*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Chamberlain College of Nursing - NR 509NR509_SOAP_Note_week3. Grade A (All)
Chamberlain College of Nursing - NR 509NR509_SOAP_Note_week3. Grade A
Document Content and Description Below
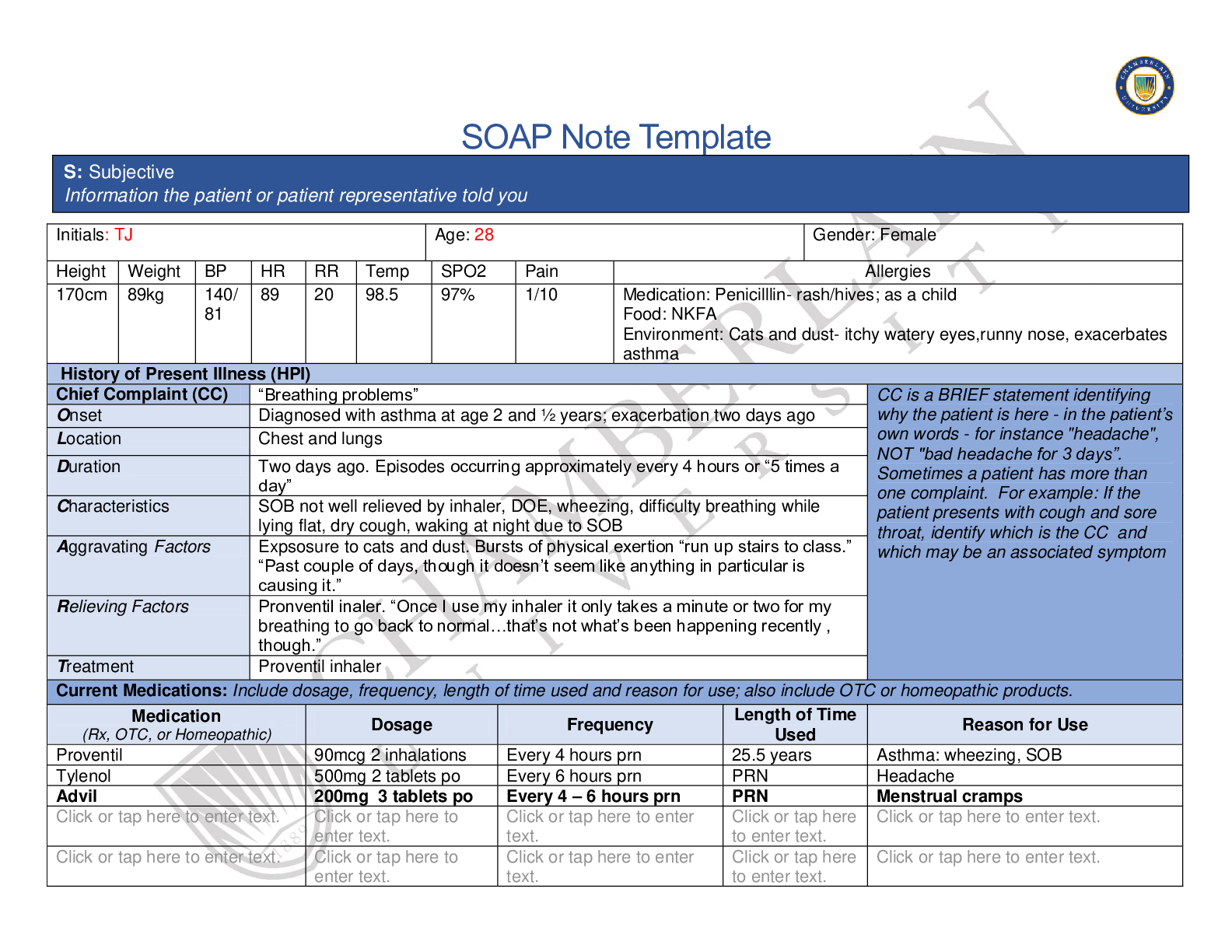
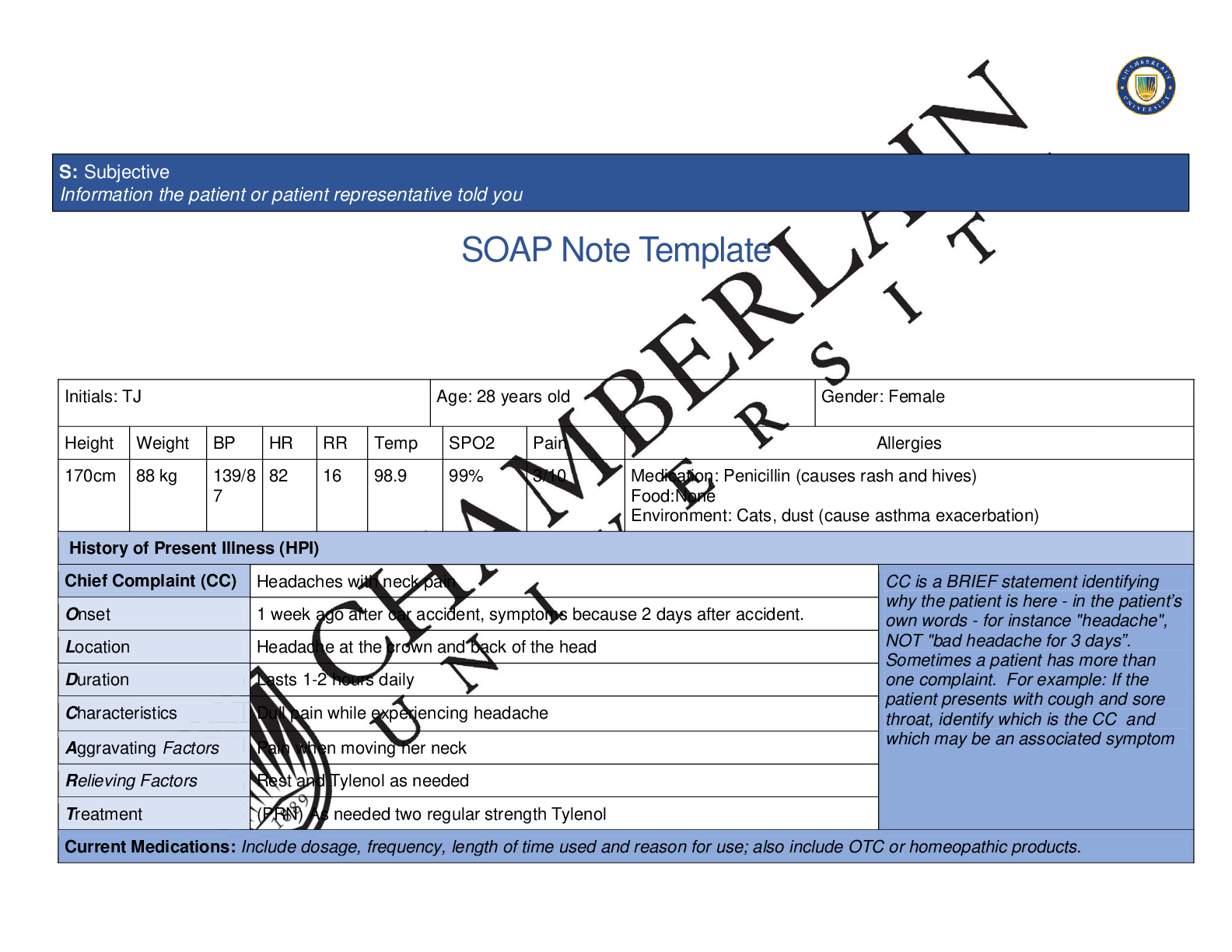
SOAP Note Template Initials: TJ Age: 28 years old Gender: Female Height Weight BP HR RR Temp SPO2 Pain Allergies 170cm 88 kg 139/8 7 82 16 98.9 99% 3/10 Medication: Penicillin (causes rash and hi... ves) Food:None Environment: Cats, dust (cause asthma exacerbation) History of Present Illness (HPI) Chief Complaint (CC) Headaches with neck pain CC is a BRIEF statement identifying why the patient is here - in the patient’s own words - for instance "headache", NOT "bad headache for 3 days”. Sometimes a patient has more than one complaint. For example: If the patient presents with cough and sore throat, identify which is the CC and which may be an associated symptom Onset 1 week ago after car accident, symptoms because 2 days after accident. Location Headache at the crown and back of the head Duration Lasts 1-2 hours daily Characteristics Dull pain while experiencing headache Aggravating Factors Pain when moving her neck Relieving Factors Rest and Tylenol as needed Treatment (PRN) As needed two regular strength Tylenol Current Medications: Include dosage, frequency, length of time used and reason for use; also include OTC or homeopathic products. S: Subjective Information the patient or patient representative told youMedication (Rx, OTC, or Homeopathic) Dosage Frequency Length Used of Time Reason for Use Proventil Inhaler 90 mcg 2 puffs as needed Every 4 hours as needed Wheezing Shortness of breath Tylenol 650 mg (states she takes two tablets) Once a day The past few days Headaches Advil 200 mg TID PRN First couple of days of menstrual cycle Cramping Flovent inhaler enter text. enter text. here . Asthma . enter text. enter text. here . . Past Medical History (PMHx) – Includes but not limited to immunization status (note date of last tetanus for all adults), past major illnesses, hospitalizations, and surgeries. Depending on the CC, more info may be needed. Tina was diagnosed with Diabetes Mellitus type 2 at the age of 24 years old. She is non-compliant with taking her metformin, as well as checking blood sugar on a regular basis. Diagnosed with asthma at the age of 2 and a half. Has been taking her inhaler as needed for asthma exacerbation; currently it is not being as effective as it was. Is now on Flovent which has been providing relief for maintenance. Suffers from heavy periods that include cramping as well as tenderness. Tina has irregular periods which last between 9-10 days. Immunizations are current, has received vaccinations for childhood. Flu shot received last 5 to 6 years ago. Last tetanus shot was about two years ago. Last pap smear was done about 4 years ago, and was normal. Tina has Polycystic ovarian syndrome. Social History (Soc Hx) - Includes but not limited to occupation and major hobbies, family status, tobacco and alcohol use, and any other pertinent data. Include health promotion such as use seat belts all the time or working smoke detectors in the house.Patient denies smoking, denies recreational drug use. Patient is a former pot smoker who quit when she was 20 or 21 years old. She is occasionally exposed to second hand smoke socially as her friends smoke. Drinks alcohol occasionally, about 6 drinks a month. Patient is currently a student working on obtaining her bachelors degree in accounting. Patient lives with her mother and sister who support her dreams. Patient became sexually active at the age of 18 and has had 3 male sexual partners in total. Denies using birth control at the moment. Family History (Fam Hx) - Includes but not limited to illnesses with possible genetic predisposition, contagious or chronic illnesses. Reason for death of any deceased first degree relatives should be included. Include parents, grandparents, siblings, and children. Include grandchildren if pertinent. Mother history of HTN and high cholesterol. Father history of HTN, diabetes mellitus type 2, high cholesterol ( Passed away in car accident). Paternal grandmother history of HTN and high cholesterol. Paternal grandfather history of HTN, diabetes, colon cancer (passed away from colon cancer). Brother is obese. Sister has asthma. Maternal grandmother history of hypertension, and high cholesterol (deceased from stroke at 73 years old) Maternal grandfather HTN, high cholesterol. Review of Systems (ROS): Address all body systems that may help rule in or out a differential diagnosis Check the box next to each positive symptom and provide additional details. Constitutional Skin HEENT☐Fatigue here . ☐Weakness . ☐Fever/Chills . ☐Weight Gain . ☐Weight Loss . ☐Trouble Sleeping Click or tap . ☐Night Sweats . ☐Other: enter text. ☐Itching . ☐Rashes . ☐Nail Changes Click or tap . ☐Skin Color Changes enter text. ☐Other: enter text. ☐Diplopia . ☐Eye Pain . ☐Eye redness . ☐XVision changes Click or tap . ☐Photophobia Click or tap . ☐Eye discharge Click or tap . ☐Earache here . ☐Tinnitus here . ☐Epistaxis . ☐Vertigo here . ☐Hearing Changes Click or tap . ☐Hoarseness here . ☐Oral Ulcers here . ☐Sore Throat here . ☐Congestion here . ☐Rhinorrhea here . ☐Other: . Respiratory Neuro Cardiovascular☐Cough enter text. ☐Hemoptysis enter text. ☐Dyspnea enter text. ☐Wheezing enter text. ☐Pain on Inspiration here . ☐Sputum Production Choose an item. Choose an item. Choose an item. ☐Other: . ☐Syncope or Lightheadedness . ☐XHeadache Started recently 2 days after low speed car accident, headache occurs daily for 1-2 hours at a time. Pain is described as dull, and located at the crown and back of the head. ☐Numbness here . ☐Tingling enter text. ☐Sensation Changes Choose an item. ☐Speech Deficits . ☐Other: enter text. ☐Chest pain enter text. ☐SOB . ☐Exercise Intolerance here . ☐Orthopnea enter text. ☐Edema . ☐Murmurs enter text. ☐Palpitations here . ☐Faintness here . ☐OC Changes . ☐Claudications . ☐PND enter text. ☐Other: enter text. MSK GI GU PSYCH☐XPain Neck pain with movement of head and neck ☐XStiffness stiffness to neck ☐Crepitus enter text. ☐Swelling enter text. ☐xLimited ROM ☐Redness enter text. ☐Misalignment enter text. ☐Other: enter text. ☐Nausea/Vomiting enter text. ☐Dysphasia enter text. ☐Diarrhea enter text. ☐Appetite Change enter text. ☐Heartburn enter text. ☐Blood in Stool enter text. ☐Abdominal Pain enter text. ☐Excessive Flatus enter text. ☐Food Intolerance enter text. ☐Rectal Bleeding enter text. ☐Other: . ☐Urgency enter text. ☐Dysuria enter text. ☐Burning enter text. ☐Hematuria here . ☐Polyuria enter text. ☐Nocturia enter text. ☐Incontinence . ☐Other: enter text. ☐Stress enter text. ☐Anxiety enter text. ☐Depression here . ☐Suicidal/Homicidal Ideation . ☐Memory Deficits . ☐Mood Changes . ☐Trouble Concentrating Click or tap . ☐Other: enter text. GYN ☐Rash . ☐Discharge . ☐Itching . ☐Irregular Menses . ☐Dysmenorrhea . ☐Foul Odor . ☐Amenorrhea . ☐XLMP: N/A ☐Contraception . ☐Other:.Body System Positive Findings Negative Findings General . . Skin . . HEENT . . Respiratory . . O: Objective Information gathered during the physical examination by inspection, palpation, auscultation, and palpation. If a body system, write “”. Document pertinent positive and negative assessment findings.Neuro Cranial nerve 2 (optic) Right Fundus has cotton wool bodies present. Decreased sensation to bilateral feet. Tina is oriented to person, place and time Her abstract thinking responses were intact and relevant She is able to follow simple commands Attention span was accurate, intact as well as general knowledge was accurate Remote memory and immediate memory are intact Vocabulary is complex as expected for her age, education level and general ability. No apparent problems with pronunciation or expression. Cranials Nerves: Olfatory I: sense of smell is intact, nose symmetrical bilaterally Optic II: Right eye 20/40 , left eye 20/20, no visible abnormal findings on the left fundus, and sharp disc margins noted bilaterally. Optic II and Oculomotor III: PERRLA pupils reactive to light bilaterally. III (Oculomotor), IV (Trochlear) and VI (Abducens) Cardinal fields and convergence equal bilaterally Trigeminal V: Facial sensation intact Facial VII: Skull and facial feature symmetric Auditory VIII: Weber test and bilateral Rinne test normal Glossopharyngeal IX and Vagus X Gag reflex intact Spinal AccessoryXI: Shoulder shrugging symmetric, 5-full range of motion against gravity, with resistance and Neck strength, 5-full range of motion against gravity, with resistance Hypoglossal XII:Tongue symmetric with no abnormalities Expected deep tendon reflexes to bilateral triceps, bilateral biceps, bilateral brachioradialis, bilateral patellar, and bilateral Achilles tendon Point-to-point movements smooth and accurate bilaterally Tina was able to perform coordination with rapid alternating hand movements without difficulty Her gait observed to be steady with continuous, symmetric stepsGraphesthesia indentified bilaterally Expected sensation in proximal and distal bilateral arms and legs to dull, soft, and sharp touch. Position sense intact in fingers and toes Stereognosis intact bilaterallyCardiovascular . . Musculoskeletal . . Gastrointestinal . . Genitourinary Psychiatric Gynecological Problem List 1. Headache 6 Hypertension 11 Activity intolerance 2 Diabetes Mellitus type 2 7 Stress 12 . 3 Asthma 8 Dysmenorrhea 13 . 4 Neck pain 9 Menorrhagia 14 . 5 Obesity 10 Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome 15 .Diagnosis ICD-10 Code Pertinent Findings Traumatic Headache (Acute post) G44.31 Chief complain of headaches, pain is on the crown of the head and back of the head. It started a couples of days after the low speed accident lasting from 1 to 2 hours daily. Strain of muscle, fascia and tendon at the neck level S16.1 Chief complain is pain that is located on the back of the neck muscles when moving the head and neck P: Plan Address all 5 parts of the comprehensive treatment plan. If you do not wish to order an intervention for any part of the treatment plan, write “None at this time” but do not leave any heading blank. No intervention is self-evident. Provide a rationale and evidence-based in-text citation for each intervention. A: Assessment Medical Diagnoses. Provide 3 differential diagnoses which may provide an etiology for the CC. The first diagnosis (presumptive diagnosis) is the diagnosis with the highest priority. Provide the ICD-10 code and pertinent findings to support each diagnosis.Type 2 Diabetis Mellitus with unspecified diabetic retinopathy E 11.31 Cotton wool spots noted on the right fundus upon examination with opthalmoscope Diagnostics: List tests you will order this visit Test Rationale/Citation Medications: List medications/treatments including OTC drugs you will order and “continue previous meds” if pertinent. Drug Dosage Length of Treatment Rationale/CitationIbuprofen 400 mg Take one tablet every 4-6 hours for pain or headaches Ibuprofen is effective in decreasing the number of headaches daily as well as the intensity. Manzano, S., Doyon-Trottier, E., & Bailey, B. (2010). Myth: Ibuprofen is superior to acetaminophen for the treatment of benign headaches in children and adults. CJEM: Canadian Journal of Emergency Medicine, 12(3), 220–222. https://doiorg.chamberlainuniversity.idm.oclc. org/10.1017/S1481803500012276 Robaxin 500mg QID ( 4 times a day) As per the article the use of muscle relaxants are stated to be effective with managing acute pain. Kumbham, S., Ghate, V., & Lewis, S. A. (2019). Approaches for the Delivery of Skeletal Muscle Relaxants: A Review. Indian Drugs, 56(7), 7–15. Retrieved from https://search-ebscohostcom.chamberlainuniversity.idm.ocl c.org/login.aspx?direct=true&db=a 9h&AN=137805231&site=ehostlive&scope=site . . . .Referral/Consults: Consult with a Neurologist for headaches that continue to persist after 4 weeks Ophthalmologist Rationale/Citation Tina should follow up with a neurologist if the headaches and pain persist for another 4 weeks. Tina needs further workup with an ophthalmologist in order to receive a comprehensive dilated eye exam. By having her pupils dilated the ophthalmologist will have a clearer view of her eyes, and then be able to get a better picture of the eyes. Ho, K. C., Stapleton, F., Wiles, L., Hibbert, P., Alkhawajah, S., White, A., & Jalbert, I. (2019). Systematic review of the appropriateness of eye care delivery in eye care practice. BMC Health Services Research, 19(1), N.PAG. https://doiorg.chamberlainuniversity.idm.oclc. org/10.1186/s12913-019-4493-3 Education:Patient has been educated to be careful when taking robaxin as it can cause drowsiness and dizziness. Robaxin could also impair the patients mental status; This medication should be taken with precaution, avoid driving when on this medication. Patient instructed to return to the clinic if the signs and symptoms persist, if not to go to the ER. Patient was instructed to report any new changes in her level of consciousness, example such as if she is not capable to keep her balance, if she develops double vision, or sudden confusion to urgently go the nearest emergency department. Rationale/Citation Patient needs to have a clear understanding of possible side effects, and so follow the education provided in order to increase quality of life. Patient should also be aware of when to visit the ER in case of emergency. Follow Up: Indicate when patient should return to clinic and provide detailed instructions indicating if the patient should return sooner than scheduled or seek attention elsewhere. Tina should return to the clinic and follow up in 2 weeks. Follow up with neurologist as well as ophthalmologist. Return to the clinic in case of emergency if any adverse effects arise. Rationale/Citation The provider should see Tina in 2 weeks as follow up to check is medications are working properly. Also, to assess the severity of the headaches and neck pain. See if there is some relief, if not it is important to follow up with neurology for a more in depth treatment. References Include at least one evidence-based peer-reviewed journal article which relates to this case. Use the correct APA 6th edition formatting.Manzano, S., Doyon-Trottier, E., & Bailey, B. (2010). Myth: Ibuprofen is superior to acetaminophen for the treatment of benign headaches in children and adults. CJEM: Canadian Journal of Emergency Medicine, 12(3), 220–222. https://doiorg.chamberlainuniversity.idm.oclc.org/10.1017/S1481803500012276 Kumbham, S., Ghate, V., & Lewis, S. A. (2019). Approaches for the Delivery of Skeletal Muscle Relaxants: A Review. Indian Drugs, 56(7), 7–15. Retrieved from https://search-ebscohost-com.chamberlainuniversity.idm.oclc.org/login.aspx?direct=true&db=a9h&AN=137805231&site=ehostlive&scope=site Ho, K. C., Stapleton, F., Wiles, L., Hibbert, P., Alkhawajah, S., White, A., & Jalbert, I. (2019). Systematic review of the appropriateness of eye care delivery in eye care practice. BMC Health Services Research, 19(1), N.PAG. https://doi-org.chamberlainuniversity.idm.oclc.org/10.1186/s12913- 019-4493-3 . [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 20 pages
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$11.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 07, 2020
Number of pages
20
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 07, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
84


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)