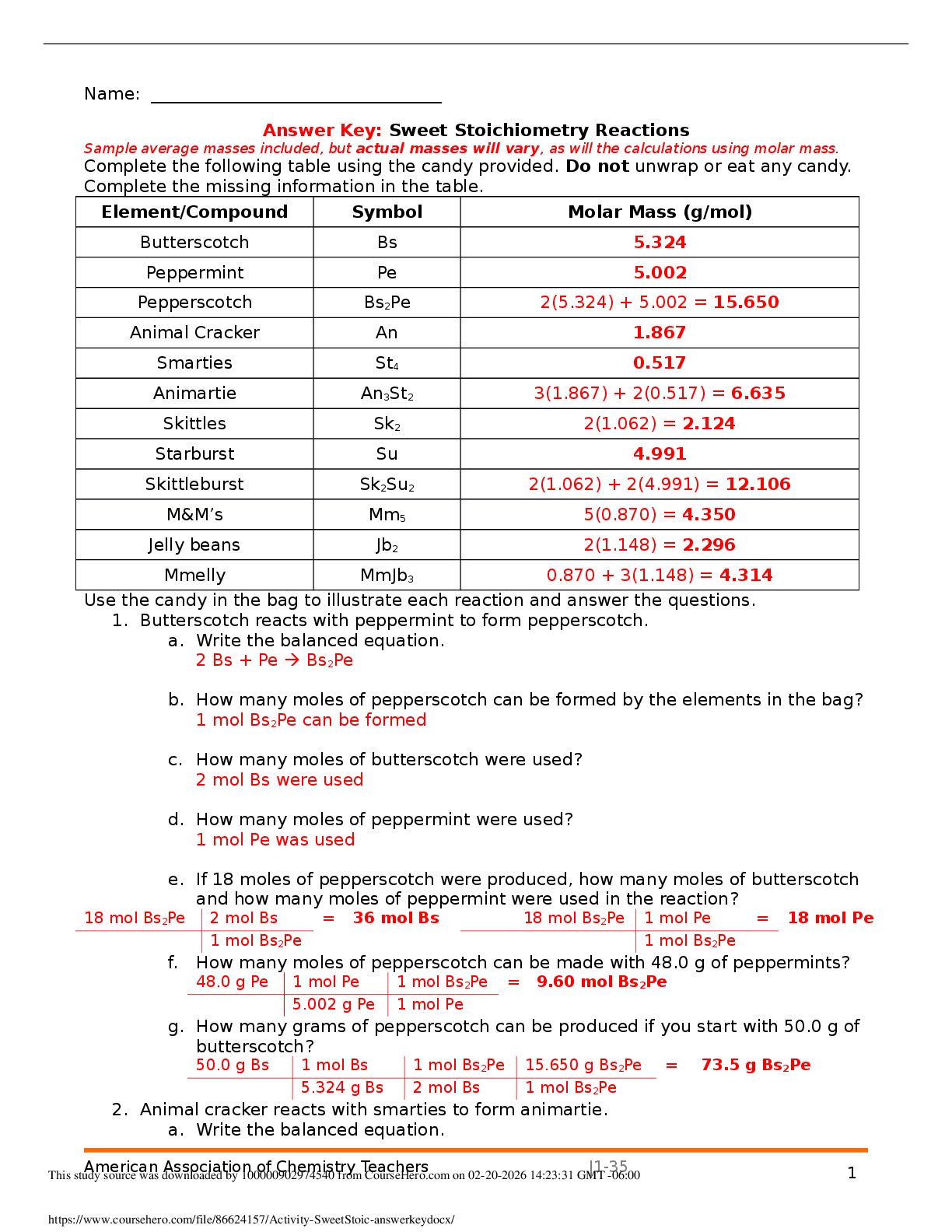
• Discuss the influences that we highlighted that made up the style of Alfred Hitchcock. Give specific people and artistic influences as well as personal influences and idiosyncrasies.
• The films of Dario Argento sho
...
• Discuss the influences that we highlighted that made up the style of Alfred Hitchcock. Give specific people and artistic influences as well as personal influences and idiosyncrasies.
• The films of Dario Argento show a strong artistic influence. What movement does he follow particularly and who are some of the major artists of this movement. What are the characteristics found in his work and in the movement?
• How did the art of the 1960s which we studied get reflected in popular culture? Names some artists and works and the influence that they had.
• What in your opinion was the significance of Vera-Ellen's artistry and what do you think happened to her that caused her to end her days in the manner that she did? Discuss her secret problem and obsession. What were her particular talents and how did she display them?
Burt Williams
• (1874-1922)
• First major black star to cross color lines
• Performed in Black Face
•
Bill "bojangles" Robinson
• (1878-1949)
• Famous vaudevillian tap dancer
• Grandson of slaves who became one of the best tap dancers of his age
clarity of steps, slow pace, stair dance, shuffle dancer
•
Nicholas Brothers
• Fayard Nicholas (1914-2006) and Harold Nicholas (1921-2000)
• Flash dancing, acrobatic dancing, leaps, somersaults, slipping and sliding all over floor/Bakelite floor
•
Loreena McKennitt
• (1957-present)
• Canadian Celtic and Romantic musician
• Pre-Raphaelite
• songs: The Bonny Swans and Lady of Shallot
Fred Astaire
• (1899-1987)
• American dance icon 1930s
• Famously paired w/ Ginger Rogers and Vera Ellen
• Depression modernistic style (streamlining)
• Curvilinear patterns
• Symbol of the Great Depression
•
Vera-Ellen Westmeier Rohe
• (1921-1981)
• Origins in Ohio
• Billy Rose showgirl
• MGM star; made her change her body shape
• American actress and dancer known for her versatile dancing
• Anorexia and OCD
• Crying scene in Call Me Madame
• modern dance and jazz dance
Gene Kelly
• Trained Vera-Ellen
•
Clara Bow
• 1920s
• "It girl"
• drinking, smoking, dancing
• coined the American flapper style
•
Busby Berkeley
• (1896-1976)
• Highly influential Hollywood movie director and musical choreographer for Warner Bros and MGM
• Daredevil dance designer
• Sex, closeups, cosmetics, racism
• Sadistic and sexist treatment of women
• Used lots of geometric shapes, kaleidoscope shots and tiers when choreographing
• Gold-diggers film 1933
• Footlight Parade film 1934
• The Gang's All Here film 1943
• Always drunk when working; killed someone
•
Gold-diggers
• Film by Busby Berkley 1933
•
Footlight Parade
• Film by Busby Berkeley 1934
•
The Gang's All Here
• Film by Busby Berkeley 1943
•
Alfred Hitchcock
• (1899-1982)
• master of suspense
• movie producer, director and designer
• poultry dealer and fruit importer in London
• desire to distrust and punish blonde women
• Henley's art department
• says "Achtung" for "action"
5 facts in Hitchcock's movies
• kamospeal lighting
• original sin
• incompetence of police
• characters w/ obsessions
• appearance vs. reality
Saboteur
• 1942
• Film by Alfred Hitchcock
• With Robert Cummings and Priscilla Lane
•
Psycho
• Film by Alfred Hitchcock
•
Blackmail
• film by Alfred Hitchcock
•
Andy Warhol
• (1928-1987)
• American pop artist
• Obsession with mass production
• Work showed from precision and lacked any visible reference of paint texture
• Question social values
• Anti commercialism
•
The Beatles
• Influences of Pop Art and Surrealism
• The Yellow Submarine
• International pop icons of the 60s
The Yellow Submarine
• 1968
• Magritte, Kelley and Lictienstein influences
• Highly saturated color and flatness
Timothy Leary
• (1920-1996)
• Connected to surrealism
• Harvard Psychology Professor who experimented with LSD
• LSD tests in 1964
• Created lab at Harvard for testing
• Believed there was a better world beyond this world
• Fired from Harvard- labeled dangerous
•
"Turn on, tune in, drop out"
• Timothy Leary
Allen Ginsberg
• 1950s Beat Generation leader and poet
• Strong feelings about the misuse of the mentally ill, care for the poor and the indifference/evil of the rich
• Buddhism
• Anti-commercialism
•
Raymond Loewy
• (1893-1986)
• Paris, France
• Streamlined
• Modern, industrial, simple, easily mass-produced
• Depression modern style
•
Universal Studios
• Frankenstein, Dracula, The Wolf Man
• Start of the Horror Film in the 30s
• Characteristics: remote haunted rooms, damsels in distress, Gothic Revival feel
The Scream
• Edvard Munch
• 1893
• Cubism
• Pre-Express/Post-Impress
• Psychic aguish, existential loneliness, morbid, disorienting diagonal
Night Café
•
• Van Gogh
• 1888
• Pre-Expressionist/Post-Impressionist
• Background is alive and is fertilized by the artist's emotions
• Shows intense emotional expression
Target with 4 Faces
• Jasper Johns
• 1955
• Pop Art and Post-painterly abstraction
• Hard edges, disciplined lines, geometric, color saturation, full strength of primary colors
•
Persistence of Memory
• Salvador Dali
• 1929
• Surrealist
• Presents many aspects of Surrealist art; wasted time, subconscious, reality
•
Caress of the Sphinx
• Fernand Khnopff
• 1896
• Symbolist
• Angelic woman vs. dangerous woman
•
Orpheus
• Jean Delville
• 1893
• Symbolist
• Jean Delville never discussed his ideas for his painting because he wanted the interpretation of his work to be left to viewers
•
L.H.O.O.Q
• Marcel Duchamp
• 1912
• Dada Art
• Ready-made art that reflects nonsense
•
Spirit of the Dead Watching
• Paul Gauguin
• 1928
• Synthetism and symbolism
• Combined expressive qualities of line and color with a simplified or exaggerated depiction of reality
•
Melancholy of the Street
• Giorgio De Chirico
• 1913
• Surrealism
• De Chirico was the father of surrealist art
• "Sizeless, timeless, airless"
•
Red, Blue, Green
• Ellsworth K
• 1963
• Minimalist
• Color-feel painting
• Popular 50s and 60s
• Celebration of color saturation
•
Johnson's Wax Factory
• (1936-1939)
• Constructed under Frank Lloyd Wright
• Example of the Depression-modern style
• Wisconsin
•
Empire State Building
• 1930
• King Kong movie scene
• Depression Modern Style
• Raymon Shree, William Lamb, Arthur Hormon
Bauhaus
• 1919
• Art school
• College of Fine Arts in Weiner, Germany
• International-style
• Walter Grofius
• Shut down in 1933 by Nazis
Chrysler Building
• Art Deco
• Modernistic
• 1928
• William Van Allen
•
Art Deco
• A popular architectural style in the 1920s
Coke bottle design
• Raymond Loewy
Campbell's soup can
• Andy Warhol
Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque
• Worked closely together in order to create a new style known as Cubism
Les Demoiselles d' Avignon
• Picasso
• 1907
• Cubism
• Shattered pictorial traditions of Renaissance: radical style, critical subject matter
•
Dario Argento
• Master of Italian Horror
• Surrealism
• Directed Inferno (1980)
the Fauves
• "wild beasts"
• Exhibited at 1905 Paris Autumn Salon
• Capitalized on expressive potential of non-local color and the deliberate disharmonies produced from it
Giorgio de Chirico
• Father of Surrealism
Die Brucke
• Members of German Expressionist group who thought their art could pave the way for a more perfect age; to build a bridge from the old to new
Dada
• Movement that arose out of a sense of despair and betrayal in the wake of WWI
Frankenstein
• By Mary Shelly
• 1931
Dracula
• By Bram Stoker
• 1931
Surrealists
• Influenced by Freud and his "logos" theory
• Artists that sought to depict the world of dreams and the unconscious
Jacques Tati
• French actor/director that actor Michael Richards compares his character Cosmo Kramer with on Seinfeld
•
John Wayne
• supported McCarthyism
J. Robert Oppenheimer
• Father of Atomic Bomb
• Greatest teacher in America for Quantum and Nuclear Physics
• The Manhattan Project 1941
Conceptual Art
• Trend in the 20th century modern art
• So radical that is dismissed notion of art as an object
Synthetism
• building up of color
Pop Art
• 1950s
• Style both validated and criticized mass, consumer culture
Androgynes
• Wore the finest, softest clothes, were admired by others, loved the classical tradition and were known for their elongated and sexless looking bodies
Crisscrossing
• Refers to giving the characteristics of one person/object to another
Used by Larry David in "Seinfeld" and "Curb Your Enthusiasm"
• Crisscrossing
Used by Hitchcock in "Saboteur"
• Crisscrossing
blacklisted
• McCarthy era
• Meant you couldn't work
• If you were a screenwriter, you had to have someone take credit for you
Impressionism
• 1860s-early 20th century
• More concerned with optical realism and the natural properties of light
• Rarely responded to political events
• Preferred genre subjects
• Term derived from a critic's negative view of Monet's Impression Sunrise
Pre-Expressionism/Post-Impressionism
• Work of 19th century painters who were greatly influenced by impressionism
• Bright colors and visible brush stokes
Paul Gaugin
• leader of pre-expressionism/post-impressionism
Symbolism
• 19th century
• More psychological and less objective
• Began as literary movement
• Rejected both social consciousness of realism and the impressionist interest in nature
Gustave Moreau and Joseph Peladen
• leaders of symbolist movement
Expressionism
• 20th century
• Tendency of an artist to distort reality for an emotional effect
• Leading painter= Edvard Munch
Analytical cubism
• 1910s
• 1st main branch of cubism
• Analyzed natural forms and reduced them to basic geometric parts on the 2 dimensional plane
• Cylinders, spheres, cones
Synthetic cubism
• 1910s
• 2nd main branch of cubism
• Picasso, Braque and Juan Gris
• Pushing several objects together
Louis Sullivan
• Father of modernism
• creator of skyscraper
• Wainwright building
Art deco knock off (modernistic)
• Cheap material
• 1920-1930
•
Bow house
• Vaulter gropius
• 1919
• Egalitarian nature
• Based on metropolis
•
[Show More]












.png)
.png)
.png)