*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Chamberlain College of Nursing - NR 507Specific MidTerm Study Guide. Complete (All)
Chamberlain College of Nursing - NR 507Specific MidTerm Study Guide. Complete
Document Content and Description Below
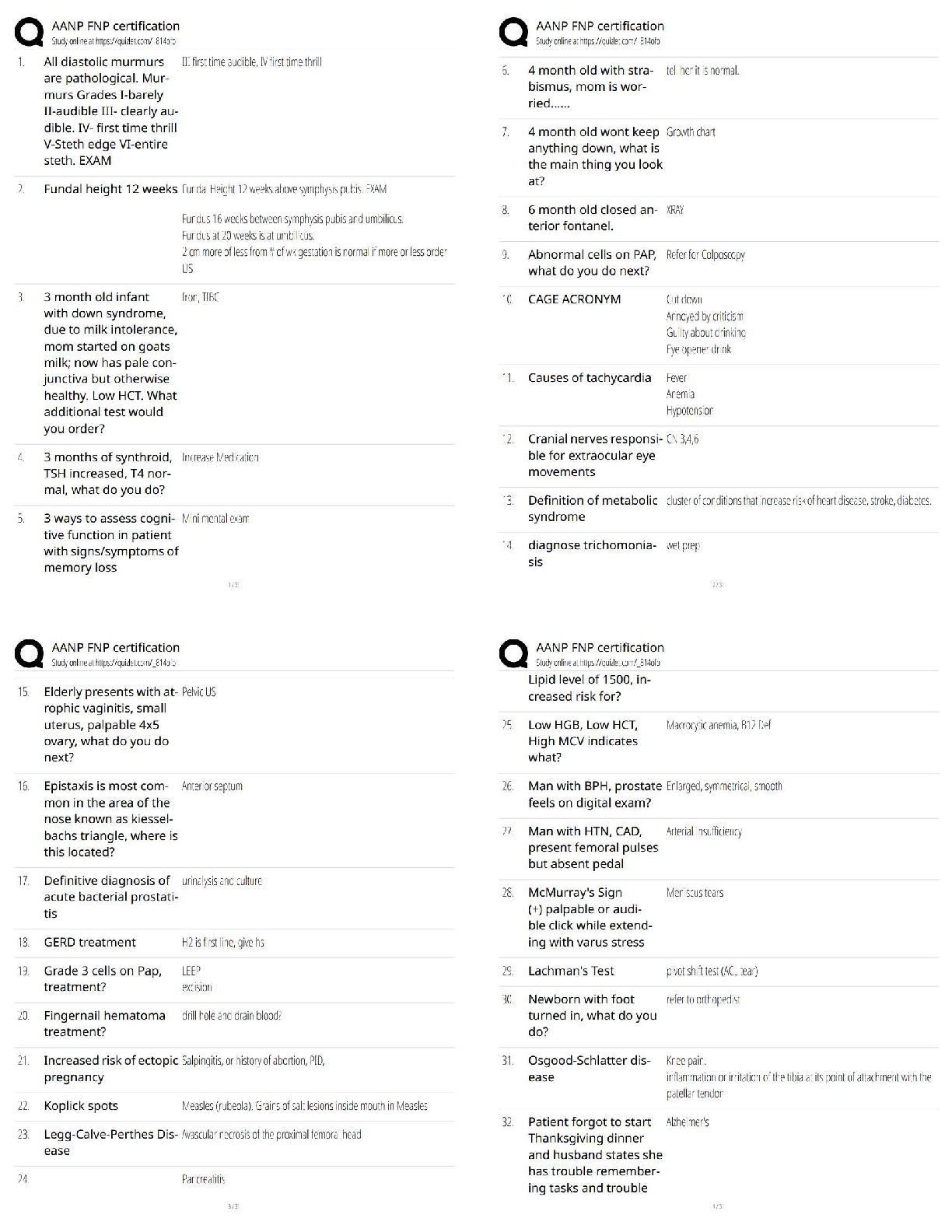
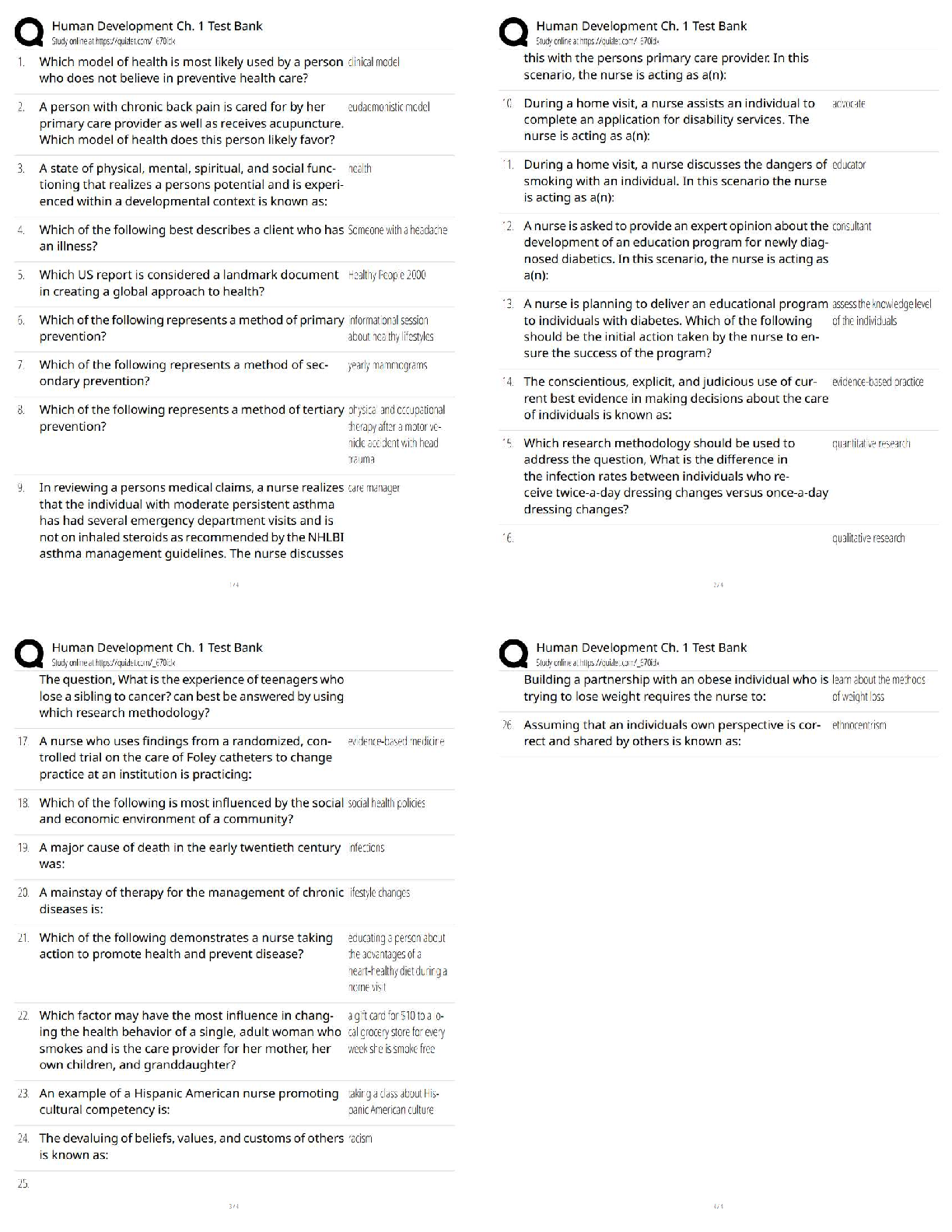
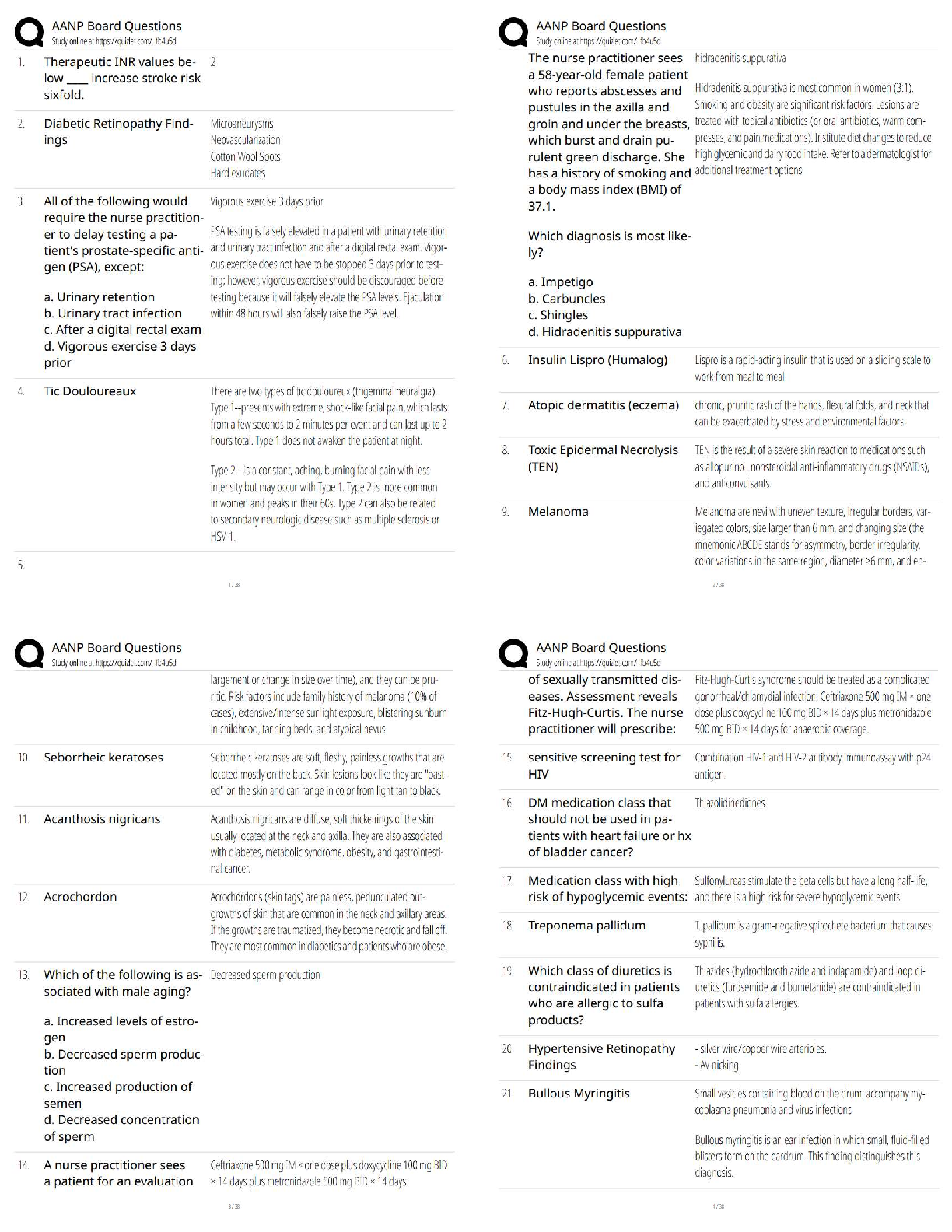
Epigenetics 1.Defects in the encoding of histone-modifying proteins (Chp 6 and 12 wk 1) are chemical modifications of DNA sequences that alter the expression of genes, resulting in disease and p ... henotypical variations (upon genetics) types of epigenetic modifications Histone modifications- in diverse biological processes such as transcriptional Histone modifications (e.g. histone acetylation and deacetylation, chromatin alterations)- quantitative detection of various histone modifications- would provide useful information Histone Modification- Results: 2. Epigenetics and (45) its role on human development. (chp 6) diseases and other phenotypic variation are caused by mechanisms other than changes in 3. Totipotent cells and (49) its ability to differentiate into any type of cell 50. Prader-Willi syndrome and – missing the PATERNALLY imprinted copy of chromosome behavioral characteristics of prader willi 4. Angelman syndrome? – loss of the maternal copy of UBE3A 2 major causes of angelman phenotype of angelman syndrome Gene responsible for Anglemman syndrome encodes a ligase- involved in protein degradation during brain development. Cellular Proliferation 5. 5-Azacytidine and the(44) treatment of cancer (Chap 6 & Chp 12- wk 1) What does 5-azaC do to Dcm? Inhibits Dcm. Dcm becomes covalently trapped to DNA & degraded What were the 3 effects of 5-azaC tested? 1. On DNA methylation 2. Bacterial growth 3. Site specific methylation 4. On transcriptome changes 5-azacytidine 6. the role of inactive MLH1 in the development of some forms of inherited colon cancer. 7. Effects of ethanol on neural stem cells ability to differentiate into functional neurons (chap 13,wk 1) (Chap 2 The molecular actions of ethanol are believed to include site-specific changes to histone modifications and alterations of one-carbon metabolism causing methylation changes. 8. Inflammation as an etiology for cancer-note conditions in which this may occur Chronic inflammation can result from many causes: -Solar irradiation -Asbestos exposure (mesothelioma) -Pancreatitis -Infection -GU tract -Prostate -Thyroid -Pancreas -Urinary bladder -Pleura -Skin In both inflammation and cancer, inflammatory cells (neutrophils, lymphocytes, and Cancer 9. In terms of epigenetic modifications, the role of environmental stressors associated with development of cancer. Environmental stressors can markedly increase the risk of aberrant epigenetic Cancer is the second leading cause of death in the United States. It is well established that The emerging focus in the biology of aging includes epigenetic and genetic changes, Defects in Mechanism of Defense 10. Hemolytic defects in the newborn What is HDFN? 3 prerequisites for the Dz- What are 3 classes of HDN? What is Rh incompatibility? RBCs. anti-D is igG and can cross the placenta What is the most common form of HDN? - anti-D, more rare is anti-E, c, e, C What is ABO incompatability? What is erythroblastosis fetalis? What happens to the baby as a result for compensating the anemia? What is Hydrops fetalis? What is Kernicterus? What are some sxs of surviving kernicterus? What must be done to monitor risk of kernicterus? What is a new procedure done to monitor bilirubin? - trans cutaneous bilirubinometry What are lab findings of HDN? What does the blood smear show in HDN 11. Understand the meaning of infectivity ( chap 10 ) 12. Most effective treatment for HIV- 13. Defected cells of HIV 14. Signs of T-Lymphocyte deficiency Pulmonary Alterations 15. Pulmonary function tests 16. Relationship of lung compliance and (46) residual volume 17. Shifts in the oxyhemoglobin dissociation- (chap 3, 17, 34) 18. CO2 transport in the blood ( chap 34) 19. Characteristics of alveoli- 20. Arterial perfusion pressure in the lung base and (21) alveolar gas pressure in the lung base 22. How do determine the partial pressure of oxygen given the percentage of oxygen in the air and (23) the barometric pressure 24. Results of increased work of breathingLabored breathing occurs whenever there is an increased work of breathing, especially if Know terms: Chapter 34 25.Vital capacity (VC), The maximum volume of air that a person can exhale after maximum inhalation VC = IRV + TV + ERV 26.Total lung capacity 27.Functional capacity- 28.Residual volume (RV) 29. Functional residual capacity (FRC) – Renal Alterations 30. Types of nephrons and (48) their functions (chap 37) what are the 4 sections of the nephron Superfical Cortical nephrons- located in the cortex – most numerous, which extend Midcortical nephrons- with short or long loops Juxtamedullary nephrons – concentrating urine- location extend from the cortex deep into the Renal Corpuscle Glomerulus Afferent Arteriole Efferent Arteriole Bowman's Capsule Proximal Convoluted Tubule - functions in reabsorption (2nd part of nephron) What is the normal Tm value for both men and women? What happens if blood glucose exceeds the normal Tm value? What do the microvilli on the proximal convoluted tubule do? Loop of Henle Thin decending limb of loop of henle water permeable thick ascending limb of loop of henle Capillary bed function in the loop of henle Distal Convoluted Tubule - Collecting Duct Water reabsorption with ADH in collecting duct 31. Overall renal physiology- 32. Substances that are actively secreted by the renal tubules (Chap39) 33. Activation of the renin-angiotensin system Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System. 34. Glomerular filtration rate- clearance 35. Mesangial cells- 36. Renal system anatomy 37. Why plasma proteins should be absent from the urine- 38. Effects of urinary tract obstruction- hydronephrosis and a (39) decreased glomerular filtration rate 40. Effect of urinary retention Most common type of renal stone most common stone types include calcium oxalate or phosphate (70% to 80%), struvite 41. Epispadias An abnormal urethral opening on the dorsal or top of the penis. signs and symptoms medial surgical management 42. Glomerulonephritis- ( chap 38) Glomerulonephritis is an inflammation of the glomerulus caused by primary glomerular 43. Nephrotic syndrome- ( chap 38) Nephrotic syndrome is the excretion of 3.0 g or more of protein in the urine per day, hypoalbuminemia ( Primary causes of nephrotic syndrome include minimal change disease Secondary forms of nephrotic syndrome occur in systemic diseases including diabetes [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 24 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$5.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 22, 2020
Number of pages
24
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 22, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
150








.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)