Economics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > ECON 201 Micro Economics Quizz 4 | California State University, San Marcos (All)
ECON 201 Micro Economics Quizz 4 | California State University, San Marcos
Document Content and Description Below
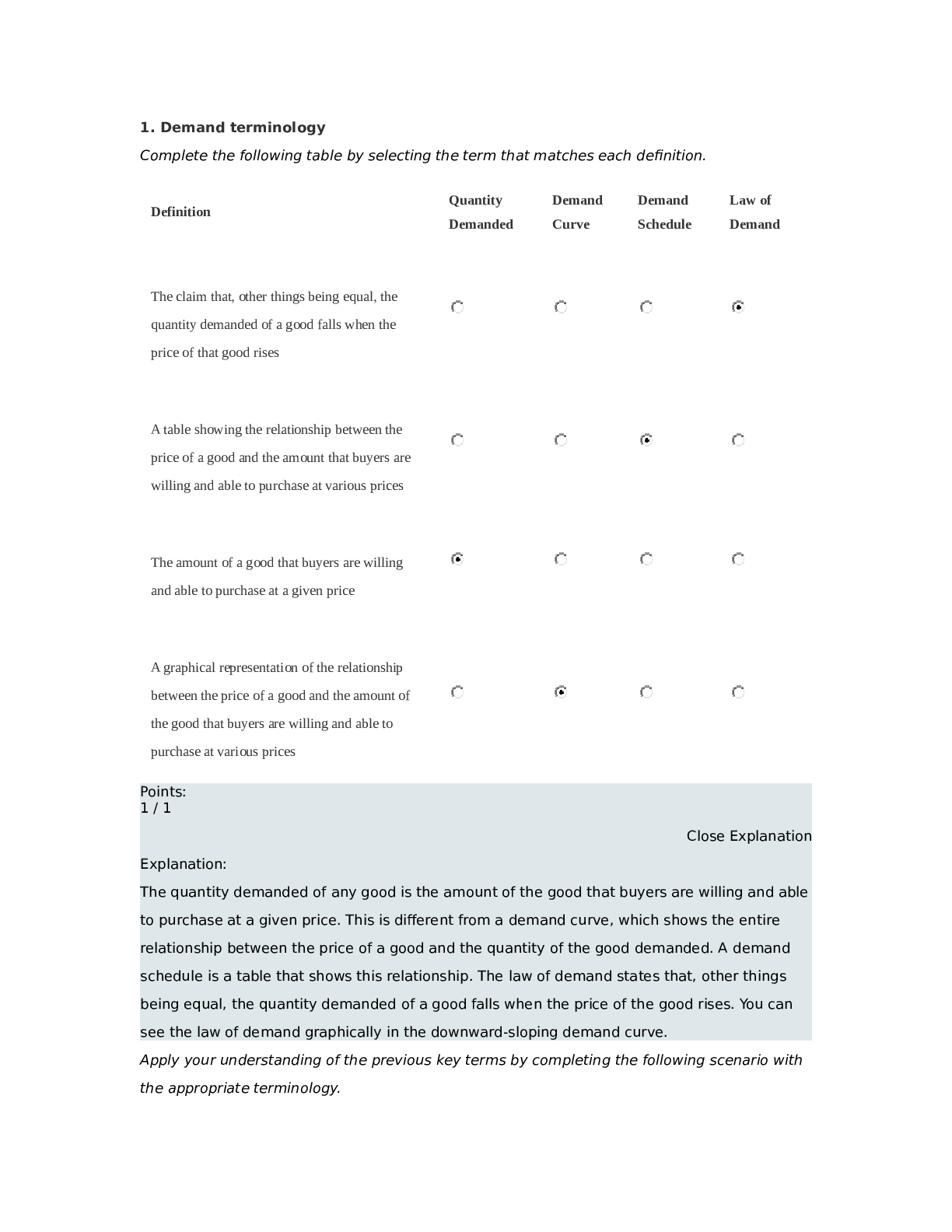
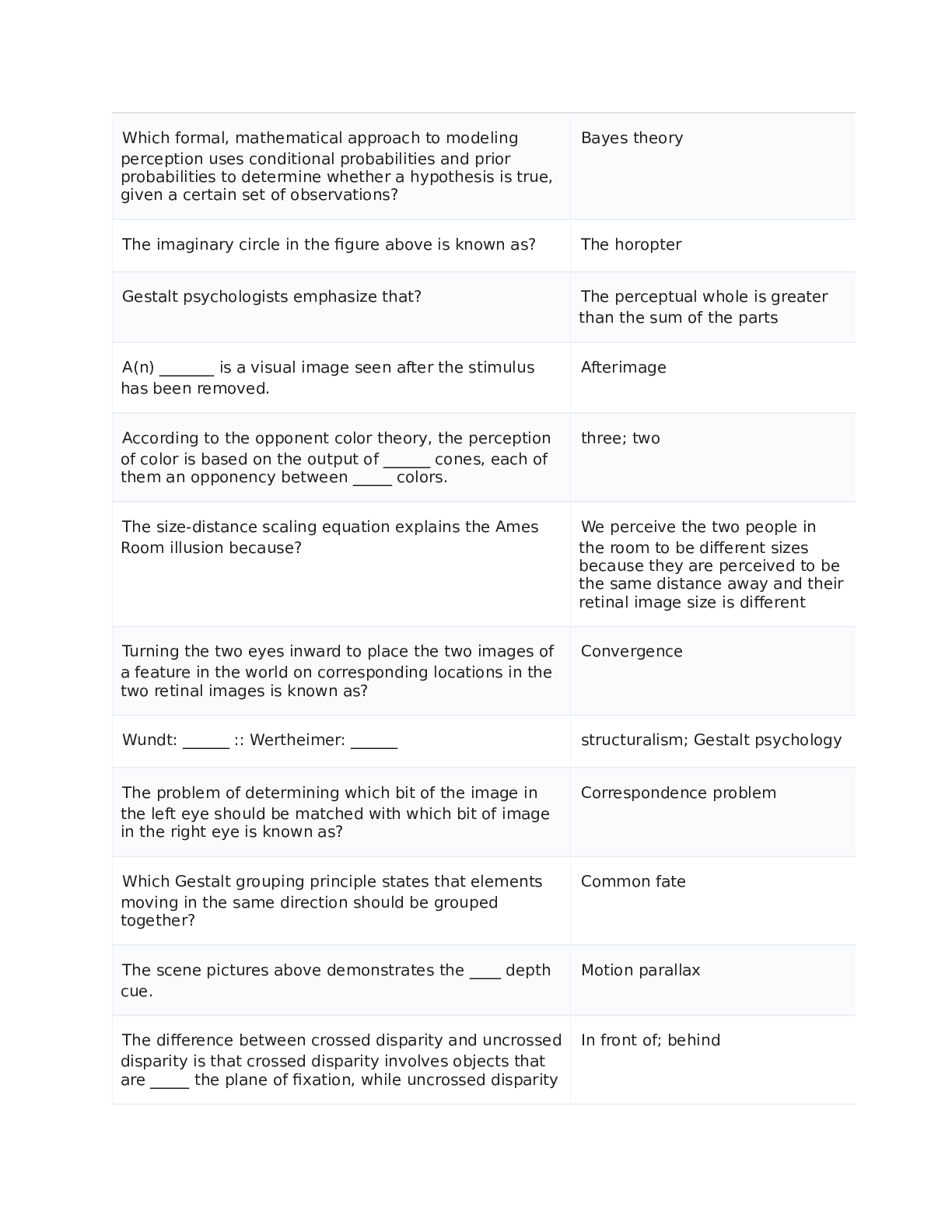
1. Price as a rationing device Suppose that there are three beachfront parcels of land available for sale in Huntington, and six people who would each like to purchase one parcel. Assume that the pa... rcels are essentially identical and that the minimum selling price of each is $575,000. The following table states each person's willingness and ability to purchase a parcel. Willingness and Ability to Purchase (Dollars) Brian 750,000 Crystal 660,000 Edison 600,000 Hilary 550,000 Kevin 520,000 Maria 510,000 Which of these people will buy one of the three beachfront parcels? Check all that apply. Brian Crystal Edison Hilary Kevin Maria Points: 1 / 1 Close Explanation Explanation: Brian, Crystal, and Edison will purchase the parcels because they are the only ones willing and able to meet the minimum selling price of $575,000. One or more of the other three people might have the ability but not the willingness to pay the required price. Moreover, perhaps Hilary, Kevin, and Maria have a strong desire to own beachfront land in Huntington, but they do not have the ability to pay the selling price. Assume that the three beachfront parcels are sold to the people that you indicated in the previous section. Suppose that a few days after the last of those beachfront parcels is sold, another essentially identical beachfront parcel becomes available for sale at a minimum price of $535,000. This fourth parcel will be sold because Hilary will purchase it from the seller for at least the minimum price.Points: 1 / 1 Close Explanation Explanation: To determine what will happen with the fourth parcel, compare the minimum selling price with the willingness and ability to pay of the remaining buyers. The remaining buyer with the highest willingness and ability to pay is Hilary at $550,000. Since $550,000 is greater than the minimum selling price of $535,000 for this parcel, Hilary will purchase the parcel. 1. Price as a rationing device Suppose that there are three beachfront parcels of land available for sale in Huntington, and six people who would each like to purchase one parcel. Assume that the parcels are essentially identical and that the minimum selling price of each is $745,000. The following table states each person's willingness and ability to purchase a parcel. Willingness and Ability to Purchase (Dollars) Felix 900,000 Janet 810,000 Larry 770,000 Megan 720,000 Raphael 690,000 Susan 680,000 Which of these people will buy one of the three beachfront parcels? Check all that apply. Felix Janet Larry Megan Raphael Susan Points: 1 / 1 Close Explanation Explanation: Felix, Janet, and Larry will purchase the parcels because they are the only ones willing and able to meet the minimum selling price of $745,000. One or more of the other three people might have the ability but not the willingness to pay the required price. Moreover, perhaps Megan,Raphael, and Susan have a strong desire to own beachfront land in Huntington, but they do not have the ability to pay the selling price. Assume that the three beachfront parcels are sold to the people that you indicated in the previous section. Suppose that a few days after the last of those beachfront parcels is sold, another essentially identical beachfront parcel becomes available for sale at a minimum price of $732,500. This fourth parcel will not be sold because no one will purchase it from the seller for at least the minimum price. Points: 1 / 1 Close Explanation Explanation: To determine what will happen with the fourth parcel, compare the minimum selling price with the willingness and ability to pay of the remaining buyers. The remaining buyer with the highest willingness and ability to pay is Megan at $720,000. However, since $720,000 is less than the minimum selling price of $732,500 for this parcel, no one will purchase the parcel. The seller will have to lower his minimum selling price if he wants to find a buyer. 2. Price controls in the Florida orange market The following graph shows the annual market for Florida oranges, which are sold in units of 90- pound boxes. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph. Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly.Graph Input Tool Market for Florida Oranges Price (Dollars per box) 15 Quantity Demanded (Millions of boxes) 500 Quantity Supplied (Millions of boxes) 210 In this market, the equilibrium price is $25per box, and the equilibrium quantity of oranges is 250 million boxes. Points: 1 / 1 Close Explanation Explanation: The equilibrium price and quantity of oranges occur at the intersection of the demand and supply curves. Using the graph input tool, you can see that this occurs at a price of $25 per box, which is where the quantity of oranges that producers are willing to supply is equal to the quantity consumers demand (250 million boxes). For each price listed in the following table, determine the quantity of oranges demanded, the quantity of oranges supplied, and the direction of pressure exerted on prices in the absence of any price controls. Price Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied Pressure on Prices (Dollars per box) (Millions of boxes) (Millions of boxes) 30 145 270 Downward 20 375 230 Upward Points: 0.67 / 1 Close Explanation Explanation: At a price of $20 per box, consumers demand 375 million boxes of oranges, but producers supply only 230 million boxes. Therefore, there is a shortage of 145 million boxes. In the absence of a price ceiling, a shortage exerts upward pressure on prices until there is neither a surplus nor a shortage.At a price of $30 per box, consumers demand 125 million boxes of oranges, but producers supply 270 million boxes. Therefore, there is a surplus of 145 million boxes. In the absence of a price floor, a surplus exerts downward pressure on prices until there is neither a surplus nor a shortage. True or False: A price ceiling above $25 per box is a binding price ceiling in this market. (Economists call a price ceiling that prevents the market from reaching equilibrium a binding price ceiling.) True False Points: 1 / 1 Close Explanation Explanation: In order for a price ceiling to be binding—that is, for it to prevent the market from reaching equilibrium—it must be set below the equilibrium price. In this case, you found that the equilibrium price was $25 per box. Therefore, any price ceiling below $25 per box would be binding, and any price ceiling set at or above $25 per box would not. 2. Price controls in the Florida orange market The following graph shows the annual market for Florida oranges, which are sold in units of 90- pound boxes. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph. Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly.In this market, the equilibrium price is $25 per box, and the equilibrium quantity of oranges is 450 million boxes. Points: 1 / 1 Close Explanation Explanation: The equilibrium price and quantity of oranges occur at the intersection of the demand and supply curves. Using the graph input tool, you can see that this occurs at a price of $25 per box, which is where the quantity of oranges that producers are willing to supply is equal to the quantity consumers demand (450 million boxes). For each price listed in the following table, determine the quantity of oranges demanded, the quantity of oranges supplied, and the direction of pressure exerted on prices in the absence of any price controls. Price Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied Pressure on Prices (Dollars per box) (Millions of boxes) (Millions of boxes) 15 530 270 Upward 35 350 630 Downward Points: 0.67 / 1 Close ExplanationExplanation: At a price of $15 per box, consumers demand 522 million boxes of oranges, but producers supply only 270 million boxes. Therefore, there is a shortage of 252 million boxes. In the absence of a price ceiling, a shortage exerts upward pressure on prices until there is neither a surplus nor a shortage. At a price of $35 per box, consumers demand 378 million boxes of oranges, but producers supply 630 million boxes. Therefore, there is a surplus of 252 million boxes. In the absence of a price floor, a surplus exerts downward pressure on prices until there is neither a surplus nor a shortage. True or False: A price ceiling above $25 per box is not a binding price ceiling in this market. (Economists call a price ceiling that prevents the market from reaching equilibrium a binding price ceiling.) True False Points: 1 / 1 Close Explanation Explanation: In order for a price ceiling to be binding—that is, for it to prevent the market from reaching equilibrium—it must be set below the equilibrium price. In this case, you found that the equilibrium price was $25 per box. Therefore, any price ceiling below $25 per box would be binding, and any price ceiling set at or above $25 per box would not. 2. Price controls in the Florida orange market The following graph shows the annual market for Florida oranges, which are sold in units of 90- pound boxes. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph. Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly. In this market, the equilibrium price is $25 per box, and the equilibrium quantity of oranges is 400 [Show More]
Last updated: 11 months ago
Preview 4 out of 27 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$9.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 04, 2022
Number of pages
27
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 04, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
102






.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)






.png)