? Note that Q TVC AVC . On the graph, we are presented with the AVC curve, and given a level of output. We can use the equation and use multiplication to find the TVC.ECON102 – Dr. Dave Brown – Exam 2 More Practice Key 36. Use the above figure. The TFC at output level 10 is A. $10. B. $3. C. $2. D. $1. 37. The AFC at output level 20 is A. $10.00. B. $0.50. C. $3.00. D. $1.00. 38. The ATC at output 10 is A. $30.00. B. $2.67. C. $2.00. D. $3.00. 39. The AVC at output 10 is A. $20.00. B. $1.00. C. $2.00. D. $3.00. 40. The ATC at output 5 is A. $25.00. B. $2.00. C. $3.00. D. $5.00. 41. The AVC at output 5 is A. $35.00. B. $2.00. C. $3.00. D. $5.00.ECON102 – Dr. Dave Brown – Exam 2 More Practice Key 42. Which of the following statement is correct? A. When Marginal Product is greater than Average Physical Product, Average Physical Product is increasing. B. When Marginal Product is greater than Average Physical Product, Average Physical Product is decreasing. C. When Marginal Product is greater than Average Physical Product, Average Physical Product is equal to Total Product. D. When Marginal Product is greater than Average Physical Product, Total Product is increasing at a decreasing rate. 43. Suppose the total output curve increases at an increasing rate for workers 1-50, increases at a decreasing rate from workers 51-101, and decreases beyond 101 workers. We would know that A. marginal product is increasing from workers 1-50 and then becomes negative after worker 51. B. marginal product is increasing from workers 1-50, decreasing after 51 workers, and becomes negative after the 101st worker. C. marginal product is decreasing from workers 1-101, becoming negative at the 102nd worker. D. marginal product is increasing from workers 1-50, constant from workers 51 to 101, and is decreasing after that. 44. A firm's long-run average cost curve is A. the locus of points representing the minimum unit cost of producing any given rate of output when all inputs may be adjusted. B. the locus of points made up of the minimum point on each short-run average total cost curve when only one input may be adjusted. C. the envelope of the firm's variable cost curves. D. identical to the lowest short-run average cost curve the firm has. 45. The long run is A. over one year. B. over five years. C. when all factors of production are fixed. D. the time period in which all factors of production can be varied. 46. Which of the following is TRUE for a firm in the long run? A. Variable costs will initially increase and then decrease. B. The law of diminishing marginal product holds. C. All costs are variable costs. D. Variable costs will equal marginal cost at all output levels.ECON102 – Dr. Dave Brown – Exam 2 More Practice Key 47. Constant returns to scale are illustrated by A. a downward sloping long-run average cost curve. B. a horizontal long-run average cost curve. C. an upward sloping long-run average cost curve. D. a long-run average cost curve that is shaped like an upside down U. 48. Economies to scale are illustrated by A. a downward sloping long-run average cost curve. B. a horizontal long-run average cost curve. C. an upward sloping long-run average cost curve. D. a long-run average cost curve that is shaped like an upside down U. 49. Diseconomies to scale are illustrated by A. a downward sloping long-run average cost curve. B. a horizontal long-run average cost curve. C. an upward sloping long-run average cost curve. D. a long-run average cost curve that is shaped like an upside down U. 50. When a firm is at its minimum efficient scale of operation, it produces the A. maximum rate of output at which long-run average cost is minimized. B. minimum rate of output at which long-run average cost is minimized. C. maximum rate of output consistent with lowest long-run marginal cost. D. minimum rate of output consistent with lowest long-run marginal cost [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 10 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$12.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 28, 2021
Number of pages
10
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 28, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
78






.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)